* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DO NOW Monday 2/12
Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Lactoylglutathione lyase wikipedia , lookup
Beta-lactamase wikipedia , lookup
Transferase wikipedia , lookup
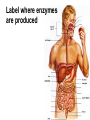
Enzyme Structure and Function Why do we study molecules in biology? Review the large molecules of life: break down into break down into break down into Large molecules in food are broken down into smaller molecules to: – Provide energy to the body – Provide building blocks to make new molecules Enzymes Are specialized proteins that help: – Catalyze (“speed up”) reactions – Break down molecules – Build up new molecules And can be affected by changes in the enzyme’s environment – their activity or effectiveness Enzymes are specific in how they work! – Substrate – Active Site For the audio-visual learners… • Enzyme video clip from Bozeman Biology • The enzyme song! • Enzymes lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction. • Activation energy is the amount of energy it takes for a reaction to “go” • Inhibitors can get in the way! • These are molecules that interfere with enzyme function. – Competitive Inhibitors – Non-competitive Inhibitors (“allosteric”) • Can slow the work of enzymes, or stop it altogether. Enzyme Structure and Function Your Tasks/Homework • Read text excerpts, – A specific enzyme catalyzes each cellular reaction – Enzyme inhibitors block enzyme action and can regulate enzyme activity in a cell • Answer follow-up questions on sheet Respond to these questions in the spaces below. • What does “induced fit” refer to, when talking about enzymes? • Explain how an enzyme speeds up a specific reaction. • What does it mean to be an optimal condition for an enzyme”? • List 2 optimal enzyme conditions for humans. • Compare and contrast cofactors and coenzymes. • Compare and contrast competitive inhibitors and noncompetitive inhibitors. • What is the advantage of feedback inhibition to a cell? Label where enzymes are produced Quick Review! From essay, What Happens to the Food You Eat? 1. Why is saliva an important component of the digestive system? 2. Explain what happens to food as it passes through the stomach into the small intestine. 3. Why is chewing food such an important function to digestion? 4. How are large molecules broken down into smaller ones? You Are What You Eat!