* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 Ancient Rome and the Rise of Christianity
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
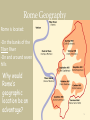
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
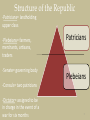
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
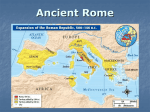
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Treaties between Rome and Carthage wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Rome and the Roman Republic 1 Early Civilization -Italy was originally occupied by many different groups of people -Two main groups were Greek colonists and the Etruscans -The Etruscans ruled much of central Italy and Rome itself -Ancestors of the Romans, the Latins, settled in the area that is now Rome around 800 B.C. 2 Legend of the Founding of Rome -Legend has it that twin brothers, Romulus and Remus founded the city -According to the tale, the twins’ mother was a Latin woman and their father was the war god Mars -This led Romans to believe that they had a divine origin 3 Geography -Located on the Italian peninsula, in the center of the Mediterranean Sea -The Alps are in the North -The Apennine Mts. are on the eastern coast -broad, fertile plains in the north and west 4 Rome Geography Rome is located: -On the banks of the Tiber River -On and around seven hills Why would Rome’s geographic location be an advantage? 5 Politics - 509 B.C. Rome Republic is Founded -Romans drove out their Etruscan ruler and established a republic - They did not want one person to have all the power 6 Structure of the Republic -Patricians= landholding upper class -Plebeians= farmers, merchants, artisans, traders -Senate= governing body Patricians Plebeians -Consuls= two patricians -Dictator= assigned to be in charge in the event of a war for six months 7 Roman Bingo 1 Patrician 2 Plebian 3 Consul 4 Assembly 5 Tribune 6 Veto 7 Checks & Balances 8 legion 9 republic 10 dictator 11 Crucifixion 12 praetor 13 Anarchy 14 Pax Romana 15 Cleisthenes 16 Senate 8 Timeline • • • • • • • • • • • • Etruscan Rule Republic Plebeian Rebel Political Equality for Plebeians Twelve Tables First Period of Expansion Second Period of Expansion Third Period of Expansion Fourth Period of Expansion Punic Wars End of the Republic Rome becomes an Empire 9 The Punic Wars -Carthage had an empire throughout the Mediterranean -Rome fought Carthage in three wars from 264 B.C. to 146 B.C. (118 years!) -By the Third Punic War, Rome had completely destroyed Carthage and gained all of Carthage’s territory 10 Patricians vs. Plebeians -Plebeians have no say in the government - Eventually get to elect their own officials called tribunes in 494 B.C. - For 84 years, (421-337 B.C.) plebeians fought to have a role in each part of the government 11 Social Structures -A man was the head of the household and his wife and children did not question his authority -Over centuries, women received more rights. These included: -Owning property -Running businesses -All children were taught to learn to read and write -Wealthy had private tutors for their children 12 Religion -Romans were polytheistic-they believed in many gods and goddesses -Many of the gods were adapted from the Greek gods Greek God Roman God Zeus-ruler of all gods Jupiter-ruler of all gods Hera-wife of Zeus, protected marriage Juno-wife of Jupiter, protected marriage Poseidon-god of the sea Neptune-god of the sea -Roman calendar is full of feasts and celebrations to honor the gods and goddesses -Temples for worship to ask for divine assistance 13 Politics -Rome grows strong and begins conquering the rest of Italy -By 270 B.C., Rome controls most of the Italian peninsula -Military is made up of citizens -Rome conquered justly- allowing those conquered to keep their culture, customs, and government- as long as they supplied soldiers, paid taxes, and acknowledge Roman leadership 14 Economics -Conquests brought much wealth to Rome -Wealthy families bought huge estates called latifundia. -Romans forced the people they conquered to work as slaves on the latifundia -Slave labor hurt the small farmers because it cost them more to produce food, and the price was driven down by the immense quantities coming into Rome -Farmers fell into debt, sold their land, and moved to the city looking for work -gap between rich and poor widens=riots and chaos 15 The Gracchus Brothers -Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus were patricians who were elected tribunes •The brothers worked to get the state to distribute the land to the poor farmers •They also worked to get the state to buy grain to feed the poor •Senate felt they were a threat to its power, and hired thugs to kill the brothers and their followers 16 Republic to Empire -Civil wars break out to decide who should hold power. The senate wanted to keep the status quo; political leaders wanted to weaken the senate and enact reforms -Slave uprisings throughout the republic -Armies became loyal to their commanders because they gave them benefits such as captured land 17 Blockbusters • BLockbusters Government & Laws http://www.teachersdirect.co.uk/resources/quiz-busters/quizbusters-game.aspx?game_id=47291 18 Essay Response • How did the Athenians prevent one person from gaining too much power? Explain this in relation to the system of checks and balances developed during the Democratic Age in Athens. Roman Citizenship • Citizens were the people who could participate in government. • Citizens had the right to vote and hold public office. • Duties of citizenship included – Paying taxes – Serving in the army when needed • Rome’s emperors gave citizenship to groups that the Romans had conquered. – This act helped keep people loyal to Rome. Main Idea 2: Roman advancements in engineering, architecture, art, and philosophy helped shape later • Engineering civilizations. – Roads lasted for centuries, and bridges spanned raging rivers. – Aqueducts, human-made channels that carried water from distant mountain ranges into Rome or other cities • Architecture and Art – Romans borrowed from Greek ideas, such as using columns and open space, but made their buildings larger and grander. – Roman art borrowed ideas from the Greeks, such as making their art look realistic. • Philosophy – Wanted to show the world as it really was – Wanted their ideas to improve people’s lives