* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download French Revolution - Beavercreek City Schools
Society of the Friends of the Blacks wikipedia , lookup
Arnaud II de La Porte wikipedia , lookup
Charles X of France wikipedia , lookup
Germaine de Staël wikipedia , lookup
National Convention wikipedia , lookup
Louis XVII of France wikipedia , lookup
Insurrection of 10 August 1792 wikipedia , lookup
Reign of Terror wikipedia , lookup
Demonstration of 20 June 1792 wikipedia , lookup
Causes of the French Revolution wikipedia , lookup
Vincent-Marie Viénot, Count of Vaublanc wikipedia , lookup
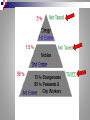
French Revolution UNREST 1. Bad harvests 2. High prices 3. High taxes 4. Questions raised by the Enlightenment Old Regime 3 Estates st 1 Estate Catholic Church (clergy ) 1% of population 2nd Estate Nobles 2% of population st 1 and Access nd 2 Estates to gov’t offices Exempt from taxes Rejected Enlightenment Owned 30 % of land rd 3 Everyone Estate else Bourgeoisie ( middle class ) Bankers, factory owners, merchants Well educated Believed strongly in Enlightenment Payed high taxes Wealth ≠status and power rd 3 Estate cont. Workers Poorest Low wages High unemployment Peasants Largest Farmers 80% of population Paid ½ income to nobles, church, gov’t Factors New ideas about gov’t Economic troubles Debt Louis XVI Inherited Backed American Revolution Spent Factors cont. Weak leader – Louis XVI Indecisive Paid little attention to advisors Queen interfered Ignored problems Estates-General Louis XVI decides to try to tax 2nd Estate Forced to call meeting of Estates-General First in 175 years May 5, 1789 Versailles Estates General cont. Each estate met separately to vote Each estate had one vote st nd 1 and 2 outvoted the 3rd Estates General cont. 3rd Estate wanted changes All 3 meet together Each delegate have a vote Give advantage to 3rd King denied Leaders of 3rd called for National Assembly Pass laws and reforms for people of France National Assembly June 17, 1789 voted to form National Assembly Proclaimed end of monarchy Representative gov’t First deliberate act of revolution National Assembly Locked out of meeting room Broke into indoor tennis court Tennis Court Oath Pledge not to disband until new constitution is written Joined by nobles and clergy in favor of reform Louis XVI stationed military around Versailles Storming of Bastille Rumors spread People began to arm themselves July 14, 1789 stormed Bastille Prison built in 1300 In search of gunpowder Mob overwhelmed guards Symbolic act of revolt Great Fear Rebellion spread to countryside Wave of panic Peasants armed themselves Broke in nobles homes October 1789 Angry women of Paris march on Versailles Demand action to provide bread Force Louis and Marie to return to Paris The Rights of Man By August 5th, Old Regime was dead Commoners equal to nobles Nat’l Assembly adopts statement of ideals The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen Rights of Man “Men are born free and remain free and equal in rights” “Life, liberty, security, and resistance to oppression” Equal justice Freedom of speech and religion Liberty, Equality, Fraternity The Church Took over Church lands Church officials and priests were to be elected an paid as gov’t officials Many peasants alarmed Opposed assembly’s reforms June 1791 Louis and Marie try to escape Captured and returned to Paris New Plan for Gov’t September 1791 New constitution Creates limited monarchy Creates new legislative body Legislative Assembly Power to create laws Declare war Divisions Legislative Assembly split into 3 groups To the left – RADICALS Opposed monarchy; lots of change In center – MODERATES Some change To the Right – CONSERVATIVES Limited monarchy; few changes War with Europe Austria and Prussia urge for restoration of monarchy April 1792 Legislative Assembly declares war War with Europe Prussian forces advance quickly outside of Paris Threaten to destroy Paris if royals harmed August 10th 20,000 men storm palace Kill guards Arrest Louis and family Paris Commune Paris radicals More radical, more violent Took king captive Wanted universal male suffrage Sans-culottes Wanted greater changes Discovered ways to exert power September Massacres Rumors that royal supporters would break out of prison and seize city Citizens take law into own hands Raid prison Murder over 1000 prisoners New Constitution Legislative Assembly pressured Set aside Constitution of 1791 2. Deposes king 3. Dissolves assembly 4. Calls for election of new legislature 1. New Government September 21 National Convention takes office Abolishes monarchy Declares France a republic Adult male citizens granted right to vote and hold office Political Clubs Girondins Moderate Represent areas outside of Paris Feared radical mobs The Mountain Radicals of Paris Jacobins Jacobins Jacobins – radical political organization takes charge Jean-Paul Marot Georges Danton Tried Louis XVI for treason Convicted January 21, 1793 - beheaded Problems Within Many enemies within France Peasant horrified by execution of king Priests angered by gov’t control Rival leaders stirring up rebellions in other provinces of France Committee of Public Safety To oversee war efforts created Committee of Public Safety Maximillien Robespierre headed Governed France as dictator REIGN OF TERROR Reign of Terror Protect France from its enemies Many fellow revolutionaries were sentenced to death 1793 – 1794 45,000-55,000 people executed Reign cont. Revolutionary armies bring rebellious cities under control Lyon – 1880 citizens executed Nantes – sunk in barges 85% from 3rd Estate Violence was temporary Republic of Virtue Republic of Virtue Republic composed of good citizens Good education – primary education for all “citizen” replaced mister Tried to control prices Women attended National convention sessions De-Christianization Cult of the Supreme Being Superstition rather than reason New calendar (Sept 22, 1792) End of Terror June 1794 Law of 22 Prairial July 1794 National Convention turns on Robespierre July 28, 1794 Robespierre is beheaded New Government Following terror moderate leaders draft new plan for gov’t (3rd since 1789) Power with upper middle class 2 house legislature Executive body of 5 men (moderates) Directory Directory Corrupt Gave country period of order Chose right general to lead army Napoleon Bonaparte