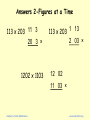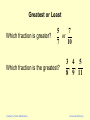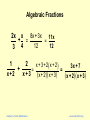* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Secondary Presentation PowerPoint
Numbers (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and art wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Critical mathematics pedagogy wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum Improvement Study wikipedia , lookup
Historical Background
• “Veda” means “knowledge”
• Age of Vedic texts: from 300BC to several
millennia BC
• Sections on medicine, ethics, metaphysics,
psychology, architecture, music, astronomy,
grammar and so on. And ‘ganita sutras’
• Sri Bharati Krsna Tirthaji (1884 – 1960)
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Historical Background
• Vedic system was reconstructed between 1911
and 1918
• Bharati Krsna wrote one introductory volume in
1958: “Vedic Mathematics” published in 1965
• Shankaracharya
of Govardhan Matha ,Puri
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Sixteen Sutras
• They cover all of mathematics, pure and
applied
• These relate to natural mental functions
• This explains why Vedic Maths is so easy
• It works the way the mind naturally works
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Features of Vedic Mathematics
• Natural, powerful
• Coherent, unified
• Easy to do, easy to understand
• Flexible
• Creative, fun
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
“By One More than the One Before”
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
752 =
(4½)2 =
43 x 47 =
88 x 46 =
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
8
9 . . . .
www.vedicmaths.org
Digit Sums
A Digit is a single-figure number: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
Sum means add.
So ‘Digit Sum’ means adding the digits in a number.
17
19
123
38
5030
7531
The Digit Sum is found by adding the digits in a number,
and adding again if necessary
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
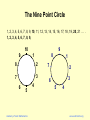
The Nine Point Circle
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21 . . . .
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
10
9
9
1
8
8
2
7
3
6
5
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
4
1
7
2
3
6
5
4
www.vedicmaths.org
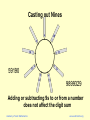
Casting out Nines
59190
9899329
Adding or subtracting 9s to or from a number
does not affect the digit sum
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Groups adding to 9
Any group of figures in a number that add up to 9
can be "cast out“
7312
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
42134
61395
www.vedicmaths.org
Left to Right
•
123
We read, pronounce and write numbers
from left to right
•
The most important/significant figures in a
number are at the left
•
In the Vedic system we can add, subtract,
multiply and divide from left to right
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Left to Right
So:1. Mental calculations are easier
2. We can get at the most significant figures in
a calculation first, not last
3. We can combine the operations
2
2
314 + 432 = 534.06....
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Addition
8 8
4 6 +
7 6
5 5 +
1 8 7
4 4 6 +
Practice Add from left to right:
1) 7 7
66
2) 4 3 7
871
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
3) 6 5 4
727
4) 2 4 6 8
3865
www.vedicmaths.org
The Digit Sum Check for Addition
Find 32 + 39 and check the answer using digit sums.
32
39+
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
77
124 +
279
121 +
490
www.vedicmaths.org
Mental Multiplication
7 8
3x
67
7x
88
6x
63
8x
Practice Multiply from left to right:
1) 6 6
6x
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
2) 5 3
5x
3) 8 6
7x
4) 6 4
6x
5) 4 9
4x
5 3
4
6
8
7
7x
9
6
www.vedicmaths.org
Longer Multiplications
3 8 5
3x
627
4x
5347
7x
Practice Multiply from left to right:
1) 7 2 7
6x
2) 4 3 2
7x
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
3) 6 5 4
3x
4) 2 4 6 8
5x
www.vedicmaths.org
The Digit Sum Check for Multiplication
3 8
3x
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
627
4x
www.vedicmaths.org
Subtraction from left to right
6
2
5
1
6
7
3
7 –
5
7 –
5
1
6
7
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
6
2
5
5
6
1 –
8
3
3
5
5
7 –
4
2 –
7
3
7
2
3
3
5
2
3
8
6
7
3
8 –
4
1 –
www.vedicmaths.org
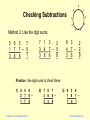
Checking Subtractions
Method 1: Add the second and third rows to get the first
row.
8
5 6 5
3 –
1 7 7 –
5
3 8 8
Practice Which is/are wrong?
1) 7
2
4
6
7
8
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
3
8 –
5
2) 8 0 5
4 5 8 –
3 5 7
3) 7 8 3
1 4 7 –
6 3 6
www.vedicmaths.org
9
1
8
Checking Subtractions
2
7
3
6
5
Method 2: Use the digit sums.
