* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7-4 Lesson Overview (PowerPoint)
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
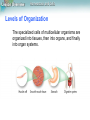
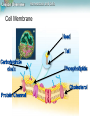
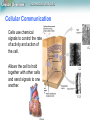
Lesson Overview Homeostasis and Cells Lesson Overview 7.4 Homeostasis and Cells Lesson Overview Homeostasis and Cells The Cell as an Organism Multicellular and unicellular organisms must achieve homeostasis, relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions. Lesson Overview Homeostasis and Cells The Cell as an Organism In terms of their numbers, unicellular organisms dominate life on Earth. Unicellular organisms include both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Lesson Overview Homeostasis and Cells Multicellular Life The cells of multicellular organisms are interdependent. Cells in a multicellular organism become specialized for particular tasks and communicate with one another in order to maintain homeostasis. Lesson Overview Homeostasis and Cells Levels of Organization The specialized cells of multicellular organisms are organized into tissues, then into organs, and finally into organ systems. Lesson Overview Homeostasis and Cells Cell Membrane Lesson Overview Homeostasis and Cells Cellular Communication Cells use chemical signals to control the rate of activity and action of the cell. Allows the cell to hold together with other cells and send signals to one another.