* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
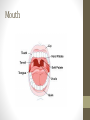
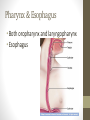
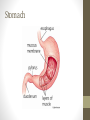
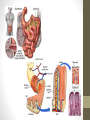
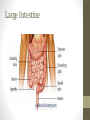
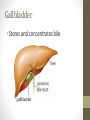
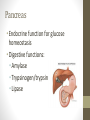
The Digestive System Functions • Ingestion • Mechanical digestion • Chemical digestion • Movements • Absorption • Elimination Mouth Teeth Pharynx & Esophagus • Both oropharynx and laryngopharynx • Esophagus Stomach Gastric Secretions •Mucus •HCl •Intrinsic factor •Pepsinogen •Gastrin Regulation of Gastric Secretion • Cephalic • Gastric • Intestinal • Stomach emptying • 4 hours • Liquids and carbs move out fast • Proteins and fatty acids take longer Small Intestine • Functions • Finishes digestion • Absorbs nutrients • Passes waste to large intestine Small Intestine Secretions • Neutral/alkaline fluid • Mucus • Peptidase • Maltase, sucrase, lactase • Lipase • Secretin & cholecystokinin Large Intestine Large Intestine Functions • Absorption of fluids and electrolytes • Waste elimination Liver • Produces and secretes bile • Bile salts • Many other non-digestive functions including: plasma proteins, storing glucose, detoxification of blood, and biomolecule metabolism Gallbladder • Stores and concentrates bile Pancreas • Endocrine function for glucose homeostasis • Digestive functions: • Amylase • Trypsinogen/trypsin • Lipase Chemical Digestion • Breaks down complex molecules into smaller ones that can be absorbed by cells • Uses the process of hydrolysis Carbohydrate Digestion • Begins in the mouth • Polysaccharides are broken down to disaccharides • In the small intestines, disaccharides are broken down into monosaccharides – glucose, fructose, and galactose Protein Digestion • Begins in the stomach • Breaks proteins into polypeptides • In the small intestines, peptides are reduced to amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) Lipid Digestion • Only occurs in the small intestine • Fats are emulsified by bile to decrease attraction between the molecules • Lipids are broken down to monoglycerides and fatty acids (the building blocks of lipids) The Bottom Line • We ingest approximately 10 liters of materials a day. • 9 liters or more are absorbed in the small intestine. • A meal takes approximately 24-72 hours to make a complete journey through the digestive tract.