* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 19-Viruses
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
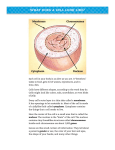
VIRUSES The Genetics of Viruses (L) poison First identified by Stanley in 1935Tobacco Mosaic Virus A genome w/in a protective coat Viral Structure Capsid-protein coat that encloses the genome Envelope-membrane that cloaks some capsids Genome Life Cycle Obligate intracellular parasites Range varies, depends upon receptor sites Some with broad range-ex. Rabies Some with very narrow range-ex. Human cold virus Genome Replication DNADNA uses host DNA polymerase RNARNA virus has gene for RNA replicase RNADNARNA usually virus contains gene for reverse transcriptase Lytic Cycle Virus uses cells enzymes, ribosomes, tRNAs, amino acids ATP, etc. Viral particles selfassemble Lytic cycle is fatal to cell Called Virulent viruses Lysogenic Cycle Virus coexists within the host Called temperate viruses Viral genome is incorporated into the host’s genome Called a Prophage Animal Viruses Reproductive Cycle of Animal Viruses Attachment-glycoprotein spikes attach to receptor sites Entry-envelope fuses with plasma membrane, entire virus moves in via receptor mediated endocytsis Uncoating- genome exposed Viral RNA and protein synthesis Assembly and release- virion “buds” through the surface, envelope is cells phospholipids with virus-specific glycoproteins Emerging Viruses Make a sudden appearance. Not new, just a new territory Examples: HIV, hantavirus, Ebola Flu Viruses and Cancer Some tumor viruses cause cancer in animals VIRAL GROUP Retrovirus Herpesvirus Papovavirus Hepatititis B virus CANCER TYPE Leukemia Burkitt’s lymphoma Cervical cancer Liver cancer Plant Viruses RNA viruses Spread by horizontal transmissionfrom an external source Vertical transmission-from parent Viroids and Prions Viroids are naked circular RNA Probably disrupt metabolism, development, and growth Plant pathogen Prions are proteins Cause degenerative brain diseases “mad cow” disease Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease How? Hypothesismisfolded and convert normal proteins to the prion version. Chain reaction. Prion “proteinaceous infectious particles” Found in brains of all mammals Products of gene expression Some exist in a misfolded state, leads to ability to resist conventional sterilization Infectious types are able to “latch” onto normal prions and convert them to that infectious type How Prions reproduce 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 1 Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Intracellular membrane Scrapie PrP Normal PrP Original scrapie PrP molecule Converted molecule Normal PrP Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. All scrapie PrP 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 2 Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 3 Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Intracellular membrane Scrapie PrP Normal PrP Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 4 Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Intracellular membrane Scrapie PrP Normal PrP Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 5 Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Intracellular membrane Scrapie PrP Normal PrP Original scrapie PrP molecule Converted molecule Normal PrP Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 6 Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Intracellular membrane Scrapie PrP Normal PrP Original scrapie PrP molecule Converted molecule Normal PrP Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 7 Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Intracellular membrane Scrapie PrP Normal PrP Original scrapie PrP molecule Converted molecule Normal PrP Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. All scrapie PrP 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 8 Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 9 Intracellular membrane Scrapie PrP Neuron Normal PrP Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 10 Intracellular membrane Neuron Converted molecule Normal PrP Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 11 Intracellular membrane Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 12 Intracellular membrane Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 13 Intracellular membrane Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 14 Intracellular membrane Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 15 Intracellular membrane Neuron Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 19.12 Prions Change Shape Slide number: 16 Intracellular membrane Neuron All scrapie PrP Nucleus Cytoplasm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w 5aAPEYIL9A