* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download New marketing strategies for airports
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
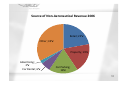
New marketing strategies for airports Heather Jones AIRDEV Seminar IST, 20 October 2011 1 Outline Introduction What is marketing? Marketing frameworks Four P’s Framework Non-aeronautical business units Marketing Strategy Tactics Next Steps Questions 2 1945 1948 1951 1954 1957 1960 1963 1966 1969 1972 1975 1978 1981 1984 1987 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Passengers (000) Annual Passengers Per Year World Airlines 2008 2.500.000 2.000.000 1.500.000 1.000.000 500.000 0 3 Airport Marketing Timeline First record of “marketing” 1884 First Airline 1909 Marketing as standard practice Emergence of Airport Marketing Industry Acceptance 1915 1993 2001 4 What is marketing? “A coordinated, integrated, and formal process of managing the marketing mix in relation to a clear set of measurable objectives. Furthermore, this process is captured in a formal document or plan” (Coviello, Brodie and Munro 2000). “Marketing Mix” (Borden 1984) “elements of the mix and the forces that bear on the mix”. “Marketing deals with identifying and meeting human and social needs. One of the shortest definitions of marketing is "meeting needs profitably."” (Kotler and Keller 2006). 5 What is marketing? “Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders.” (American Marketing Association 2011b). (Airport) “Fundamental step for establishing new “rules of conduct” and later implementing them in a consistent way” (Jarach 2005a). “Marketing is the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably” (Shaw 2007). 6 Marketing frameworks TDIN • Transaction • Database • Interaction • Networking Holistic • Relationship • Integrated • Internal • Social Responsibility Four C’s • Concept • Cost • Communication • Channel Four P’s • Product • Price • Promotion • Physical Distribution 7 Product Primary Hub Secondary Hub Regional/ Business Low Cost Cargo Location Close to city More remote to city Regional tends to remote, Business close to city More remote to city Varies but tends to be more remote Flight Frequency Level NonStop Flights P-to-P/ Connecting Fare Higher Medium Lower Higher Higher Higher Lower Varies Higher Higher Enables connecting Higher Point to point Varies Point to point Point to point Lower Varies Lowest NA Retail Prominence Capacity High Lower Lower Lower None Constrained Available Available Varies Congestion Congested Uncongested Uncongested Operating Hours Quotas Night curfew 24 hours Varies Varies, tends to available Varies, more uncongested Varies 24 hours Yes No Varies No No Service Level Higher Lower Lower Lower NA NA 8 Price Promotion Physical Distribution Primary Hub Secondary Hub Regional/ Business Low Cost Cargo Fees to Airlines Higher Lower Lower Lowest NA Level of Importance Lower Higher Higher Higher NA Areas of Promotion Facilities to connecting traffic Awareness to airlines and passengers Low fares, destinations , low costs for airlines Level of Importance High High Closeness to city (business) or proximity to several areas (regional) High Location, connectivity to other modes, tax free zone Higher Highest 9 Source of Non-Aeronautical Revenue 2006 Retail; 22% Other; 33% Property; 19% Advertising; 2% Car Rental; 6% Car Parking; 18% 10 Marketing Strategy Tactics Marketing Support System Plan Service Quality Branding Consumer Marketing Airline Marketing 11 Marketing Strategy Tactics Airline Marketing • • • • • • • • • • Modify facilities or services Promote a recognized brand Target airlines for new or existing routes Provide and present market research Lobby for the removal of obstacles Use strategic marketing partnerships Offer flexibility on pricing Develop joint advertising or promotions Provide travel planning support to passengers Improve management processes 12 Airport Evolution 13 Next Steps Further refine aeronautical four P’s framework Develop framework for non-aeronautical business units Continue to collect marketing strategy tactics and market research tools 14 Questions? 15 New marketing strategies for airports Heather Jones [email protected] 16