* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Survey
Document related concepts
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
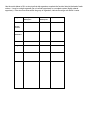
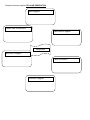
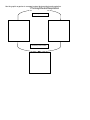
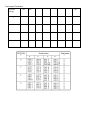
Name:_____________________ Period:_____ Biology EOC Review Topics Scientific Method Ecology Population Ecology Evolution Inorganic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Cell Structure Cell Transport Cell Cycle-Mitosis Meiosis Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Genetics Transcription/Translation Safety Be able to interpret and identify major safety precautions and safety violations in specific scenarios. Scientific Method Know the steps of the scientific method. What is a hypothesis? How is it different from a scientific theory? What is data? Be able to read data/charts and graph such data on a line graph, bar graph, etc. What is the control in an experiment? What is the independent (manipulated) variable in an experiment? a. Be able to identify this is in a scientific scenario (EX a paragraph about an experiment). What is the dependent (responding) variable in an experiment? b. Be able to identify this is in a scientific scenario (EX a paragraph about an experiment). Ecology From the list provided, order the items from simplest level or organization to most complex. With the ordered list, explain the rationale for the order. Biome Body system Community Organ Population Biosphere Cell Ecosystem Organism Tissue Starting with the sun, construct a simple food chain up to a 3rd order consumer. Around this food chain and in a different color, construct a food web listing trophic levels. How are the following 3 ecological pyramids related? Energy Pyramid What do environmental changes have to do with successional changes (either primary or secondary succession) in a community? How are these environmental changes related to descent with modification? Evolution Write a 1-sentence summary about the following contributing factors to Darwin’s observations and ideas that influenced his thinking in the formation of his theory of evolution. There were patterns of diversity that Darwin observed in his travels. Living organisms compared with fossils Darwin collected. The close proximity and very different climates of the Galapagos Is. Lamarck’s theory of evolution 16. What are the 5 main points of the Theory of Natural Selection? Natural selection 17. Resistance to pesticides and bacterial resistance are 2 examples of organisms, insects and bacteria, respectively, showing variation in their ability to survive stressful (to them) environmental conditions. Explain how this might occur and the relationship to natural selection. Use the matrix below to summarize the important points that each area provides as evidence for evolution. Evidence of evolution Fossil record Geographic distribution of living organisms (Biogeography) Homologous structures Embryology Genetics Biochemistry Importance to theory Use the matrix below to fill in a structure that aids organisms complete the function listed at the head of each column. It may be a single organelle (for uni-cellular organisms) or a complete system (highly ordered organisms). If the structure varies within the group of organisms, indicate the range over which it varies. Kingdom Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protist Fungi Plants Animals Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Hetero or Autotrophs? Reproduce Inorganic Chemistry: Draw an atom and label the parts of the atom. What are different chemical bonds we have learned about this year? Properties of Water Property Description Organic Chemistry There are 4 major classes of organic compounds, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Many people see these as polymers being made up of smaller components (these may or may not be identical). In the matrix below, for each organic molecule, fill in what the smaller units are of which it’s made, list one functional role, and one structural role in living systems. Organic molecule Carbohydrate Monomer Polymer Function Lipid Protein Nucleic acid Draw a concept map with the central concept being ‘enzymes’. Include in your concept map the following terms: substrate, protein, reactions, activation energy, 3-D structure. Cell Structure Using the Venn Diagram, compare/contrast a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. prokaryote eukaryote 2. In the following matrix, put a check in the box to show the organelle is present in prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells, or both, and state in 1 sentence what the function of the organelle is. Organelle Cell membrane Cell wall Nucleus Mitochondria Chloroplast Endoplasmic reticulum (smooth) Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum (rough) Vacuole Prokaryote Eukaryote Function What is homeostasis? Explain or illustrate what function the cell membrane plays in homeostasis. Cell Transport Types of Passive Transport Description and Example Types of Active Transport Description and Example Cell Cycle-Mitosis Complete the following matrix about DNA. In the column for ‘structure’ describe what the part is made of and in the ‘function’ column, describe what it does. Part DNA molecule Nucleotide Nitrogen bases Structure 8. DNA Replication Steps: Write them and draw the process Function Mitosis and Meiosis Use the following Venn diagram to compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis. mitosis meiosis Many scientists point to 4 principles that summarize Mendel’s work. They are: Traits are inherited by individual units called genes If there are 2 or more forms of a gene, some forms may be dominant, others recessive In most organisms that have sexual reproduction, there are 2 copies of each gene, one from the father, the other one from the mother The different forms of genes usually segregate independently from one another For each of the above principles, make a connection to the increased genetic variation that one gets as a result of the meiotic divisions. Complete the event map below for PHOTOSNYTHESIS. What happens? Where does it take place? When does it happen? Photosynthesis Why does it happen? ‘Who’ is involved? How does it happen? Complete the event map for CELLULAR RESPIRATION. What happens? Where does it take place? When does it happen? Respiration Why does it happen? ‘Who’ is involved? How does it happen? Use the graphic organizer to compare/contrast photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthesis/Respiration How they’re different How they’re the same Genetics You are responsible for knowing the following crosses: Complete Dominance Incomplete dominance Co-dominance Multiple Alleles Sex-linked Complete Dominance: Cross two heterozygous green plants. Yellow is the recessive trait. What are the genotype and ratios, phenotype and ratios of the offspring of this cross? Multiple Alleles: A man with blood type AB marries a woman who is heterozygous for type A. What is the probability that they will have a child who has a blood group A, B, AB, O? Incomplete dominance: The Japanese four O Clock plants, flower color shows incomplete dominance. Predict the genotype and phenotype and ratios of the offspring of a cross of homozygous red flower with a homozygous white flower. Cross two pink Japanese four O Clock plant plants. Write the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 generation. Sex-linked: A woman who is heterozygous for hemophilia marries a normal man. What are the possible phenotypes and the probability of occurrence? Co-dominance: A black cat is crossed with a white cat. The F1 generation are all gray. Predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the F2 generation after crossing the F1 generation. Transcription/Translation DNA (non coding) TAC AAG ATC (Coding) DNA mRNA AUG tRNA UAC Amino acid Met AUC UCC Phe His Glu Stop