* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive Disorders
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
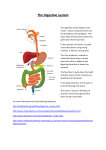
Digestive Disorders • Acid Reflux • Symp- burning sensation • RX- avoid chocolate and peppermint, coffee, citrus, fried or fatty foods, tomato products – stop smoking- take antacids – don’t lay down 2-3 hours after eating. • When small quantities of stomach acid are regurgitated into the esophagus • Inflammation of mucous membrane lining of stomach and intestine • Common cause = Virus • Symps – diarrhea and vomiting for 24-36 hours • Complication = dehydration • Sore or lesion that forms in the mucosal lining of the stomach • Gastric ulcers in the stomach and duodenal ulcer in the duodenum • Cause – H. pylori (bacteria) is primary cause • Lifestyle factors that contribute: cigarette smoking, alcohol, stress, certain drugs. • Symp – burning pain in abdomen, between meals and early morning, may be relieved by eating or taking antacids. • Diagnosis – x-ray, presence of bacteria • Rx – H2 blockers ( drugs) that block release of histamine • A blind sac attached to the cecum and has no known function. • When appendix becomes inflamed • If it ruptures, bacteria from appendix can spread to peritoneal cavity. • Symptoms- RLQ pain, rebound tenderness, fever, nausea, and vomiting • RX - appendectomy • Infectious hepatitis • Cause – virus • Spread through contaminated food or H2O • Serum Hepatitis • Caused by virus found in blood • Transmitted by blood transfusion or being stuck with contaminated needles (drug addicts) • Health care workers at risk and should be vaccinated • Use standard precautions for prevention Cirrhois • Chronic progressive disease of the liver • Normal tissue replaced by fibrous connective tissue • 75% caused by excessive alcohol consumption Cholecystitis: Inflammation of gallbladder. • Gallstones • Can block the bile duct causing pain in the shoulder blades and digestive disorders and jaundice • Small ones may pass on their own, large ones surgically removed • Surgical removal of gallbladder = Cholecystectomy Diarrhea Constipation Jaundice Loose, watery, frequent bowel movements when feces pass along colon to rapidly Caused by infection , poor diet, nervousness, toxic substances or irritants in food When defecation delayed, feces becomes dry and hard RX –diet with cereals, fruits, vegetables, (roughage) drinking plenty of fluids, exercise, and avoiding tension Yellow color of the skin Mumps A) Mumps is an acute viral infection of the parotid glands (Parotitis) B) The mumps virus belongs to the paramyxovirus family 1) RNA virus C) Humans are the only source of the virus D) Symptoms include fever, headache, sore throat, face pain and swelling of the parotid glands E) In addition to targeting the parotid gland, the virus also targets the testes, ovaries, meninges and pancreas F) Transmission is by direct contact or by inhaled respiratory droplets SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE 1. Food & water-borne infections A) Cholera 1) Caused by Vibrio cholera 2) V. cholera is acquired via fecal-oral transmission, binds to cells in the small intestine, and produces a powerful enterotoxin (cholera toxin) that results in the loss of ~20L of fluid daily (10x normal) a) Commonly referred to as “ricewater stool” 4) Most common source of infection results from fecally contaminated water and some foods such as shellfish or crab harvested from contaminated waters and vegetables fertilized with human feces 5) If untreated , can cause death in 48 hours and has a 55% mortality rate B) Shigellosis (Dysentery) 1) Primarily caused by Shigella dysenteriae (not common is U.S.), Shigella flexneri, and Shigella sonnei a) The bacteria attack the large intestine 2) It is transmitted via a fecal-oral route 3) Humans are generally the only reservoir a) Commonly fatal in infants Diseases of the Digestive System 4) Produces a potent toxin known as Shiga toxin which causes a breakdown of the intestinal lining 5) Symptoms include fever, inflammation of the gut wall, profuse diarrhea often containing blood & mucus 6) Some strains can cause damage to nervous tissue (causing seizures), anemia, and kidney failure Diseases of the Digestive System C) Traveler’s Diarrhea 1) Caused by Escherichia coli a) Gram-negative, lactose-positive rod b) The most virulent strain is E. coli O157:H7 2) Virulent strains include: Diseases of the Digestive System a) Enterotoxigenic E. coli – produce enterotoxins and adhesins that allow for attachment i) Causes severe diarrheal illness in the small intestine b) Enteroinvasive E. coli – entry into the intestinal epithelium results in cell destruction i) Causes an inflammatory disease of the large intestine VIRUSES Viral Disease of the Lower Digestive Tract 1. Norovirus (Norwalk Virus) A) Noroviruses are responsible for half of all cases of viral gastroenteritis in the U.S. B) Infects the upper small intestinal epithelium and produces cell death and decreased digestive enzyme production C) Transmission is fecal-oral route or from eating shellfish D) Has been linked to recent cruise ship outbreaks E) Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and stomach cramps which usually pass in 12-60 hours even without treatment 2. Rotavirus A) Causes most cases of viral gastroenteritis in infants and children B) Initial symptoms include vomiting and a slight fever followed shortly by profuse, watery diarrhea 1) symptoms generally pass in about a week but can last for weeks in some cases C) A vaccine is available but has to be administered at 2, 4, and 6 months to be effective Protozoan Diseases 1. Giardiasis A) Most common waterborne illness in the U.S. B) Caused by Giardia lamblia C) Symptoms are generally mild including indigestion, nausea, diarrhea with a floating stool, flatulence, and abdominal cramps 1) Symptoms may last for several weeks D) Transmitted via fecal-oral route usually via contaminated drinking water 1) They are ingested as dormant cysts that survive stomach juices to emerge as trophozoites 2) The trophozoites reproduce, releasing new cysts into feces E) Symptomatic & asymptomatic patients become long-term carriers 2. Amebiasis (amoebic dysentery) A) Caused by Entamoeba histolytica B) Causes diarrhea, abdominal pain and blood in the feces C) Ingestion of the cyst from fecally contaminated water or food liberates the trophozoites in the small intestines Test Your Gray Matter Kenny is jaundiced. What could have caused this? The medical term that means inflammation of the mucous membrane lining of the stomach and intestines is: When small quantities of stomach acid are regurgitated into the esophagus, the resulting condition is called: Eating proper foods such as cereals, fruits, vegetables, and drinking plenty of fluids can help avoid what condition? The medical term that means surgical removal of the gallbladder is: What disorder would cause pain in the back between the shoulder blades? It is recommended that all healthcare workers be vaccinated for what disease? Hepatitis is caused by? A condition in which a sore or lesion forms in the mucosal lining of the stomachs called?