* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s layers core, mantle, crust
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
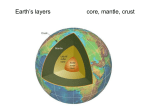
Earth’s layers core, mantle, crust CORE Core center of earth; divided into outer core and inner core INNER CORE Inner core solid and innermost layer ● made of solid iron and nickel ● temperatures up to 5,000 C ● greatest amount of pressure of all layers ● believed to be responsible for earth’s magnetic field ● depth = 5150 km OUTER CORE Outer core surrounds inner core ● 2nd layer of the core ● depth = 2,900 km ● thickness = 2,250 km ● made of liquid iron and nickel ● temperatures = 2,200 C in upper part to almost 5,000 C near inner core MANTLE Mantle second layer of the earth ● thickest of all layers ● temperature and pressure increase with depth; 870 C in upper mantle to 2200 C in lower mantle Plasticity property which allows solid rock to flow slowly; mantle has this property CRUST Crust thin, outermost layer of earth (3rd layer) ● all life exists on or within a few hundred meters above crust ● made of 3 types of solid rock: igneous rock, metamorphic rock, sedimentary rock 2 types continental crust – under continents (thicker) oceanic crust – under oceans (thinner) BY TEMPERATURE COOLEST TO HOTTEST: CRUST → MANTLE → OUTER CORE → INNER CORE BY THICKNESS THINNEST TO THICKEST: CRUST → INNER CORE → OUTER CORE → MANTLE LITHOSPHERE Lithosphere: solid, topmost part of the earth; 50 – 100 km thick and broken up into large sections called lithospheric plates; there are at least 7 major plates ASTHENOSPHERE Asthenosphere: the layer directly beneath the lithosphere; the upper edge of the mantle; Made of hot molten material, which has the property of plasticity; ● lithospheric plates move on the hot molten material that forms the asthenosphere