* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download According to this cartoon, which European countries were fighting
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
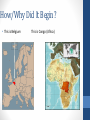
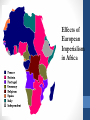
Wednesday/Thursday: February 13th/14th • Happy Valentine’s Day • History of Valentine’s Day??? • Look at Imperialism • Map Activity; Primary Document Activity • Video Warm Up: • Name two advantages of communism • Name two disadvantages of communism • Name two advantages of capitalism • Name two disadvantages of capitalism History of Valentine’s Day • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rs6xesanxNM The Age of Imperialism Chapter 27 1850-1914 What is imperialism? • The seizure (takeover) of a country or territory by a stronger country What is Imperialism? • Why do Europeans do this? • Industrialization sparks the need for: • Land perfect for establishing trading and military posts • Natural resources and raw materials • New markets for products Remember this? Well, they need this Control • Europeans want to control all aspects of their colonies • Politics • Society • Economy • Culture and customs Methods of Management • Direct Control • Paternalism – Europeans provide for local people but grant no rights • Assimilation – adaptation of local people to ruling culture • Indirect Control • Limited self-rule for local governments • Legislative body includes colonial & local officials Africa Before European Domination • Divided into hundreds of ethnic groups • Followed traditional beliefs, Islam or Christianity • Nations ranged from large empires to independent villages • Africans controlled their own trade networks • Europeans only had contact on African coasts Nations Compete • Europeans wanted more land • Contained large amounts of gold, diamonds, and rubber • Africa was a mystery to many • Europeans who penetrated Africa were: • Explorers – seeking wealth and notoriety • Missionaries – trying to convert Africans to Christianity • Humanitarians – “westernize” the “savages” How/Why Did It Begin? • This is Belgium This is Congo (Africa) How/Why Did It begin? • Congo River Valley Chiefs signed treaties that gave King Leopold II of Belgium personal control of these lands • Leopold claimed he planned on ending the slave trade there • He licensed companies that brutally exploited Africans • The Belgian Congo is 80 times larger than Belgium • This alarms other European countries, who start claiming lands of their own all over Africa Forces Driving Imperialism • Belief in European superiority • Racism • Social Darwinism • Factors Promoting Imperialism in Africa • European technological superiority • Europeans had means to control • New medicines prevent diseases Activity: • David Livingston Explores Southern Africa • Read and look at map • Answer questions directly after The Division of Africa • The Berlin Conference (1884) • Europeans leaders divide Africa • No African ruler invited • Little or no thought about the complex differences in ethnic groups • By 1914 – Only independent nations • Liberia • Ethiopia According to this cartoon, which European countries were fighting for a position in Africa? How did the Berlin Conference lead to the situation shown in the cartoon? South Africa • Three Groups Clash for Power • Africans • Zulu nation, led by Shaka, fought the British • Zulu nation lost to British in 1887 • Boers • Dutch settlers that had controlled South Africa since the mid 1600s • Also known as Afrikaners • British • Gained control of South Africa after the Berlin Conference Boer War • Fought between the Boers and the British • Many Africans fought with the Boers • First example of “total war” • British win in 1910 • Established the Union of South Africa (British Rule) Effects of European Imperialism in Africa British Imperialism in India • British Expand Control over India • East India Company • Controls India thru economic imperialism • Company uses an army including Indian soldiers known as “sepoys” • India was seen as the most important colony • Due to its production of raw materials • Known as the “Jewel in the Crown” Effects of British Rule • Impact of Colonialism • • • • • Railroads move cash crops and goods faster British control political and economic power Cash crops resulted in loss of self-sufficiency and caused famine Indian culture is disrupted due to racism and missionaries Britain sought to “modernize” India The Sepoy Rebellion • Indians Rebel • Sepoys refuse to use cartridges due to religious reasons • They had to bite them open – greased with pork fat • Considered unclean by Muslims • Many sepoys were jailed, others rebelled • British put down the rebellion • Results • Britain takes direct control of India • Increased distrust between Indians and British England’s Empire Grows THE END Imperialism Documents • BY YOURSELF! • Read the documents-analyze them • Then in complete sentences…answer the questions Guns, Germs, Steel Video • Start today….finish tomorrow