* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 15 Student Lecture Notes
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
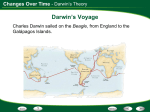
Ch 15 Student Lecture Notes Darwin’s Theory of Evolution _________________________________: Change in a kind of organism over time. The process of modern organisms descending from ancient organisms. ______________________________________: Process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully: AKA survival of the fittest. Look at the map on pg. 369. This is the voyage that Darwin made. At each stop, he took notes on the plants and animals. During the voyages at sea, he would read about the area and then collect data. He also drew many sketches of animals that he had never seen. In the Amazon, he collected 8 different species of beetles. He began to observe how all the species of plants and animals seemed perfectly suited for the climate. He wondered why there were no rabbits in Australia or kangaroos in England. Australia and Argentina both had grasslands, yet different animals in those grasslands, and also different from the European grasslands. Darwin also began to collect fossils to see how ancient organisms looked. Some looked almost exactly the same as living species, and some had modifications. 1000 miles west of South America, Darwin spent a great deal of time at the Galapagos Islands. Many of these tiny islands had different climates. Hood Island had little vegetation. Isabelle Island had increased rainfall and vegetation on the ground. p. 371- Look at the differences in each tortoise from the different islands. The largest tortoise has a mass of 230 kg=460 lbs. What differences do you see? Why do you think they are different? Hood: Pinta: Isabella: He also noted that the similar looking birds had different shaped ____________________ on different islands. He began to look at ___________________ found on the island. He compared beak shape to seeds. Were they from the same species, but changed to survive? James Hutton and Charles Lyell, geologists, produced evidence that the earth was millions of years old and has gone through several climate changes over the years. The geological findings of Hutton and Lyell explained to Darwin how the environment affected the type of _______________________ living there. Darwin believed that if the earth could change over time, so could organisms. Before Darwin was even born, Jean Baptiste Lamarck proposed that organisms have to be suited to their _______________________ or die. p. 376 If an organism has a body part that is not being used, then over hundreds of generations that part may become smaller or not show up at all. In contrast, if a body part is needed or perceived as desirable, it will become more prevalent with each generation. Could this explain why your mom has eyes in the back of her head? Note the crab claw. What other evidence have you heard about to support this? Thomas Malthus, English economist, noticed that babies were being born at an alarming rate. He predicted that human ___________________________ would outpace the resources of food and space. He hypothesized that to reduce the population, wars would break out, diseases would spread, and famine would take place. Darwin read Malthus’ hypothesis and applied the same principles to plants and animals. Humans reproduce slowly, but an oyster can produce _______________________ of eggs each year. If every oyster egg, from every oyster, survived, there wouldn’t be room in the oceans. Why doesn’t this happen? Why do most eggs not make it? Only 2 out of 100 sea turtle eggs make it to adulthood. Natural Variation Within a Species Each zebra has a different banding of______________________, yet all are zebras. Each person in this room has a different phenotype, yet all are Homo sapiens. Humans have taken traits from plants or animals and artificially enhanced them. TurkeyCowRadishDogsIn nature, organisms must ___________________________ for food space, water, and mating. The fastest predator will be able to obtain more food and survive. The bug that blends in with the leaves won’t be eaten and will be able to reproduce. An adaptation is a characteristic that ____________________________ an organism’s ability to survive. These characteristics can also allow the organism to become better suited to the environment. Camels: Feet, lashes, lips, hump Polar Bears: black skin, holes in hair follicle, large paws p. 380 – Only the __________________________ survive. Natural selection cannot be _________________________ directly, and it can only be observed. _____________________________ (change over time) cannot be observed directly. Over time, organisms have different ________________________________ and have different niches or occupy different ____________________________. This may mean they look different from ancestors. A _______________________: a way in which an organism lives and functions in an ecosystem. Darwin noticed that some species looked similar, lived in similar habitats, but were on different continents. List some examples. Beavers, p.383 Darwin noticed homologous structures. Many skeletons look similar, but have modifications. Compare an alligator arm with a human arm. Vestigial parts are parts that the organism no longer _______, such as a human appendix. Pg. 385 some skinks have vestigial legs. Summary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. There is variation within a species. More organisms are produced than survive. Organisms must compete for resources. Variation within a species may enhance survival or decrease chances of survival. Survivors pass their traits on to the next generation. Species today may have modifications from that of their ancestors. All organisms come from one ancestor (Darwin’s theory, not proven) Chapter 16 Gene Pool: combined _________________________ information of all members. Genetic variation occurs when ______________________occurs and when a mutation occurs. The number of phenotypes in a population is determined by the number of __________________ that control that trait. Height, skin, hair, and eye color are all polygenic traits. There is a bell curve. White sand crabs blended into the sand in Kauai. After Hurricane Iniki, the population drastically went down because the sand was no longer white. Directional Selection One end of the bell curve survives better than the general bell. A giraffe’s longer neck allows it to have more food from tall trees. Longer necks breed with other long neck survivors. Stabilizing Selection The center of the bell curve has the greatest chances of survival. The bell curve is narrower. Weight of newborns—low birth weight babies are less likely to survive and large babies may have difficulty being born. Disruptive Selection Both ends of the bell curve have better chances of survival. This usually offers two distinct phenotypes. In a population of birds, birds with large beaks and birds with small beaks will survive if the seeds are very small or very big. Speciation Why doesn’t the Siberian tiger and a Bengal tiger mate? Grizzly Bears and Polar Bears? What about a liger? (Tiger * Lion) What are determining factors that allow a bird to mate with the other bird of the same species? How does the bird ‘know’ which bird is the same species? When does a new species evolve? Species: a group of organisms that breed together to create _______________________offspring. Evolution Study for Quiz Write out Darwin’s 7 Evolution Rules found in your lecture notes. 1. 2 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Matching a. b. c. d. e. f. Alleles Stabilizing Selection Hutton and Lyell Bell Curve Directional Selection Disruptive Selection g. h. i. j. k. l. Homologous Structures Evolution Malthus Adaptation Natural Selection Niche m. n. o. p. q. r. Lamarck Speciation Species Galapagos Islands Gene Pool Genetic Variation 1. ______Formation of a new species due to isolation. 2. ______ Group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring. 3. ______Combined genetic information of all members of a species within an area. 4. ______Physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way it interacts with the habitat and other organisms. 5. ______ Change in a kind of organism over time. 6. ______ Individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce. 7. ______ Location where Darwin spent time researching finches and tortoises. 8. ______ Similar looking structures from different species. (bat wing and human hand). 9. ______ Proposed that organisms must be suited to their environment or die. 10. ______ Differences of individuals within the same species. 11. ______ Different forms of a gene 12. ______ A shift in the bell curve, moving to one extreme or the other. 13. ______A Curve showing the natural variation within a species, where most are found in the middle, with fewer at the ends 14. ______The center of the bell curve becomes narrower and more steep, with few individuals are at the ends of the curve. 15. ______When the bell curve splits into to curves, where more individuals are at the end of the normal curve than in the middle. 16. ______ Geologists that said the earth was very old and had changed over time. 17. ______ Economist that said that war, disease, and famine will happen due to over population. 18. ______ Inherited characteristics that increase the organisms chances of survival. 1. N 2. O 3. Q 4. L 5. H 6. K 7. P 8. G 9. M 10. R 11. A 12. E 13. D 14. B 15. F 16. C 17. I 18. J