* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download From Republic to Empire
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Illyricum (Roman province) wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Marcus Aemilius Lepidus (triumvir) wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
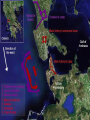
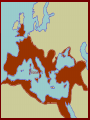
From Republic to Empire Caesars Dead Caesar’s death prompted another round of Civil wars in Rome. On One side were the men who had killed Caesar On the other side were Octavian, Mark Antony, and Lepidus. They defeated the men who had killed Caesar and formed the second Triumvirate. Friends or Enemies? Soon after taking power, Octavian forced Lepidus in to retirement. He and Marc Antony divided the empire into the east (Octavian) and the west (Marc Antony.) They soon went to war. At the battle of Actium Octavian defeated all of Marc Antony’s forces. He was now in charge of the empire. OCTAVIAN Octavian was the Great Nephew of Caesar He had been with Caesar throughout many of the battle he fought. Caesar adopted him in his will and left all of his money to him. He installed himself as the emperor and was in charge of the entire empire. He changed his name to Augustus MARK ANTONY Marc Antony was once a general that had been in alliance with Octavian However, by putting himself against Octavian, he was doomed to lose. He went to Egypt where he fell in love with Cleopatra. Since he was no longer in Rome, Octavian was able to spread rumors about Marc Antony. This allowed Octavian to have public support behind him and defeat Marc Antony. A year later Marc Antony and Cleopatra committed suicide. PAX ROMANA The PAX ROMANA lasted from the time that Augustus took power until two centuries later. During this time, Rome experienced several different rulers. Some of these rulers were very good to the people and treated them very well. However, others were not so worried about the people, and were very cruel. GOOD EMPERORS NERVA reformed land laws in favor of the poor HADRIAN made laws easier to understand and apply. TRAJAN gave money to the poor for the education of their children. Expanded the empire to its largest size PIUS passed laws to help orphans MARCUS AURELIUS was a philosopher who was very fair to the people. BAD EMPERORS Domitian married his niece, persecuted early Christians mass executions, and destroyed the Roman economy. Nero married his step sister, killed his mother, burned christians at the stake, and executed on a scale that would have made Hitler proud. Caligula made his horse consul. He had incestuous relationships with three of his sisters, executed thousands of people, raped the wives of head senate members, and went insane! All three were murdered or committed suicide. Extent of the Roman Empire The Romans continued to conquer other peoples and culture through a series of military conquests. This spread the influence of the Romans throughout the world and made their culture very prevalent. However, the empire became too large and lost some of its power, mostly through poor leadership. Roman Architecture Roman Society Families were very large in Roman Society. The head of the family was a male called the paterfamilias. He arranged marriages, disciplined children or other family members, and had complete control over the family. Children were educated (if they were citizens and had money), but men were more educated than women. Roman Culture Roman culture could be described as “feel good”. They were interested in being entertained and amused. This led to the growth of events such as the gladiator combats. Roman emperors were charged with keeping the people entertained.