* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam File - Northwest ISD Moodle
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
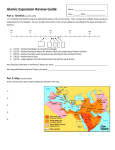
APWH: INTRODUCTION TO ISLAM I. Global Context: • By the 6th century C.E. the Byzantine government was the only centralized authority in what remained of the Roman Empire. • Its only rival was the Sasanid Empire of Persia (224-651 C.E.), who guarded the Silk Road. • Social and economic transformation was underway in the Middle East. •The outcome would not be a return to a fragmented less urbanized pattern of life (Unlike Western Europe) •Sassanid and Byzantine Empires set the stage for a new and powerful religiouspolitical movement called Islam. A note about modern Islam 42 modern nations are completely Islamic. There are 1 billion Muslims in the world. Only 20% of the world’s Muslims are Arabs Pre-Islamic Arabia Medina Mecca Bedouins -Arabia was fragmented into dozens, of tribal, nomadic clans, called Bedouins. -Each clan had its own deity (usually associated with the goddess of heaven or the moon) which nomadic people could worship anywhere. The city of Mecca was the main religious and trading center for the Bedouin tribes of Arabia. Before Islam, the Bedouins believed that their many gods were housed in the Kaaba, a black stone shrine in the heart of Mecca. - The leader of a clan was called the shaykh. He was elected by a council of elders and usually had large herds of animals, and several wives. His will was enforced by a class of warriors. - The struggle for subsistence in the harsh Arabian desert created strong loyalties - To be cut off from the clan was fatal. - War often broke out over minor conflicts. - Arabia was a world of constant fighting. II. Muhammad -Muhammad was born in Mecca in 570C.E.. He was orphaned at age 6, and was raised by his uncle, who owned a caravan trading business. - Working for his uncle brought Muhammad in contact with Jews and Christians living in Palestine (Damascus & Jerusalem). This is during the Ummyad dynasty • Muhammad became very acquainted with Judaism and Christianity, and his religion shows similarities with both beliefs. • On one of his many trading trips to Palestine, Muhammad met and married Khadija, a wealthy merchant widow. - Muhammad became a wealthy merchant - Bored and spent lots of free time in the mountains outside Mecca. - In 610 C.E., while meditating in the Mountains, Muhammad began to receive revelations from the angel - these revelations Gabriel continue for 20 years. Islamic revelations attacked idolatry and the traditional beliefs of the Bedouins; these revelations were rejected and mocked in Mecca - In 622 C.E., Muhammad fled Mecca and traveled to Medina to establishes his new government. This event is called the “hijra,” and it marks the beginning of the Muslim calendar. • In 629 C.E., after converting the people of Medina to Islam, Muhammad led them in the conquest of Mecca. The Spread of Islam: • While in Medina, Muhammad was able to create the umma (Community of the faithful.) • Muhammad knew that his religion would not be safe until he created an empire to protect it. • By 632 C.E., he had conquered most of Arabia. Muhammad dies suddenly in 632 C.E., without appointing a successor. This leads to arguments over who should be Caliph of Islam • Caliph (Deputy) refers to the Islamic rulers after the death of Muhammad. A Caliph had both religious & civil authority • The first four caliphs continue the expansion of the Islamic kingdom The Sunni vs Shi’ite split: Sunnis believe the true Caliph should be chosen by those close to Muhammad; but he did not have to be a relative. Most (85%) Muslims are Sunni. Shi’ite (word means “division”) believe Muhammad appointed Ali, his son-in-law, before he died. They maintain that the true Caliph must be a direct descendant of Muhammad. III. The Islamic Faith: • Islam’s sacred text is the Qu’ran. Written in the Arabic language it means “recitation” because the faithful recite it daily. • Any version of the Qu’ran that is not in Arabic is considered a transliteration (not a translation). Basic Islamic Beliefs: -The foundation of Islam is submission to God’s will. The word Islam means submission. The term Muslim means, one who submits. • The Qu’ran teaches that Muhammad was God’s last prophet (following others such as Moses and Jesus.) • Jews, and Christians, like Muslims are considered “People of the Book.” (God’s people) • Thus Muslims do not consider Islam as a new religion, but a correction of Judaism & Christianity, which had been corrupted. • Man is a creation by Allah (God); he is free to reject God, but will be an outsider of God’s community. • Judgment Day of the World; everyone will receive either eternal paradise or eternal torment. • The Priesthood of the faithful; personal faith in and fellowship with God is obtained without intermediaries (clergy). The Qu’ran requires all believers to follow certain practices, called the “five pillars of Islam”. 1. Shahada; A profession of faith that there is only one God and Mohammed is his Prophet. 2. Salat; the activity of praying five times daily, towards Mecca. 3. Zakata; Almsgiving, Muslims are required to give 4% of their income to the poor. 4. Hajj; a pilgrimage to Mecca once during your life, if you are able. A simple white garment is worn, symbolizing the equality of believers. 5. Siyam; Fasting in the daylight hours during Ramadan, the month of the first revelation. Forbidden Practices: • • • • • Drinking alcohol. Gambling. Eating unclean meat (pork, shellfish, etc.) Enslaving “people of the book.” The use of violence to spread Islam. (Violence can be used against non-Muslims to protect Islam.) • The Islamic holy lands must never be violated by non-Muslims. Any violations gives just cause for Jihad.