* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Physical World
Water quality wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
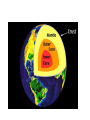
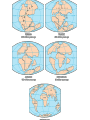
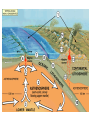
THE PHYSICAL WORLD Chapter 2 The Solar System Our solar system is made up of the sun and objects that rotate around it The sun is at the center The Largest star, or ball of burning gas The sun’s mass creates a strong gravitational pull keeping all objects revolving around it The Planets Largest objects in the Solar system behind the sun 8 planets Inner planets/Terrestrial Planets Mercury – Venus – Earth- Mars Solid rocky crusts Outer Planets/ Gas Giants Jupiter – Saturn – Uranus – Neptune More gaseous and less dense Have orbiting moons and thing rungs Asteroids, Comets, and Meteoroids Asteroid- small irregular shaped planet like objects located b/w Mars and Jupiter in the Asteroid belt Comets- made of icy dust particles and frozen gasses Meteoroids- pieces of space debris – chucks of iron and rock Meteorites- when it hits the earth Barringer Crater - Arizona The Earth - Largest of the inner planets About 70% of the earths surface is water Oceans, lakes, rivers, and other bodies of water make up the earths hydrosphere About 30% of the Earths surface is land The land makes up the part of the earth called the lithosphere The earth’s crust The Earth The air we breath is part of the earth’s atmosphere layer of gasses extended above the planets surface 78% nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, and small amounts of other gasses All people, animals and plants that live on or close to the earths surface. The part of earth that supports life is called the biosphere. Landforms Landforms are the natural features of the earth’s surface Includes bodies of water Underwater landforms exist as well. Continental Shelf- underwater extension of the costal plain. Continental Slope – sharp drop to the ocean floor Pg 33 Heights and Depths Highest point- Mt. Everest Lowest Dry Land Spot –Shore of the Dead Sea Deepest Spot – Mariana Trench Activity Draw a diagram that labels the following: Hydrosphere Lithosphere Atmosphere Biosphere Continental Shelf Continental Slope FORCES OF CHANGE Layers of the Earth 1. Core Inner core- located at very center, very hot, made up of nickel and melted iron under pressure Outer Core – Made up of Nickel and iron and surrounds the core 2. Mantle Next to the outer core is a layer of thick dense rock 3. Crust rocky shell forming the earths surface Broke into more than a dozen slabs, called plates, which float on the earths mantle Plate Movement Pangaea- “super continent” before all the continents separated. Today broken apart into smaller continents Continental Drift- theory that the continents were once joined and have slowly drifted apart Plate Tectonics Physical process that has created all of the earths physical features Slowly moving plates change the earth appearance Create mountains, volcanoes. Earthquakes or trenches Magma gets pushed to the earth’s earths core and ridges are formed The lithosphere is broken up into what are called "tectonic plates". On Earth, there are currently seven to eight major and many minor plates Colliding and Spreading Plates Mountains= when continental plates collide Subduction- when a plate slides below another plate one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge Accretion-a process by which material is added to a tectonic plate or a landmass Spreading- sea plates pull apart Folds and Faults Folds- bends in layers of rock caused by plates squeezing the earth’s surface until it buckles. Faults- cracks in the earths crust cause by plates grinding or sliding past each other. Earthquakes Sudden violent movements of tectonic plates long the fault lines. result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves Ring of Fire- most earthquake prone zone on the planet Great Alaskan Earthquake 1964 Volcanoes Mountains formed by lava, or magma, that breaks through the earth’s crust Weathering and Erosion Weathering- breaks down rocks Physical- rocks physically broken down into small pieces Chemical- chemical makeup is changed Erosion- wears rocks down Wind Erosion- movement of dust sand and soil from one place to another Glacial Erosion-caused by the large sheets of ice moving a picking up dirt and rocks – destroy forests and creates large valleys When they melt they drop large amounts of rocks called morains Water Erosion- water cuts into land and wears away soil and rock EARTH’S WATER The Water Cycle Water makes up the world’s hydrosphere The total amount of water on the Earth does not change, it is just constantly moving Water Cycleregular movement of water Sun evaporates the water from the earths surface Evaporation- changing of liquid into vapor, or gas Water vapor is gathered in the air and when air cools it can not hold as much vapor. Excess water vapor changes into liquid water Condensation- process where excess water vapor turns into condensation Water droplets form water and make clouds When clouds get to heave moisture is released in the form of precipitation Precipitation- rain snow or sleet Bodies of Water 70% of the Earth is water, but most of this is salt water. Only a small percentage is fresh water. Because of the World’s growing need for fresh water scientist found a way to turn salt water into fresh water Desalination- process which ocean water is turned into fresh water by removing the salt. This is expensive and not used by many countries Freshwater Makes up 3% of the Earth’s total water supply. The Great Lakes contain the largest supply of fresh water Groundwater Some freshwater lies beneath the earth’s surface We use wells and spring taps to access this water