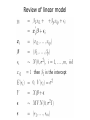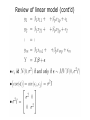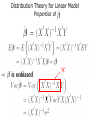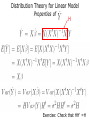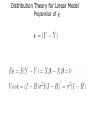* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 3
Data assimilation wikipedia , lookup
Interaction (statistics) wikipedia , lookup
Choice modelling wikipedia , lookup
Time series wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental variables estimation wikipedia , lookup
Expectation–maximization algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Regression analysis wikipedia , lookup
Lecture 3 (Chapter 4) Linear Models for Longitudinal Data • • • • Linear Regression Model (Review) Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) Maximum Likelihood Estimation Distribution Theory Linear Regression Model (A Review) • • • • • Linear Regression Model (Review) Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) Maximum Likelihood Estimation Distribution Theory Will need to remember: – Basic matrix algebra – Likelihood function – Normal distribution Regression Analysis Q: What are the goals of regression analysis? A: Estimation, Testing, and Prediction • Estimation of the effect of one variable (exposure), called the predictor of interest, after adjusting, or controlling for, other measured variables – Remove confounding variables – Remove bias • Testing whether variables are associated with the response • Prediction of a response variable given a collection of covariates Regression Analysis (cont’d) Classification of Variables • Response Variable – Dependent Variable – Outcome Variable • Predictor of interest (POI) – Exposure variable – Treatment assignment • Confounding variables – Associated with response and POI – Not intermediate • Precision variables – Associated with response and not with POI – Reduces response uncertainty Ex: Impact of maternal smoking on low birth • Measured variables – Birth weight (g) – Maternal smoking (yes/no) – Maternal age (yrs) maternal weight at last menses (kg) – Race – History of premature labor (yes/no) history of hypertension • Response: birth weight • Predictor of interest: maternal smoking • Confounder: maternal age, race, history of premature labor • Precision: maternal weight at last menses Linear Regression Model Review of linear model Review of linear model (cont’d) Review of linear model (cont’d) • We have only one measurement per subject; and measurements on difference subjects are independent Review of linear model (cont’d) • Linear Model includes as special cases: – The analysis of variance (ANOVA), xij are dummy variables – Multiple regression, xij are continuous – The analysis of covariance, xij are dummy and continuous variables • is the expected value of the response variable Y, per unit change in its corresponding explanatory variable x, all other variables held fixed. Estimation of • Principle of maximum likelihood (R.A. Fisher, 1925) – Estimate by the values that make the observations maximally likely – Likelihood P(Data| ), as a function of What is a Likelihood Function? Likelihood Inference Linear Model – I.I.D. Normal Errors Distribution Theory for Linear Model mx1 (mxp) (px1) px1 mxm Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) Estimate = Maximum Likelihood Estimate (MLE) Distribution Theory for Linear Model Properties of “A” Distribution Theory for Linear Model Properties of H Exercise: Check that HH’ =H Distribution Theory for Linear Model Properties of