* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Different Types of Evolution
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
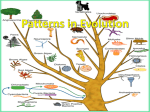
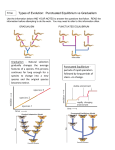
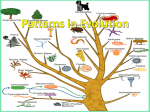
TYPES OF EVOLUTION Standards CLE 3210.5.5 Explain how evolution contributes to the amount of biodiversity CLE 3210.5.3 Explain how genetic variation in a population and changing environmental conditions are associated with adaptation and the emergence of new species. Objectives Differentiate between coevolution, divergent evolution, convergent evolution and a punctuated equilibrium Recognize action examples of each type of evolution in Important Vocabulary Population: all of the same species that live in one area Species: a group of closely related organisms with similar characteristics that are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring Adaptation vs. Acclimatization Adaptation - Changes in traits in populations over time Example: White moth population becoming a black moth population after 5 generations. Acclimatization – individual organism changes physiologically Example: growing thicker fur in winter What are the types of evolution? Natural ways: 1. 2. 3. 4. selection can result in evolution in 4 Coevolution Divergent evolution Convergent evolution Punctuated equilibrium 1. Coevolution Coevolution—two species evolve together due to their close relationship. When one evolves, the other evolves too! Examples: birds and flowers, or predators/prey Coevolution Examples: 2. Divergent Evolution Divergent evolution—species with same ancestor that live in different environments adapt with increasingly different characteristics until they are no longer the same species DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS will lead to differences in which variations of traits are most “fit” (successful) Example: Finches on the Galapagos Islands evolved into many different species to eat different foods. Adaptive Radiation an evolutionary pattern in which many species evolve from a single ancestral species Leads to homologous structures 3. Convergent Evolution Convergent evolution— species with different ancestors becoming more similar SAME ENVIRONMENT will lead to development of structures with similar functions Example: Dolphins and fish have very different ancestors (mammals vs. fish), but both have evolved flippers because they live in the sea. Convergent Evolution Leads to analogous structures Convergent Evolution Example: DIVERGENT: different environment COEVOLUTION: predator/prey CONVERGENT: same environment Punctuated Equilibrium the hypothesis that evolutionary development is marked by isolated episodes of rapid speciation between long periods of little or no change. Artificial Selection Natural Selection = environment determines desirable traits Artificial selection = humans determine desirable traits What is a Phylogenetic Tree? Shows evolutionary relationship among organisms based on genetic similarities As you go down the tree, you go back in time to a common ancestor Branching out means natural selection caused speciation How do I read Phylogenetic Trees? The closer two lines are to each other, the more closely related the species The further away, the more distantly related 1. What is the closest related species to species D in the 1st tree? 2. What species is the most different from species D in the 2nd tree? 3. Which two species share the oldest common ancestor? Practice: Complete worksheet types of evolution practice