* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Low-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
Cholesterol wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
High-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
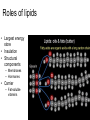
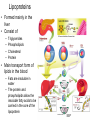
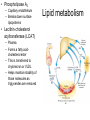
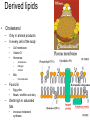
Lipid metabolism Roles of lipids • Largest energy store • Insulation • Structural components – Membranes – Hormones • Carrier – Fat-soluble vitamins Types of lipids • Simple lipids – Mostly triglycerides • Principal storage form • >95% of body fat – Mostly in adipose cells – Some in liver and skeletal muscle • Triglyceride – One glycerol – 3 fatty acids • All have linear C chain • 14-22 C long • Saturated or unsaturated • Compound lipids – Neutral fats with other chemicals • • • • Glycolipids Sphingolipids Phosphoglycerides Lipoproteins – Glycolipids • Glycerol, two fatty acids and one sugar group • Involved in cell recognition – Sphingolipids • One fatty acid and one molecule of sphingosine • Sphingomyelin – Signal transmission and cell recognition – Phosphoglycerides • Glycerol, two fatty acids, one phosphate group and one alcohol group – Important component of cell membranes Types of lipids Lipoproteins • Formed mainly in the liver • Consist of – – – – Triglycerides Phospholipids Cholesterol Protein • Main transport form of lipids in the blood – Fats are insoluble in water – The protein and phospholipids allow the insoluble fatty acids to be carried in the core of the lipoprotein Lipoproteins •Classified according to their density •HDL: Least amount of cholesterol •Carry cholesterol back to the liver •Converted to bile •Most recycled, some excreted Lipoproteins • LDL and VLDL: – Carry most of the cholesterol – Have the greatest affinity for the arterial walls • Particularly oxidized LDL • Chylomicrons: – Largest amount of triglycerides – Produced in small intestinal cells • Elevated after high fat meals Lipid metabolism • Triglycerides – Not taken up directly into the cells – Must be broken down first • Fatty acids and glycerol • Lipoprotein lipase – Located on capillary endothelium • Glycerol goes to liver • Phospholipase A2 – Capillary endothelium – Breaks down surface lipoproteins • Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) – Plasma – Forms a fatty acidcholesterol ester – This is transferred to chylomicron or VLDL – Helps maintain stability of those molecules as triglycerides are removed Lipid metabolism Derived lipids • Cholesterol – – Only in animal products In every cell of the body • • • Cell membrane Vitamin D Hormones – – – • Bile – – Fat metabolism Found in • • – Testosterone Estrogen Cortisol Egg yolks Meats, shellfish and dairy Diets high in saturated fats • Increase cholesterol synthesis Fatty acid synthesis • Occurs in the liver and adipose tissue – Essentially • Acetyl-CoA + 7 Malonyl-CoA + NADPH + 14H+ → Palmitic Acid + 8CoA + 14 NADP+ + 6H2O – Acetyl-CoA and Malonyl-CoA are reduced to Palmitic acid – NADPH is the reducing agent – Dehydration Rx – Malonyl-CoA • Created from Acetyl-CoA – Acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Thus, anything that increases Acetyl-CoA levels can lead to fat synthesis Triglyceride synthesis Fatty acyl CoA Triglyceride synthesis • Glycerol 3 phosphate + 2 Fatty acyl-CoA – Phosphatidic acid • Phosphatidic acid converted to diacylglycerol – Phosphatase • Diacylglcerol + fatt acyl CoA – Triglyceride • Acyl transferase Triglyceride metabolism • Stored in – Adipose tissue, liver, muscle • Breakdown process – Lipolysis – Whether or not triglycerides come from muscle or liver, same basic steps occur • • • • • • • Mobilization Circulation Uptake Activation Translocation B-oxidation Aerobic metabolism Lipid mobilization • Hormone sensitive lipase – Breaks down stored triglycerides – Fatty acids and glycerol released • Into blood (adipose tissue) – Glycerol • Goes to liver – – – Gluconeogenesis Glycogenesis Lipid biosynthesis – Fatty acids • Require a carrier – Albumin Lipid Mobilization • Activation of Hormone sensitive lipase – Epinephrine • Activates G protein – Stimulates adenylate cyclase – Adenylate cyclase • Produces cAMP – Activates Protein kinase A Lipid circulation • Fatty acids bound to albumin – Circulate around to active tissues • How do they know? Fatty acid uptake • Uptake – Directly related to circulating concentration – Rate of blood flow • Increased flow, increased delivery, increased uptake and utilization – Requires • Fatty acid transporter (FAT) and Fatty acid binding protein (FABP) – Costs • Two ATP Fatty acid activation • Fatty acids must be activated – ATP + CoA • Fatty acyl-CoA • Fatty acyl-CoA must be translocated – From cytoplasm to mitochondria • Carnitine acyl transferase 1 and 2 Fatty acid oxidation • B-oxidation – Sequential events which • Convert fatty acyl-CoA to – Acetyl-CoA – NADH – FADH – Number of cycles • (Number of carbon atoms/2)-1 • 16C FA – 7 cycles – Each cycle produces 1 acetylCoA, 1 NADH and 1 FADH – Each acetyl CoA = 12 ATP – Each NADH = 3 ATP – Each FADH = 2 ATP • Total for 16C palmitic acid?