* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 13.6 Pyramid Models
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Indoor air pollution in developing nations wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
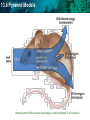
13.6 Pyramid Models KEY CONCEPT Pyramids model the distribution of energy and matter in an ecosystem. 13.6 Pyramid Models An energy pyramid shows the distribution of energy among trophic levels. • Energy pyramids compare energy used by producers and other organisms on trophic levels. • Between each tier of an energy pyramid, up to 90 percent of the energy is lost into the atmosphere as heat. • Only 10 percent of the energy at each tier is transferred from one trophic level to the next. • Energy is in the form of Proteins, carbohydrates energy energy transferred lost And fats 13.6 Pyramid Models Ninety percent of this mouse’s food energy is used to maintain its life functions. 13.6 Pyramid Models 13.6 Pyramid Models Energy is measure in calories. A kilocalorie is 1000 calories. Calculate the flow of energy from the producers to the owl. The total energy at the producer level is 1,700,000 Kcals! Put it in the First pyramid in your notes! 13.6 Pyramid Models Other pyramid models illustrate an ecosystem’s biomass and distribution of organisms. • Biomass is a measure of the total dry mass of organisms in a given area. tertiary consumers 75 g/m2 150g/m2 secondary consumers primary consumers producers producers 675g/m2 2000g/m2 13.6 Pyramid Models • A pyramid of numbers shows the numbers of individual organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem. tertiary consumers 5 secondary consumers 5000 primary consumers 500,000 producers producers 5,000,000 • A vast number of producers are required to support even a few top level consumers. 13.6 Pyramid Models Pyramids of numbers and biomass can become inverted or upside down if based on a single tree. 13.6 Pyramid Models On your note paper Use one of the energy pyramids to draw in the desert food chain introduced in section 4.