* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside the Earth
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
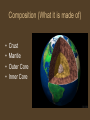
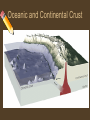
Layers of the Earth Directions Take detailed notes about the different layers of the earth. Be sure to include: • A Title • Subtitles For Each Topic • Drawings Where Applicable Let’s start with Earth’s Common Four Layers These are the layers you learned about last year. They are based on the composition of each section of the Earth. Composition (What it is made of) • • • • Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core The Crust • Outer most layer • 5-100 km thick (the thinnest layer) • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense) – Continental (less dense) • Made of oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, & magnesium Oceanic and Continental Crust The Mantle • Middle layer • Very thick layer • Mostly iron & magnesium The Core • • • • • Outer core is liquid Inner core is solid Made mostly of iron 1/3 of the earth’s mass Extremely hot There is another way to look at the layers! Tectonic Plates These layers are based on movement (mesosphere) Physical Structure of the Earth (5 Layers) • Lithosphere- rigid hard outer layer that makes up the plates (includes the crust & top mantel) • Asthenosphere- amorphous solid rock that flows slowly like putty (top part of the mantel) • Mesosphere- strong middle layer of Earth (lower mantel) • Outer Core- liquid layer made mostly of iron • Inner Core- solid, very dense, made mostly of iron Let’s Compare Click Here To See A Video!