* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Body
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
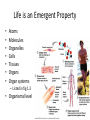
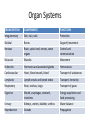
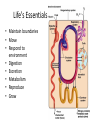
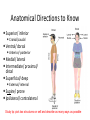
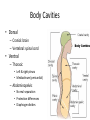
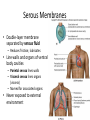
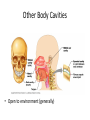
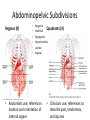
The Human Body Chapter 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of body structures and their relationships Static within a species Physiology: The study of the functions of body structures Dynamic within a species Subdivision Examples Anatomy • Gross anatomy – Regional – Systemic – Surface • Microscopic anatomy – Cytology – Histology • Embryology • Developmental anatomy • Others Physiology • Neurophysiology • Pathophysiology • Cardiovascular physiology • Renal Physiology • Others Life is an Emergent Property • • • • • • • Atoms Molecules Organelles Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems – Listed in fig 1.3 • Organismal level Organ Systems ORGAN SYSTEM COMPONENTS FUNCTIONS Integumentary Skin, hair, nails Protection Skeletal Bones Support/movement Nervous Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs Control and communication Muscular Muscles Movement Endocrine Hormones and associated glands Homeostasis Cardiovascular Heart, blood vessels, blood Transport of substances Lymphatic Lymph vessels and lymph nodes Transport, immunity Respiratory Nose, trachea, lungs Transport of gases Digestive Mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines Energy acquisition and food processing Urinary Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra Water balance Reproduction Gonads Propagation Life’s Essentials • Maintain boundaries • Move • Respond to environment • Digestion • Excretion • Metabolism • Reproduce • Grow Survival Essentials • Nutrients – Fuel for the cells – Building materials • Oxygen – Release energy from nutrients • Water – Facilitates reactions and excretions/secretions • Normal body temperature – Regulate metabolic reactions • Atmospheric pressure – Corresponds with gas exchange w/i cells • Adequate amounts, not just presence maintains a healthy state Homeostasis • Dynamic state of equilibrium • 3 components – Receptor (afferent) – Control center (set point) – Effector (efferent) • Imbalance causes illness & disease – Increase with age – Disruptions in feedback Feedback • Negative – Most homeostatic mechanisms • Turn off or slow original stimuli • Stabilizes – Body temperature, heart and breathing rate, & blood glucose • Positive – Increases the original stimuli – Oxytocin (labor) and blood clotting ANATOMICAL LANGUAGE Anatomical Position • Standing tall with upper limbs at sides and face, palms and toes forward • Reference position when describing body part locations – Left and right is specimen’s – Variations for bipeds and quadrupeds Anatomical Regions to Know Anatomical Directions to Know Superior/ inferior Cranial/caudal Ventral/ dorsal Anterior/ posterior Medial/ lateral Intermediate/ proximal/ distal Superficial/ deep External/ internal Supine/ prone Ipsilateral/ contralateral Study tip: pick two structures on self and describe as many ways as possible Body Planes are Like Breads • Frontal (coronal) section: • Sagittal section: divides divides anterior and posterior the body longitudinally – e.g.: loaf of bread into left and right – Midsagittal: equal parts • Transverse (cross) section: divides superior and inferior – Parasagittal: off – e.g.: hamburger bun or bagel midline – Oblique section: diagonal – e.g.: hotdog bun cuts Body Cavities • Dorsal – Cranial: brain – Vertebral: spinal cord • Ventral – Thoracic • Left & right pleura • Mediastinum (pericardial) – Abdominopelvic • No real separation • Protection differences • Diaphragm divides Serous Membranes • Double-layer membrane separated by serous fluid – Reduces friction; lubricates • Line walls and organs of ventral body cavities – Parietal serosa lines walls – Visceral serosa lines organs (viscera) – Named for associated organs • Never exposed to external environment Other Body Cavities • Open to environment (generally) Abdominopelvic Subdivisions Regions (9) Epigastric Umbilical Quadrants (4) Hypogastric Hypochondriac Lumbar Inguinal • Anatomists use; references location and orientation of internal organs • Clinicians use; references to describe pain, tenderness, and injuries