* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to quakes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
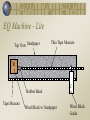
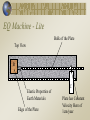
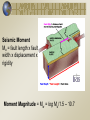
Earthquake Machine Lite Mechanical Modeling to Increase Student Understanding of Complex Earth Systems Michael Hubenthal - IRIS; Larry Braile - Purdue University; John Lahr - USGS; John Taber - IRIS Guiding Question(s) What is an earthquake? What is the role of a model in science? How are scientific ideas constantly changing? Calvin and Hobbes by Bill Watterson Have you even been outside at night and felt nervous or frightened? Will the flashlight help us feel better here? QuickTime™ and a Cinepak decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a Cinepak decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Answer the following question on your sticky note… ? ? ? ? ? ? What is an Earthquake? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Calvin and Hobbes by Bill Watterson EQ Machine - Lite Top View Sandpaper Thin Tape Measure B Rubber Band Tape Measure Wood Block w/ Sandpaper C Wood Block Guide EQ Machine - Lite Bulk of the Plate Top View B Elastic Properties of Earth Materials Edge of the Plate C Plate has Constant Velocity Here of 1cm/year Seismic Moment Mo = fault length x fault width x displacement x rigidity Moment Magnitude = Mw = log Mo/1.5 – 10.7 Visualizing magnitude with the model B Seismic Moment Mo = fault length x fault width x displacement x rigidity Moment Magnitude = Mw = log Mo/1.5 – 10.7 Elastic Rebound Theory Distant forces cause a gradual build up of stress in the earth over tens or hundreds or thousands of years, slowly distorting the earth underneath our feet. Eventually, a preexisting weakness in the earth--called a fault or a fault zone-can not resist the strain any longer and fails catastrophically.