5
1
3
6
7
8
7
3
3
5
7
7 – 6
1
8
1
4
6
3
2
7 – 5
6
6
8
4
3
4
3
2
7 – 2
9
6
Practice Use digit sums to check these:
1) 4
2
1
5
7
7
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
6
8 –
8
2) 7
3
3
0
6
3
7
8 –
9
3) 9 3 8
1 8 7 –
7 4 1
www.vedicmaths.org
“All from 9 and the Last from 10”
8 7 6
5 4
9
1 2 4
4 6
1
The formula All From 9 and the Last From 10
subtracts numbers from the next highest base number.
1000 – 864 =
1000 – 307 =
10000 – 6523 =
100 – 63 =
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
“All from 9 and the Last from 10”
Practice
1) 1000 – 777 =
2) 10,000 – 4621 =
3) 100 – 58 =
4) 100,000 – 15032 =
5) 1000,000 – 123456 =
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
6) 1000 – 730 =
www.vedicmaths.org
“All from 9 and the Last from 10”
1000 – 72 =
100,000 – 503 =
700 – 66 =
4000 – 333 =
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Variations
5000 – 47 =
40,000 – 33 =
1 – 0.763 =
Rs.100 – Rs. 53 =
Rs.500 – Rs. 77 =
Rs.1000 – Rs.835 =
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Subtraction
7312
3765–
905
447–
64332
28655–
2) 8 1 1
3) 7 6 4 2 3
Practice
1) 5 1 3 2 4
18745–
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
345–
23567–
www.vedicmaths.org
Subtraction
908
456–
8393
2865–
64935
38657–
Split the number where a bar digit is
followed by a positive digit
Practice
1) 6 1 3 8 1
48747–
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
2) 6 1 9
135–
3) 8 6 8 2 9
38564–
www.vedicmaths.org
Multiplying Numbers Near a Base
100
98 – 02
97 – 3
95 / 06
89 – 11
97 – 3
86 / 33
89 – 11
89 – 11
78 / 21 = 79/21
1
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Practice: Multiply
89
96
97
94
91
95
99
88
98
98
88
88
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
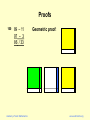
Proofs
100
89 – 11
97 – 3
86 / 33
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
Arithmetic proof:
89 × 97 = 89×100 – 89×3
= 8900 – 100×3 + 11×3
= 8900 – 300 + 11×3
= 8600 + 33
= 8633
www.vedicmaths.org
Proofs
100
89 – 11
97 – 3
86 / 33
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
Geometric proof:
www.vedicmaths.org
Proofs
100
89 – 11
97 – 3
86 / 33
(x – a)(x – b) = x(x – a – b) + ab
Algebraic proof:
(100 – a)(100 – b) = 100(100 – a – b) + ab
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Mentally
89 – 11
97 – 3
86 / 33
96 x 93
97 x 94
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Numbers Over 100
103 + 03
104 + 4
107 / 12
123 + 23
103 + 3
126 / 69
102 + 02
103 + 3
105 / 06
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Practice: Multiply
106 x 107
104 x 108
102 x 103
111 x 112
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
One Number Under and One Number Over 100
105 + 5
97 – 3
102 / 15
= 101 / 85
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
104 + 4
93 – 7
97 / 28
= 96 / 72
www.vedicmaths.org
Proportionately
204 x 107
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
48 x 97
98 x 206
www.vedicmaths.org
Proportionately
200
189 –11
197 – 3
2x 186 / 33
= 372 / 33
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
300
304
307
3x 311
= 933
+4
+7
/ 28
/ 28
www.vedicmaths.org
Practice: Multiply Using the Base Method
201
234
307
308
198
188
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Base Multiplication
8–2
7–3
5/ 6
6–4
6–4
2/ 6 =3/6
12 + 2
13 + 3
15 / 6
1
Practice Multiply:
8
8
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
12
14
13
14
www.vedicmaths.org
Proportionately
20
21 + 1
22 + 2
2x 23 / 2
= 46 / 2
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
30
28 – 2
27 – 3
3x 25 / 6
= 75 / 6
www.vedicmaths.org
Practice: Multiply Using the Base Method
41
42
33
32
51
56
19
18
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Numbers Near Large Bases
879
x 997
10003
x 12331
69978
x 99997
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
“Vertically and Crosswise”
2
4
3
1 ×
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
3
4
3
4 ×
6
5
7
2 ×
www.vedicmaths.org
Practice Multiply:
5
3
3
2 ×
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
7
7
2
3 ×
4
4
4
4 ×
www.vedicmaths.org
The Vedic Method
• Can multiply numbers of any size in one line
• The simple pattern makes it easy to remember
• Easy to explain
• Can multiply from left to right or from right to left
• Reversible
• Algebraic products can be done the same way
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Division
3 x 8 = 24
3 1 ×
9 9 2
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
24 ÷ 8 = 3
?
