* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
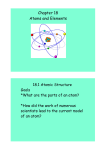
Chemistry The Organization of Matter The Organization of Matter • Chemistry is the study of how all of the substances that we know are structured and organized. • Chemists are looking to try to better understand how our world functions. • What are the ingredients of matter? • How do those ingredients form all of the matter that we know? • How do we classify the different types of matter that exist? The Atom • All matter is composed of tiny particles that are invisible to the naked eye. They are called atoms. • Atoms are like the letters of the alphabet: they allow us to arrange and re-arrange them in order to create new substances. • Atoms can be combined to create different molecules. These molecules create all of the matter that we know. Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. 2. Atoms themselves are formed of even smaller particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. 3. Atoms are distinguished one from the other by the number of protons, neutrons and electrons that they have. … 4. Atoms which have the same number of protons are called elements. ▫ ▫ Atoms of the same element are identical to each other. Atoms of different elements have different properties and masses. 5. Atoms can be combined in chemical reactions to form molecules. The Atomic Model in History • Many chemists in our history have contributed to the understanding of atoms. • Each of these chemists have propsed different models to show this understanding of atoms and to show how different atoms are related to one another. The Atom according to Democritus, 400 BCE. • Democritus was the first to suggest that atoms made up matter. The problem? The technology didn’t exist to prove his theory. • Atom = Greek for ‘cannot be divided’. John Dalton, (1766-1844) • Towards thw 1800’s, John Dalton, an English scientist, proved the existence of atoms based on his experiments with gases. He isolated and classified six atoms: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. … • Dalton’s model includes the use of balls of different sizes and colours. These represent the different atoms. • A bar connects atoms together to show a chemical bond, (a molecule). The others… • Many scientists have since improved atomic theory in the 1800’s ad 1900’s, (Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Chadwick). • Today, we use the Bohr-Rutherford model, represented like this: Protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Electrons orbit the nucleus on orbitals, (2 on the first, 8 on the second, 8 on the third). The Structure of the Atom • Each atom contains protons, neutrons and electrons. These are called subatomic particles. • The protons have a positive charge, are found in the nucleus of the atom and contribute to the mass of the atom. • The neutrons have no charge – they are neutral. They are also found in the nucleus and contribute to the mass of the atom. • The electrons are found around the nucleus on orbitals. They have a negative charge and no mass. There are the same number of protons and electrons. Molecules • Atoms that are chemically linked together are called molecules. The atoms in molecules can be the same or different. • Atoms link together after chemical reactions, when the electrons of the two atoms react together. • Molecules make up most of the matter that we know. It is relatively rare for atoms to exist on their own. Chemical Formulas Symbol for Hydrogen Symbol for Oxygen Indicates that there are 2 atoms of hydrogen. No number means that there is only one of that atom. Rules for Writing Chemical Formulas • Each capital letter indicates a new atom. ▫ If there is a lower-case letter, it is simply the seond letter in the symbol of one atom. • A small number, (subscript), indicates the quantity of atoms. When there is no subscript, there is only one of that atom. • A large number before a chemical formula means that there are multiples of that particular molecule. ▫ 2 H₂O Mixtures • Many types of matter are actually mixtures. A mixture contains many elements and compunds which are not chemically linked together, but just exist together. • Ex – Air, juice, tap water, etc. Elements • An element is all atoms with the same number of protons. • Ex – oxygen, hydrogen, gold. • The number of protons is a characteristic property of the elements. • There are 118 different elements, 92 of which are found naturally. The others were created in a lab. The Periodic Table: The Building Blocks of Matter • The periodic table contains all of the elements, natural and artificial that are currently known. • These elements form all of the visible and invisible matter that surround us. • The periodic table is organized in a specific way to show how the elements are related to one another, and to tell us important informations about them. … • The elements are classified according to their horizontal and vertical axes. • Horizontally: ▫ The elements are placed in increasing order of their atomic number. ▫ The atomic number is the number of protons. ▫ Each horizontal line is called a period. • Vertically: ▫ Each column represents a family. ▫ A family groups together elements with similar properties. ▫ Ex – Group 18 is called the noble gases. … • Each box in the periodic table includes the same information. • Name of the Element: ▫ Hydrogen, oxygen, potassium, etc. • Symbol of the Element: ▫ Either one capital letter or a capital letter and a lowercase letter. Ex – H, O, Ca • Atomic Number: ▫ Indicates the number of protons that the element has. • Atomic Mass: ▫ Indicates the number of protons + the number of neutrons. Summary Atom One type of matter. Na Cl O Element Multiple atoms of the same type. Molecule Two atoms or more, O₂ same or different. H₂ Compound Two atoms or more, NaCl but they are H₂O different. A CO₂ molecule that contains two different atoms. O₂ H₂ Na Ar NaCl CO₂