* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ovulation through implantation
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
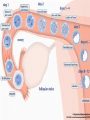
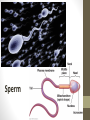
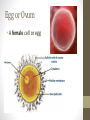
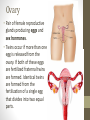
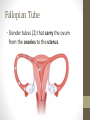
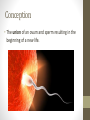
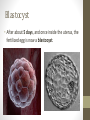
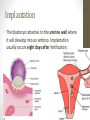
Ovulation through Implantation Chromosome & Gene Video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ubq4eu_TDFc Chromosome • Within the sex cells of every man and woman there are 23 pairs of chromosomes (a thread like structure which has a string of tiny particles called genes.) As the sex cell matures the 23 pairs of chromosomes divide to contain only 23 single chromosomes. Gene • The part of the chromosome that determines all the inherited characteristics Karyotype • General appearance, including the size, number and shape of somatic chromosomes Where do your genes come from? • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Yg89GY61DE Sperm Sperm • Sperm carry the genetic blueprint for gender. There are between 105-106 boys born for every 100 girls. • The male sperm is the smallest cell in the human body and the female ovum is the largest cell; 90,000 times heavier that the male sperm. • Everyday a healthy young male produces 100 million sperm (1000 sperms a second). Each sperm contains a unique selection of the father’s genetic material. • The male body constantly forms new sperm (from sexual maturity to a very advanced age). While all of the women’s eggs are formed during the fetal stage. • At ejaculation, 500 million mobile sperm are discharged but almost half have defects that prevent them from fertilization. Egg or Ovum • A female cell or egg Ovary • Pair of female reproductive glands producing eggs and sex hormones. • Twins occur if more than one egg is released from the ovary. If both of these eggs are fertilized fraternal twins are formed. Identical twins are formed from the fertilization of a single egg that divides into two equal parts. Fallopian Tube • Slender tubes (2) that carry the ovum from the ovaries to the uterus. Uterus • Hollow organ in which the fertilized ovum is deposited and the embryo and fetus are developed. Ovulation • Two weeks after the onset of menstruation the follicle containing the egg is discharged at the surface of the ovary and is caught in the fallopian tube. For approximately 24 hours the egg awaits possible fertilization by a sperm. If this does not occur, the egg begins to disintegrate and dies. Once this occurs, large quantities of the hormone progesterone are released into the woman’s bloodstream cueing the lining of the uterus to be shed. This is called menstruation. • https://youtu.be/nLmg4wSHdxQ Fertilization • The journey from the vagina to the fallopian tube (about 6 to 7 inches) takes several hours. If there is no egg present, the sperm swim back and forth and can survive for up to five days. • A few hundred sperm reach the destination of the egg. They all begin to try to penetrate the wall of the egg. Some perish in this process. Once one sperm breaks all the way through the ovum wall, the chemical structure of the egg changes shutting out all other sperm. • Two cells (egg and sperm) joined to make a single cell. Conception • The union of an ovum and sperm resulting in the beginning of a new life. https://www.youtube.com/wa tch?v=BFrVmDgh4v4 Zygote • Once the sperm has penetrated the egg, the tail separates from the head. This first cell is called the zygote. (fertilized egg; at least 2 cells) • The head of the sperms (which holds the genetic make up) travels to the nucleus of the egg and the genetic blueprints are combined into one. Morula • Solid mass of cells ins the early stages of embryonic development. • Roughly 12 hours after the fusion of the chromosomes, the first cell division takes place and continues to divide every 12-15 hours. At approximately the third day, when there are 16 identical cells, a morula is formed. Blastocyst • After about 5 days, and once inside the uterus, the fertilized egg is now a blastocyst. Implantation • The blastocyst attaches to the uterine wall where it will develop into an embryo. Implantation usually occurs eight days after fertilization. The Role of Genetics • We inherit genes from both parents in sets of chromosomes. • No people, except identical twins have identical DNA. • Dominant vs. Recessive Genes • Recessive genes are only expressed when received from both parents (ie. Red hair) • Gender: women carry X chromosome, males carry either an X or Y chromosome. • XX is female • XY is male Genetics Activity #1 • What are the chances that this child will have red hair? • Hint: brown is dominant and red is recessive Brown Brown Red Red Genetics Activity #2 • What are the chances that this child will have blue eyes? • Hint: brown is dominant, blue recessive Brown Brown Blue Brown Infertility • The inability to conceive a child • Adoption: legally takes on responsibilities for child • Artificial Insemination: sperm injection • In Vitro Fertilization: ovum and sperm are combined and then implanted • Ovum Transfer: donated egg • Surrogate Mother: woman becomes pregnant for another woman. Infertility Reflection • Answer the following questions at the end of your notes on genetics and infertility. Answer in 4 complete sentences per question. • Do you think struggling with infertility is an emotional battle? Why or why not? • If you and your partner were struggling with infertility, what method do you think you would do? Why?