* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleic Acids
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
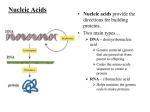
Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acid Basics • Contain instructions to build proteins • 2 types: – DNA – RNA • Composed of smaller units called nucleotides – Monomer: Nucleotide – Polymer: Nucleic acid Nucleotide Structure • Three parts – Sugar molecule – Phosphate group – Nitrogen base (A, T, C, or G) • Nucleotides combine to make nucleic acids • Instructions for cell to make proteins Monomers link to make polymers! Nucleic Acids Monomer = Nucleotide Polymer = Nucleic acid How many nucleotides are pictured? Six What is this chain of nucleotides called? Nucleic acid DNA • Double Helix: 2 chains of nucleotides • Four DNA bases: Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine – A pairs with T – C pairs with G T C C G (can you predict the missing bases?) • Gene: section of DNA that codes for a protein A RNA • Single chain of nucleotides • RNA bases: Adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine • Function: Help cells with the creation of proteins U C U G A Review 1) Name the monomer of nucleic acids. 2) How are the four nitrogen bases of DNA abbreviated? 3) What does the phosphate molecule of a nucleotide bond with? 4) If the DNA nitrogen bases were TACCGGAT, how would the attached DNA strand read? 5) How are DNA and RNA different?