* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Risk Mgmt - WCU Computer Science
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Cross-site scripting wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
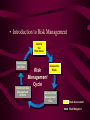
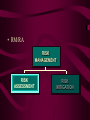
Risk Management October 1998 • What is RISK MANAGEMENT? – The process concerned with identification, measurement, control and minimization of security risks in information systems to a level commensurate with the value of the assets protected. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) Course Objective – The student will be able to DETERMINE a risk index. • Introduction to Risk Management Identify the Risk Areas Re-evaluate the Risks Risk Management Cycle Implement Risk Management Actions Assess the Risks Develop Risk Management Plan Risk Assessment Risk Mitigation • Balance of Risk Management Risk Management Risk Ignorance Risk Avoidance • RISK - The likelihood that a particular threat using a specific attack, will exploit a particular vulnerability of a system that results in an undesirable consequence. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) • THREAT -Any circumstance or event with the potential to cause harm to an information system in the form of destruction, disclosure, adverse modification of data, and/or the denial of service. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) • Threat Example - Hackers • Threat Example - Electrical Storms • Definition of Likelihood – LIKELIHOOD of the threat occurring is the estimation of the probability that a threat will succeed in achieving an undesirable event. • Considerations in Assessing the Likelihood of Threat – – – – Presence of threats Tenacity of threats Strengths of threats Effectiveness of safeguards • Statistical Threat Data • Two Schools of Thought on Likelihood Calculation Assume Don’t Assume • ATTACK – An attempt to gain unauthorized access to an information system’s services, resources, or information, or the attempt to compromise an information system’s integrity, availability, or confidentiality, as applicable. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) • VULNERABILITY -Weakness in an information system, cryptographic system, or other components (e.g... , system security procedures, hardware design, internal controls) that could be exploited by a threat. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) • Vulnerability Example • CONSEQUENCE – A consequence is that which logically or naturally follows an action or condition. • RM/RA RISK MANAGEMENT RISK ASSESSMENT RISK MITIGATION • RISK ASSESSMENT -A process of analyzing THREATS to and VULNERABILITIES of an information system and the POTENTIAL IMPACT the loss of information or capabilities of a system would have. The resulting analysis is used as a basis for identifying appropriate and cost-effective counter-measures. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) • Why Risk Assessment? • Benefits of Risk Assessment – – – – Increased awareness Assets, vulnerabilities, and controls Improved basis for decisions Justification of expenditures • Risk Assessment Process – – – – Identify assets Determine vulnerabilities Estimate likelihood of exploitation Compute expected loss • Identify Assets – People, documentation, supplies •Properties of Value Analysis -Confidentiality -Integrity -Availability -Non-repudiation •Definition -Confidentiality: Assurance that information is not disclosed to unauthorized persons, processes, or devices. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) •Definition - Integrity: Quality of an information system reflecting the logical correctness and reliability of the operating system; the logical completeness of the hardware and software implementing the protection mechanisms; and the consistency of the data structures and occurrence of the stored data. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) •Definition -Availability: Timely, reliable access to data and information services for authorized users. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) •Definition -Non-repudiation: Assurance the sender of data is provided with proof of delivery and the recipient is provided with proof of the sender’s identity, so neither can later deny having processed the data. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) • Determine Vulnerabilities Open Communications Lines Open Network • Likelihood • Expected Loss • Risk Measure – RISK MEASURE is a description of the kinds and degrees of risk to which the organization or system is exposed. • Communicating Risk – To be useful, the measurement should reflect what is truly important to the organization. • How do we calculate risk? • Primary Risk Calculation Methodologies Quantitative & Qualitative • The Quantitative Method • The Qualitative Method • Qualitative Example: – “The system is weak in this area and we know that our adversary has the capability and motivation to get to the data in the system so the likelihood of this event occurring is high.” • Quantitative and Qualitative Merged • Delphi Approach • Probability Density Function • Examples of documented risk assessment systems – Aggregated Countermeasures Effectiveness (ACE) Model – Risk Assessment Tool – Information Security Risk Assessment Model (ISRAM) – Dollar-based OPSEC Risk Analysis (DORA) – Analysis of Networked Systems Security Risks (ANSSR) – Profiles – NSA ISSO INFOSEC Risk Assessment Tool • Formula for Risk • Threat and Vulnerability Revisited The capability or intention to exploit, or any circumstance or event with the potential to cause harm such as a hacker. A weakness in a system that can be exploited. Threat + Vulnerability • Likelihood Vs. Consequence • Likelihood – The Likelihood of a successful attack is the probability that an adversary would succeed in carrying out an attack. • Factors influencing an attack – Level of threat – Vulnerabilities – Countermeasures applied • Determine Level of Threat – Criteria for evaluating the level of threat: • History • Capability • Intention or