* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Muhammad the Prophet without videos
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
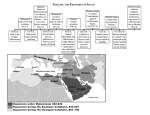
Muhammad the Prophet Life and Times of Muhammad – “The Praised” Mecca • Crossroads for trading • Birthplace of Muhammad – 570 A.D. • Major pilgrimage site – the Hajj • The Kaaba • Polytheism Birth of Mohammad – 570 A.D. Main Sources for Muhammad’s Life : • Quran or Koran - Muslim “Word of God” as revealed through the angel Gabriel • Early Biographies • Hadith – Saying, Act, or Islamic Law seen as coming directly from Muhammad. • Christian Byzantine Sources - (Different Perspective Obviously) They indicate that both Jews and Christians saw Muhammad as a deceiving prophet, or at least certain circles did. “Do prophets come with a sword and chariot?” Muhammad - Childhood • Father died just before his birth • Mother died before six years old • Sent out of Mecca to get a better education in a healthier environment • Grandfather sent him to work with the Bedouins until. Grandfather died. • Uncle – Abu -Talib was a merchant • Much of what we know could be considered legend. The Legend • While sitting at the Ka’bah Muhammad’s Grandfather was worried about his birth. • Father died before his birth. The Legend Continued • • • • Birth and named “Muhammad” or “Praised One” The donkey overtaking the others. Five year dream of Angels cleansing his heart. Christian Hermit saw a mark of prophethood between his shoulders. Marriage - Khadijah • Muhammad ran caravans for widow named Khadijah • She proposed marriage • Muhammad was 25 • Khadijah was 40 • Supposedly a happy marriage • 2 sons – died in childhood • 4 daughters • Died after 25 years of marriage. 40 years old – Idol Worship • • • • The Ka’Bah Build by Abraham Mecca Corruption and Idol Worship • Muruwwah Code • Nomads – Polytheistic and believed in jinns or genies. • There were Jews, Christians, and Hanifs who were all Monotheistic. The Ka’Bah Black Stone - al-Ḥajar al-Aswad Muhammad the Prophet and Angel Gabriel – “Night of Power” • 610 AD during the Arabic month of Ramadan • The Cave of Hira • Muhammad chosen as the last “seal of the prophets” • Revealed the Qur’an to Mohammad Abu-Talib and Ali • Abu-Talib – Muhammad’s Uncle – Never Converted • Ali – First Male Convert • Early convert to Islam • Muhammad’s cousin/son-in-law – Married to Fatimah – Muhammad’s daughter • Shia Muslims Follow Ali - “Shia Ali” means “followers or faction of Ali” • The first or 12 Imams • Shia Muslims do not follow the Caliphs (Elected Leaders)of Sunni Islam Sunni Muslims see Ali as the 4th Caliph Muhammad Returns to Mecca • Driven out of Mecca shortly after 620 – abt. 622 - Hijra • 630 AD – Muhammad returned to Mecca and destroyed the idols in the Ka’Bah or Kaaba Isra - A Journey on a Winged Horse • Told Meccans he had a night journey (Dream) on winged horse - Isra • Started in Jerusalem • Went through the seven levels of Heaven. • Received from God the fundamentals of the Islamic Creed or beliefs. • The Foundation Stone • Wailing Wall A Journey on a Winged Horse Al- Buraq – The mythological winged steed that transported the prophets to Heaven. Jerusalem - Revered by Three Religions – Jews – Christians - Muslims The Hijra: The Turning Point – Year 1 Muslim Calendar • “Islam” – Arabic word for “submission” inferring submitting to God. • “Muslim” Arabic word for “submitter” – one who submits to God. • *Controversy – “Submit” by the sword? Or Submit willingly? • Ummah – Muslim Community / Nation • New teachings angered Meccans. They threatened murder. • Left Mecca for Yathrib in 622 (Later called Medina or “City of the Prophet) • This journey became known as the “Hijra”. • The Muslim Calendar – Year 2011 = 1432 • This is why Muslim holidays are not sincrinized with our Gregorian Calendar. • 619 – Khadijah (Wife) and Abu Talib (Uncle) died. Early Survival • Reaction by early Jews and Christians • Meccan Emigrants refused to farm • Attacking Caravans (page 33) • Attacking during the Hajj month. • Victory at Badr • Controversy - “Does a prophet come with swords and chariots?” • This is where Jews and Christians disagree about Muhammad being a prophet. • Picture: Massacre of the Banu Qurayza Muslim Life in Medina • Established laws about marriage, divorce, inheritance, theft and punishment for crime, etc. • The Quran is mostly silent on these issues. • Most of this comes from the Hadith – the teachings and actions supposedly attributed to Muhammad. • Some modern day criticisms. • To be fair - *Remember we a judging a 7th century man and traditions by modern standards and many of these traditions were found in early Jewish and Christian traditions. • Treatment of Women • Muhammad’s plural marriages - polygamy • Treatment of Jews – massacres etc. Criticisms – Modern Issues Women’s Rights Criticisms – Modern Issues Blasphemy Criticisms – Modern Issues Polygamy and Honor Killings Criticisms – Modern Issues Intolerance for Other Religions Baminyan Buddhas in Afghanistan Ground Zero - 911 Memorial Mosque On the eve of expected city approval of a mosque and Islamic center two blocks from Ground Zero, backers of the project are pledging to include a memorial to the victims of the Sept. 11, 2001, terror attacks as part of an effort to allay opponents' complaints that the mosque's location is insensitive. Called - Cordoba House – Carl Palodino http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carl_Paladino "We've heard and felt their pain, and we're extending ourselves," said Daisy Khan, a partner in the building and the wife of the cleric leading the effort. "We want to repair the breach and be at the front and center to start the healing." Return to Mecca • 628 – returned to Mecca and signed a peace treaty with the Meccans – the Meccans saw Muslims as equals now. • 629 – came back as part of the Hajj • 630 – Returned with an Army • Muhammad required the Arab tribes to accept Islam and pay taxes to support Islam. • 632 – Nearly all Arabs tribes were Muslim. (By Traditional Accounts) Death of Muhammad • Appointed Abu-Bakr to lead the public worship • Final pilgrimage – Hajj – to Mecca establishing this as one of the Five Pillars of Islam. • Final sermon – “every Muslim is a brother to every other Muslim and that you are now one brotherhood – Connection – “The Muslim Brotherhood” • Died 8 June 632 • The Quran was compiled after his death. Caliphs and Early Converts • Head of an Islamic state or Ummah and Islamic community – • Means – “Successor” or “Representative” – “Commander of the Faithful” • Not Prophet – Muhammad is the last. • Big argument over who rules after Muhammad’s death • Abu-Bakr – Muhammad’s wealthy best friend – 1st Caliph • Umar – 2nd Caliph • Uthman – 3rd Caliph Read Page 256 - 257 Sultan • Arab for “strength” and Authority • Later lesser governor under a Caliphate. • Not a religious but a political leader • Turkey - The title has been defunct since the Republic of Turkey abolished the Ottoman Caliphate in 1924 Emer • • • • Prince Commander General High Ranking Sheikhs – • Sheikhs mean “Elder” a position of honor in a tribe The Roman Empire The Roman Empire Splits East and West – 395 A.D. The Roman Empire Constantinople – Justinean I and Constantine I The Fall of Constantinople – Istanbul The Spread of Islam The Ottoman Empire – 1453-1922 Muslim World Today and Modern Turkey - 1923