* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Outer Planets - Mr. Cramer
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
Jumping-Jupiter scenario wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
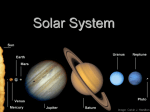
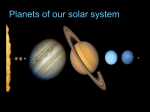
The Outer Planets Gas Giants and Pluto • The four outer planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune – are much larger and more massive than Earth, they do not have solid surfaces • The four planets are called gas giants • Pluto is classified as a dwarf planet • Gas giants are composed of hydrogen and helium, which is in liquid form • Have a stronger gravitational force than the terrestrial planets • Gravity keeps the gases from escaping, have a thick atmosphere • Outer layer is extremely cold because of the distance from the sun • Temperature increases within the planets • All have many moons • Each is surrounded by a set of ring, a thin disk of small particles of ice and rock Jupiter • Largest and most massive • 2 ½ times that of all the other planets combined Jupiter’s Atmosphere • • • • Thick atmosphere Mainly hydrogen and helium Great Red Spot – a storm larger than Earth Swirling winds blow hundreds of kilometers per hour (similar to hurricanes) • No land to weaken the storm • First observed in the mid-1600s Jupiter’s Structure • Dense core of rock or iron • Thick mantle of liquid hydrogen and helium surround the core • Pressure at Jupiter’s core is estimated to be about 30 million times greater than the pressure at Earth’s surface Jupiter’s Moons • • • • • 63 plus moons Four largest moons– Io – covered with large active volcanoes Europa – icy crust overs an ocean of liquid water Ganymede – largest in solar system, larger than Mercury or Pluto. • Callisto – icy and covered with craters • All are larger than Earth’s moon • Have discovered dozens of addition moons, most have been found in the last few years due to improved technology Saturn • • • • 2nd largest in solar system Thick atmosphere made up of hydrogen and helium Contains clouds and storms, not as big as Jupiter Average density is less than that of water Saturn’s rings • The rings are made up of chunks of ice and rock, each traveling in its own orbit around Saturn. • Each ring is divided into many thinner rings • Rings are broad and thin, like a compact disc Saturn’s Moons • The largest is Titan, larger than Mercury • Discovered in 1665 • Titan has an atmosphere so thick that little light can pass through it • Four other moons are over 1,000 kilometers in diameter • 47 plus moons Uranus • • • • • Four times the diameter of Earth Much smaller than Jupiter and Saturn Twice as far from the sun as Saturn Much colder Looks blue-green because of traces of methane gas in its atmosphere • Surrounded by thin, dark, flat rings Discovery of Uranus • Discovered in 1781 • First new planet discovered since ancient times • Started an era of active solar system study after discovery Exploring Uranus • • • • Voyager 2 sent back images of Uranus Few clouds Rotates in about 17 hours Rotation is tilted at an angle of about 90 degrees from vertical • Rotates from top to bottom • Think was hit by an object that knocked it on its side Uranus’s Moons • • • • 27 plus moons Five largest moons have icy, cratered surfaces Moons have lava flows Voyager 2 revealed 10 moons never seen before Neptune • • • • • Uranus and Neptune look like twins Similar in size and color Cold blue planet Atmosphere contains few clouds Scientists think Neptune is slowly shrinking, causing its interior to heat up • As energy rises to the surface, it produces clouds and storms in the atmosphere Discovery of Neptune • Discovered because of a mathematical prediction • 1846 mathematicians calculated the orbit of an unseen planet (Uranus) • Then observed the unknown planet in the predicted area Exploring Neptune • 1989 Voyager 2 flew by Neptune • Photographed the Great Dark Spot about the size of Earth, probably a giant storm • Storm didn’t last long, 5 years later it was gone • Storms seem to come and go in Neptune’s atmosphere Neptune’s Moons • 13 plus moons • Largest is Triton which has a thin atmosphere • Region near Triton’s south pole is covered by nitrogen ice. Pluto • • • • • Much smaller and denser Solid surface Smaller than Earth’s moon Three known moons Charon is the largest and half the size of Pluto Pluto’s Orbit • Pluto is so far away from the sun that it revolves around the sun only once every 248 Earth years • Orbit is elliptical and comes closer to the sun than Neptune on part of its orbit • Many icy objects larger and farther out than Pluto have astronomers creating a new class of objects called “dwarf planets” • Dwarf planet, is round and orbits the sun, and has not cleared out the neighborhood around its orbit. Questions 1. Compare and Contrast the 4 gas planets. 2. Describe an important characteristic of each outer planet that helps to distinguish it from the other outer planets. 3. Why do all the gas giants have thick atmospheres? 4. What is the Great Red Spot and its significance?