motivation • Determine Vulnerabilities • Criteria for Evaluating the Vulnerability – Number of vulnerabilities – Nature of vulnerability – Countermeasures • COUNTERMEASURE – A countermeasure is an action, device, procedure, or technique used to eliminate or reduce one or more vulnerabilities. • Examples of Countermeasures – Procedures: • security policies and procedures • training • personnel transfer – Hardware: • doors, window bars, fences • paper shredder • alarms, badges – Manpower: • guard force • CONSEQUENCE – A consequence is that which logically or naturally follows an action or condition. • Determination of the Consequence of the Attack – “The worse the consequence of a threat harming the system, the greater the risk” Attack Consequence Success • Risk Calculation Process – determine: • • • • the threat the vulnerability the likelihood of attack the consequence of an attack – apply this formula by: • postulating attacks • estimating the likelihood of a successful attack • evaluating the consequences of those successful attacks • NSA ISSO Risk Assessment Methodology – Developed in the NSA Information Systems Security Organization – Used for INFOSEC Products and Systems – Can Use During Entire life Cycle – Not Widely Used Outside of DI • The NSA ISSO Risk Assessment Process – – – – – Understanding the system Developing attack scenarios Understanding the severity of the consequences Creating a risk plane Generating a report • The Risk Plane Y -axis The severity of the Consequences of that successful attack. X -axis The likelihood of a successful attack • Risk Index Risk Index, as defined by the “Yellow Book”, is the disparity between the minimum clearance or authorization of system users and the maximum sensitivity of data processed by a system. • Risk Index – Minimum User Clearance=Rmin – Maximum Data Sensitivity=Rmax – Risk Index=Rmax - Rmin • Rating Scale for Minimum User Clearance (Rmin) MINIMUM USER CLEARANCE Uncleared (U) Not Cleared but Authorized Access to Sensitive Unclassified Information (N) Confidential (C) Secret (S) Top Secret (TS)/Current Background Investigation (BI) Top Secret (TS)/Current Special Background Investigation (SBI) One Category (1C) Multiple Categories (MC) RATING (Rmin) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 • Rating Scale for Maximum Data Sensitivity (Rmax) Maximum Data Sensitivity Ratings Without Categories Unclassified (U) Not Classified But Sensitive Confidential (C) Secret (S) Top Secret (TS) Rating (Rmax) Maximum Data Sensitivity With Categories 0 1 N/A Unclassified but Sensitive With One or More Categories Confidential With One or More Categories Secret With No More Than One Category Containing Secret Data 2 3 5 Secret With Two or More Categories Containing Secret Data Top Secret With One or More Categories With No More Than one Category Containing Secret or Top Secret Data Top Secret With Two or More Categories Containing Secret or Top Secret Data Rating (Rmax) 2 3 4 5 6 7 • Computer Security Requirements RISK MODE INDEX 0 Dedicated 0 System High 1 Compartmented Multilevel 2 Compartmented Multilevel 3 Multilevel 4 Multilevel 5 Multilevel 6 Multilevel 7 Multilevel MINIMUM CRITERIA FOR OPEN ENVIRONMENTS None C2 B1 MINIMUM CRITERIA FOR CLOSED ENVIRONMENTS None C2 B1 B2 B2 B3 A1 * * * B2 B3 A1 * * * = Security Requirements Beyond State of the Art • Automated Risk Assessment Tools • NIST Special Publication 500-174 • LAVA Los Alamos Vulnerability and Risk Assessment Tool • Threats Considered by LAVA – natural and environmental hazards – accidental and intentional on-site human threats (including the authorized insider) – off-site human threats • RiskPAC – a knowledge-based system that uses a questionnaire metaphor to interact with the user and measure risk in government-related and other topics. • A.L.E. Annualized Loss Exposure Calculator • RISKWATCH 7 1 2 6 3 5 4 • Risk Management Research Laboratory • Risk Mitigation – Risk Mitigation is any step taken to reduce risk. • Residual Risk – Portion of risk remaining after security measures have been applied. (Definition from National Information Systems Security (INFOSEC) Glossary, NSTISSI No. 4009, Aug. 1997) • Residual Risk and Safeguards • Summary – Risk Mitigation – Risk Calculation Methods – Risk Index ? Sampling of General INFOSEC Resources on the Web •Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) Awareness and Training Facility: http://www.disa.mil/ciss/cissitf.html •Information Security News: http://www.infosecnews.com/ •Information Security Mall: http://niim.bus.utexas.edu/ •National INFOSEC Education Colloquium: http://www.infosec.jmu.edu/ncisse •International Information Systems Security Certification Consortium: http://www.isc2.org/ •National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) Computer Security Clearinghouse:http://csrc.nist.gov/welcome.html •National INFOSEC Telecommunications and Information Systems Security Committee(NSTISSC):http://www.nstissc.gov •President’s Commission on Critical Infrastructure Protection: http://www.pccip.gov/ •Security Site Links: http://www.sscs.net/resources/secsites_list.htm Sampling of Web Addresses for Colleges and Universities with INFOSEC Courses, Programs, Centers •Dartmouth College: http://www.dartmouth.edu/pub/security/ •George Mason University Center for Secure Info Systems: http://www.isse.gmu.edu~csis/index.html •Georgia Tech Information Security Center: http://www.samnunnforum.gatech.edu/web.html •Harvard University: http://www.harvard.edu •Idaho State University: http://bibo.isu.edu/security/security.html •Indiana University: http://www.cs.indiana.edu •Iowa State: http://vulcan.ee.iastate.edu •James Madison University: http://www.jmu.edu/ •National Defense University: http://www.ndu.edu/irmc/ •North Carolina State University: http://www.ncsu.edu •Purdue University: http://www.cs.purdue.edu/coast.html •University of California at Davis: http://www.ucdavis.edu •University of Texas, Austin: http://wwwhost.ots.utexas.edu/mac/pub-mac-virus-html •Western Connecticut State University: http://www.wcsu.ctstateu.edu/mis/homepage.html