* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
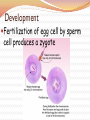
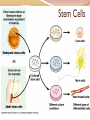
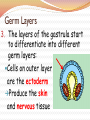
Basic Characteristics 1. Eukaryotic 2. Multicellular 3. Heterotrophic If mobile, get food by moving If sessile, get food by filter feeding 4. intracellular digestion Symmetry = is the arrangement of body structures Asymmetry= no symmetry Example: Sea Sponge Symmetry Radial Symmetry= can be divided evenly along many different planes Example: Hydra, Jellyfish Symmetry Bilateral Symmetry= can be divided equally only along length into Left and Right sides Example: Human, Dog Cephalization Cephalization: sense organs are concentrated at the head end of the body Can process info from environment much faster Directional Terminology Anterior - head end Posterior - tail end Directional Terminology Dorsal - back side Ventral - belly side Development Fertilization of egg cell by sperm cell produces a zygote Development 1. Zygote divides by mitosis to form a blastula (hollow ball of cells) Development The blastula is made of identical, unspecialized cells These are embryonic stem cells Scientists would like to harvest these to do research because they can turn into any type of cell Stem Cells Development 2. One side folds inward, forming a gastrula Germ Layers 3. The layers of the gastrula start to differentiate into different germ layers: Cells on outer layer are the ectoderm Produce the skin and nervous tissue Germ Layers Cells on inner layer are endoderm Produce the digestive system Germ Layers A 3rd layer forming between the endo- and ectoderm is called the mesoderm Produces the muscular, respiratory, circulatory, & excretory systems Skeletons All skeletons allow movement and provide support & protection 1. Exoskeleton = Hard outer covering Skeletons 2. Endoskeleton = Internal structure made of bone and/or cartilage