* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sunni vs. Shia
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
History of Nizari Ismailism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Zanj Rebellion wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Usul Fiqh in Ja'fari school wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
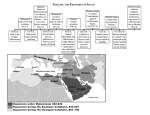
Sunni vs. Shia Deconstructing Islam for the Classroom Journal: What Do You Know about Sunni and Shia Islam? Images of Sunni and Shia Violence The Sunni-Shia Split -It’s All About FamilyMuhammad and Khadija are credited with having several daughters, although the parentage of them is questioned by scholars; they may have been adopted by Muhammad rather than sired by him. Uthman (the 3rd Caliph) was married to one of these daughters, Umm Kulthum bint Muhammad. However, historically these daughters have been marginalized, most likely because they did not bear any surviving children or survive their father. For the purposes of this presentation, all family relations have been simplified, thus we can state that Fatima was the only surviving daughter of Muhammad. Khadija First Wife Prophet Muhammad Fatima The Sunni-Shia Split -It’s All About FamilyAbu Bakr Abu Talib Muhammad’s Uncle Friend and Early Convert Khadija (First Wife) Ali Muhammad’s Cousin Prophet Muhammad Fatima Aisha The Sunni-Shia Split -It’s All About Family- Hassan 2nd Imam Fatima Ali 1st Imam Hussein 3rd Imam Zaynab Ali Zain Al-Abideen 4th Imam All Other Imams Descend from this Line. Umm Al-Kaltum Muhammad’s Succession 632- Muhammad dies, leaving no confirmed successor* Disagreement among clans on who will lead the faith- bloodline (Ali) or the one most capable The Ummah (the Islamic community) elects Muhammad’s father-in-law (through his wife Aisha) Abu Bakr to lead the faith. He becomes the first Caliph - the leader of the Ummah. The Rashidun (632-661) The Rule of the Four Righted Guided Caliphs Name Ruled Died Known For Abu Bakr 1st Caliph 632-634 elected Natural causes, appointed his successor Quelled rebellion and united Arabia Umar ibn alKhattab 2nd Caliph 634-644 appointed Stabbed in a Medina mosque by a POW with a personal grudge. Wars of expansion (power not religion but religion followed) to the greater Middle East Uthman ibn Affan 3rd Caliph 644-656 elected Assassinated by those from the elite of Medina over the rise of status and power of the Umayyad clan. Expanded the empire to North Africa and Central Asia- but with much political cost. Standardized the Qu’ran. Ali ibn Abu Talib 4th Caliph/1st Imam 656-661 elected Assassinated by Kharajiites, a group of dissenters to Ali’s rule Ruled during the first Fitnah (civil war). His place in history is denoted more for who he was rather than what he did. A Community Divided The Shia (followers of Ali) had been supporting Ali as the rightful head of the Islamic faith since the death of Muhammad. Now as Ali was being persecuted politically, the idea of being unfairly treated was being ingrained in the Shia psyche. As Ali was not actively seeking retribution for Uthman’s death, the Ummah was growing more and more discontent with the Caliph, garnering more support for challengers to the Caliphate like Mu’awiya. The Ummah was also horrified by the infighting between those that had once been a part of Muhammad’s inner circle, the community wanted a strong leader, not only for their protection but for the preservation of the faith. The true split in Islam came with the death of Ali. The Shia, who supported Ali went one way, and the Sunni, who followed Mu’awiya I (who declared himself Caliph and began the Umayyad dynasty) went the other. Sunni and Shia Today Population statistics (Sunni 90%, Shia 10%) Areas of the World where conflict between the two exist. Iraq and Bahrain Holy Places Sunni: Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem Shia: Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem, Najaf (Site of Ali’s Tomb), Karbala Umayyad Caliphate (661-750) In 661, a Muslim general seizes the office of the caliph, and moves the capital from to Damascus. Under the Umayyads, they created a hereditary dynasty, ending succession from close friends and relatives. Pushed into India, sieged Constantinople, and advanced across North Africa. Stopped by the Franks in the Battle of Tours Abbasid Caliphate (750-1000) Discontent over Umayyad rule began. Many Arab Muslims did not consider the Umayyads the rightful successful to Muhammad. In 750, Abbas, a descendent of Muhammad’s uncle overthrew the Umayyad caliphate and established the Abbasid Caliphate. Abbasid Caliphate (cont) The Abbasid Caliphate marks the peak of the Muslim empire. They controlled more territory than the Roman empire did at their peak. Its new capital was established at Baghdad (modern day Iraq), and was a leading commercial center, rivaling Constantinople. Abbasid Caliphate Crumbles Political unity began to crumble inside the Muslim empire. Disputes over succession broke out among the rival Muslim groups, and independent dynasties appeared, each proclaiming its own caliph. Opened to invasion from the Seljuk Turks. Rise of the Seljuk Turks Nomadic tribes from central Asia who were fierce and energetic warriors. They embraced Islam as their religion, and became a strong cohesive political unit. They conquered the Abbasid Caliphate, and took over the former Muslim empire. Seljuk Turks Threaten the Byzantine Empire Annihilated the Byzantine army at the Battle of Manzikert. Conquered the important territory of Asia Minor. (Still controlled by the Turks to this day) Fearful that Constantinople might fall, the Byzantine emperor appealed to the Christians in the West for help. The West responded by sending several military expeditions, known as the Crusades, to free the East (especially the Holy Land), from Muslim invaders. Constantinople Breached?!?! In 1204, an invading army breached the defenses. They captured and looted the city, slaughtering both young and old. They had drunken orgies, and raped women before the altars of the Hagia Sophia. The invading army was not the Muslims, it was instead Christian warriors from the West on a “holy” crusade. Venetian (Italian) merchants had paid them off and brought them to Constantinople to destroy Venice’s main commercial rival. “It is tragic that the assailants, who set out to secure free access for Christians to the Holy Land, turned against their brothers in the faith. The fact that they were Latin Christians fills Catholics with deep regret.“ – Pope John Paul II The Fall of Constantinople – May 30, 1453 After fighting the Muslims for over 200 years, the Byzantine Empire was severely weakened. A final wave of Muslim invaders known as the Ottoman Turks sacked Constantinople and killed the last Byzantine emperor. Ottoman Turks Secret Weapon: Gun Powder Byzantine Secret Weapon: Greek Fire An explosive mixture of naphtha oil, sulfur, and saltpeter. Greek Fire ignited spontaneously and burned even on water. Ottoman Turk Dardanelles Gun Fall of Constantinople (cont) For almost a month, the Turks had been using catapults to launch 1200 lb. rocks at the walls of the city. The wide moat kept the Turks at a distance, unable to breach the defenses. They built bridges over the moat, and siege towers to scale the walls, but the Byzantines used Greek Fire to burn the Siege Towers The Turks then tried tunneling under the walls, but the Byzantines found out their plan and dug tunnels to meet them with more “Greek Fire” Fall of Constantinople Using the gunpowder, they were able to blow a hole in the wall surrounding the city. They filled the moat with dirt, and parts of the broken down wall, and marched on Constantinople. This would mark the end of the Byzantine Empire, and a new Empire would rule all the way to the end of World War I. They would take Constantinople as their capital, and rename it Istanbul.