8 ×
2 4
4 2 ×
2 3 5 2
www.vedicmaths.org
Find the Missing Number
5 4 ×
3 4 5 6
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
7 3 ×
2 3 3 7
www.vedicmaths.org
Comparison with Conventional Methods
Multiplication
Division
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
Vedic
6 7
5 2 ×
52 ×
3484
Conventional
6 7
5 2 ×
52) 3 4 8 4
www.vedicmaths.org
Algebra
2x + 3
3x + 5 ×
2
6x + 19x + 15
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
3x – 2
x + 7 ×
2
3x + 19x – 14
www.vedicmaths.org
Algebraic Division
3x + 5 ×
2
6x + 19x + 15
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Extending to 3-figure Numbers
104 x 53
10
5
112 x 113
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
4
3 ×
11
2
11
3 ×
www.vedicmaths.org
Answers 2-Figures at a Time
113 x 203 11 3
20 3 ×
1202 x 1103
113 x 203 1 13
2 03 ×
12 02
11 03 ×
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Bar Numbers
39 x 32
Bar numbers are extremely useful
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Extending the Pattern
504 x 321
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
5 0 4
4 1 3
3 2 1
5 2 3
www.vedicmaths.org
Practice Multiply:
4 3 2
5 1 3 ×
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
3 4 5
2 0 7 ×
4 4 4
4 4 4 ×
www.vedicmaths.org
Extending the Pattern
3-figure numbers
4-figure numbers
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
4-Figure Numbers
2 4 3 2
3 5 1 3 ×
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
3 4 5 2
2 0 3 4 ×
www.vedicmaths.org
Practice Multiply:
4 1 3 2
5 4 1 3 ×
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
4 2 4 4
4 3 4 4 ×
www.vedicmaths.org
“Vertically and Crosswise”
• Numbers of any size can be multiplied in one line
• Numbers of any size can be divided in one line
• The multiplication method simplifies for squaring
numbers
• And this is reversible to do square roots (in one
line)
• And quadratic and higher order equations
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Adding/subtracting Fractions
2 1
3 5
1 3
4 7
2 1
3 5
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Adding/subtracting Fractions
3 5
4 6
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
7 11
18 30
www.vedicmaths.org
Practice: Find
3 2
7 5
4 2
5 3
5 1
6 9
11 7
15 25
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Three Fractions
1 1 2
2 3 5
1 2 4
3 5 7
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Greatest or Least
Which fraction is greater?
5
7
or
7
10
Which fraction is the greatest?
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
3 4 5
, ,
8 9 11
www.vedicmaths.org
Unifying the Four Operations
Addition
Subtraction
Multiplication
Division
4 1
+
5
3
4
1
–
5
3
4
1
×
5
3
4
1
÷
5
3
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Algebraic Fractions
2x x
8x + 3x
11x
+ =
=
12
12
3 4
1
2
x + 3 + 2 x + 2
3x + 7
+
=
=
x +2
x +3
x + 2 x + 3
x + 2 x + 3
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Equation of a Line through Two Given Points
Find the equation of the line through the points (7,4) and (5,1).
l (7,4)
l (5,1)
O
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Equation of a Line through Two given Points
Find the equation of the line through the points (0,-4) and (-2,3).
Practice 1 Find the equation of the line through the points:1) (4,9), (1,2)
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
2) (8,5), (-3,1)
3) (5,0), (-2,-5)
www.vedicmaths.org
Equation of a Line through a given Point
and Parallel to a given Line
Find the equation of the line through the point (5,7)
and parallel to the line 2x + 3y = 5.
l (5,7)
O
2x + 3y = 5
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Equation of a Line through a given Point
and Parallel to a given Line
Find the equation of the line through the point (-3,2)
and parallel to the line x - 5y = 1.
Practice 2 Find the equation of the line through the given point
and parallel to the given line:1) (4,1), 2x + y = 3
2) (-2,5), 3x – 5y = 2
3) (0,-3), 5y + 2x = 2
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Equation of a Line through a given Point
and Perpendicular to a given Line
Find the equation of the line through the point (3,1)
and perpendicular to the line 2x + 3y = 5.
l (3,1)
O
2x + 3y = 5
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Equation of a Line through a given Point
and Perpendicular to a given Line
Find the equation of the line through the point (2,5)
and perpendicular to the line 3x - y = 2.
Practice 3 Find the equation of the line through the given point
and perpendicular to the given line:1) (7,2), 2x + y = 1
2) (-3,4), 5x – 2y = 3
3) (0,-1), 4y + x = 2
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Dividing by 19
1
19
11
19
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Right to Left / 9-Point Circle
.
.
1 = 0. 0 5 2 6 3 1 5 7 8 9 4 7 3 6 8 4 2 1
1
1
1 1 1 1
1
1 1
19
1
19
9,0
1
8
7
2
3
6
5
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
4
www.vedicmaths.org
Divisor Ending in 9
17
29
15
39
29
49
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
A Short Cut
.
= 0.1 0 5 12 6 3 11 15 17 18
1
19
11
19
.
=0.1 51 718 91 4 71316 8
.
4 2 1 10 5 12 6 31 1
9 1 4 7 13 16 8 4 2 1
17
29
.
.
=0.2 51 8 6 2202628191615 5 21 71 2
.
4 11 2327 9 3 110131 42 4 8221 7
6
39
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Proportionately
4
7
8
13
4
33
7
11
5
23
3
17
(to 5 decimal places)
(to 5 decimal places)
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
COMPOUND ANGLES
4
5
If sinA = (A is obtuse) and cosB = (B is acute)
5
13
find tan(A-B).
A
-3 4 5
B
5 12 13
A-B 33 56 65
56
Tan(A-B) =
33
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
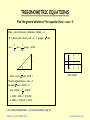
TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
Find the general solution of the equation 2sinx - cosx = 2
2sinx cosx Rsinxcos Rcosxsin Rsin(x ).
If 2 Rcos and 1 Rsin ,i.e.R2 22 12 giving R 5 and
cos
2
1
, sin
giving 26 34'.
5
5
R
1
x
x-
x
x
c
-1
2
-4
0
s
2
1
3
5
1
+
5
5
2
2sinx cosx 5 sin(x 26 34').
Vedic method
Thus the equation 2sin x cosx 2
becomes 5 sin(x 26 34') 2
2
sin(x 26 34')
0.8945
5
x 26 34' 180n ( 1)n (63 26')
x 180n ( 1)n (63 26') 26 34'
from “Advanced Mathematics 1” by Celia, Nice & Elliott, Page 119.
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
APPLICATIONS OF TRIPLES
Trigonometry
Coordinate geometry (2 & 3 dimensions)
Transformations (2 & 3 dimensions)
Simple Harmonic Motion
Projectiles
Complex numbers
Hyperbolic functions
Conics
Astronomy
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
SOLUTION OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION
Find, correct to 2 decimal places, the roots of the equation
3x2 – 5x – 7 = 0.
Comparing 3x2 – 5x – 7 = 0 with ax2 + bx + c = 0;
a = 3, b = -5, c = -7.
b b2 4ac
Then x =
.
2a
So x =
5
2
5
4.3. 7
2.3
5 25 84
6
5 109
6
5 10.44
6
15.44
5.44
or
6
6
a = 3,
D1 = 6x – 5 = 13
.
13 7 . 0 0 0
5
2
11
3. 4 3
x 2.57, 0.91.
Vedic method
2.57 or 0.91.
from “General Mathematics” Book 3, by Channon & Smith, Page 195.
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
INTEGRATION BY ‘PARTS’
Find x 2sinxdx.
Let
{
v x2
du
sin x
dx
dv
2x
dx
u cos x
du
dv
Then v
dx uv u
dx
dx
dx
gives x2sinxdx = (-cosx)(x2 ) - (-cosx)(2x)dx
x sinxdx = -x cosx +2xsinx +2cosx +K
2
2
Vedic method
x2 cos x 2 x cos xdx
Thus, for x cos xdx,
let
{
vx
du
cos x
dx
dv
1
dx
u sin x
giving x cos xdx (sin x)(x) (sin x)(1)dx
xsinx cosx K
Hence x2sinxdx = -x2cosx +2xsinx +2cosx +K
from “Mathematics: The Core Course for A-level” by Bostock & Chandler, Page 313.
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
SQUARE ROOT OF A COMPLEX NUMBER
Find 15 + 8i
Let 15 8i = a + bi, where a and b are real
15 8i (a bi)2
a2 b2 2abi
Equating real and imaginary parts gives:
a2 – b2 = 15
and
2ab = 8
Using b
(1)
(2)
15 8i 4 i
Vedic method
4
16
in (1) gives a2 2 15.
a
a
a 4 15a2 16 0
(a2 - 16)(a2 + 1) = 0
Thus a2 – 16 = 0 or a2 + 1 = 0
But a is real so a2 + 1 = 0 gives no suitable values
so a 4
Referring to equation (2) we have
Hence 15 8i = 4 + i or -4 - i
a
b
4
1
-4
-1
4 i
from “Mathematics: The Core Course for A-level” by Bostock & Chandler, Page 536.
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org
Features of Vedic Mathematics
• Works the way the mind works
• More unified
• Can be a mental system which develops memory and
mental agility
• Very flexible:
choice of methods
left to right or right to left
• Encourages creativity and innovation
Academy of Vedic Mathematics
www.vedicmaths.org