* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 - World History and Honors History 9
Survey
Document related concepts
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
List of oracular statements from Delphi wikipedia , lookup
Second Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Eurymedon wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
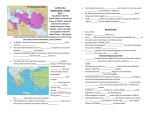
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON TEST Chapter 5 Test A Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The ______________ was a mythical half-man, half-bull beast kept in the Labyrinth by King Minos. a. Monitor c. Marathon b. Merrimack d. Minotaur 2. After the fall of Mycenaean society a. the city of Troy was destroyed in battle. b. Minoan society emerged on Crete. c. the first Greeks appeared on the Greek mainland. d. Greek civilization almost disappeared. 3. The city-state of Sparta was characterized by a. democracy. b. an emphasis on temple worship. c. an emphasis on warfare. d. dependence upon the sea. 4. Which of the following gods was the “King of the Gods”? a. Apollo c. Hades b. Zeus d. Ares 5. Greeks tried to ensure that the gods and goddesses would protect them and their city-states by a. writing epics. c. performing rituals and sacrifices. b. building them homes on Mount Olympus. d. telling stories about their lives. 6. Study the map titled “The Peloponnesian War.” According to the map, which side controlled much of the territory surrounding the Aegean Sea during the Peloponnesian War? a. the Delian League c. neutral states b. the Peloponnesian League d. Persia 7. Study the map titled “The Peloponnesian War.” What statement about the Peloponnesian War is best supported by the map? a. Athens and Sparta were both members of the Delian League. b. The Persian Empire sent a navy to aid Athens. c. Athens needed ships to communicate with its allies. d. Ionia refused to enter the Delian League. 8. Which of the following leaders set the stage for Athenian democracy by breaking up the power of noble families? a. Peisistratus c. Solon b. Cleisthenes d. Draco 9. What was the result of the first Persian invasion? a. Ionia won its independence. b. The Athenians won. c. The Spartans won. d. The Persians won. 10. The Battle of Salamis was significant because it a. finally exacted revenge for Darius’s defeat in Athens. b. made a small force of Spartans martyrs for the Greek cause. c. marked the first time the Spartans and Athenians cooperated in battle. d. stranded the Persian army in Greece without naval support. “Until philosophers are kings, or the kings and princes of this world have the spirit and power of philosophy, and political greatness and wisdom meet in one, and those commoner natures who pursue either to the exclusion of the other are compelled to stand aside, cities will never have rest from their evils—no, nor the human race.” —from the Republic 11. Read the excerpt from the Republic. Who was the writer of this work? a. Socrates c. Pericles b. Plato d. Aristotle 12. Which of the following historians examined his sources critically and excluded those that were unreliable? a. Herodotus c. Thucydides b. Homer d. Zenophon 13. Which of the following playwrights wrote the tragedy about Oedipus? a. Aeschylus c. Aristophanes b. Sophocles d. Euripides 14. Greek murals or wall paintings often a. realistically portrayed daily life. c. illustrated the daily news. b. showed scenes from the Iliad and the Odyssey. d. used Christian imagery. 15. “What is truth?” is a question associated with a. Socrates. c. Aristotle. b. Homer. d. Aristophanes. 16. Who took the throne in Macedonia after King Philip II was assassinated? a. Alexander c. Darius II b. Philip III d. Archimedes 17. In the Hellenistic world, the city-state was replaced as the main political unit by the a. kingdom. c. assembly. b. polis. d. military. 18. Alexander was forced to stop expanding his empire because a. his generals began fighting for power. c. his soldiers wanted to return home. b. the Hindu Kush defeated him. d. he reached all his goals. 19. New schools of philosophy developed during the Hellenistic period, in part because a. people sought ways to explain the violence and bloodshed of the period. b. people rejected the Greek gods. c. Alexander brought philosophers together from all over his empire. d. classical philosophy absorbed ideas from other cultures. 20. Spartan society revolved around training for war because a. warfare was their favorite activity. b. Spartans feared helot rebellions. c. Spartans wanted to dominate the entire Mediterranean world. d. Spartans believed they could not achieve immortality without proving their bravery in battle. 21. Which of the following gods or goddesses was the deity of wisdom? a. Athena c. Hera b. Apollo d. Ares 22. Known as the “Father of History” a. Thucydides c. Herodotus b. Homer d. Zenophon 23. Why did the Persian emperor Darius attack the Greek mainland? a. to gain control of Greece’s vast natural resources b. to exact revenge for the Athenians’ victory at Marathon c. to kidnap Helen, the beautiful queen of Athens d. to punish Athens for aiding the Ionians in their revolt against Persian rule 24. Macedonia was able to take control of all of Greece in the 340s BC because a. the Persian Empire had soundly defeated Athens and Sparta. b. a terrible plague had weakened Athens and Sparta. c. a long period of warfare left all of Greece vulnerable to attack. d. Xerxes was a brilliant commander of the Macedonian army. 25. Some of the earliest examples of Greek epic poetry were a. written by Aristophanes. c. written by Sappho. b. the Iliad and the Odyssey. d. written for the festival of Dionysus. 26. The art of playwriting is known as a. comedy c. drama b. reason d. tragedy 27. Public marketplace where people did business, gossiped, and discussed politics a. helot c. acropolis b. agora d. stoa 28. Spartan king who led the 300 at the Battle of Thermopylae a. Xerxes c. Darius b. Pericles d. Leonidas 29. Tight rectangle formation used by Greek armies a. phalanx c. helot b. hoplite d. polis 30. Spartan slaves were called a. agora c. helots b. hoplites d. polis 31. Led the second Persian invasion of Greece a. Xerxes c. Darius b. Philip II d. Alexander 32. The richest source of information about the Minoan way of life a. the Iliad c. the Odyssey b. frescoes d. The Histories 33. Clear and ordered thinking a. logic c. Cynicism b. rationalism d. reason 34. Type of government that is ruled by a few individuals a. democracy c. theocracy b. tyranny d. oligarchy 35. Philosophy that rejected pleasure, wealth, and social responsibility a. Cynicism c. Epicureanism b. Stoicism d. Socratic method 36. Conquered every major city-state in Greece except Sparta a. Alexander c. Philip II b. Xerxes d. Darius 37. The first Greek civilization to develop on the European mainland a. Athenians c. Minoans b. Mycenaeans d. Spartans 38. Tells the story of the last year of the Trojan War a. the Iliad c. the Odyssey b. frescoes d. The Histories 39. Developed a harsh law code where most crimes were punished with death a. Peisistratus c. Solon b. Cleisthenes d. Draco 40. Egyptian who developed many geometry concepts still used today a. Archimedes c. Euclid b. Eratosthenes d. Socrates 41. Method of learning through questioning a. Aristotle Method c. Platonic Method b. Socratic method d. Draconic Method 42. Argued that people should use reason to help them learn about the world a. Aristotle c. Plato b. Socrates d. Draco 43. Calculated the circumference of the globe a. Cleisthenes c. Euclid b. Eratosthenes d. Pythagoras 44. Greek foot soldiers a. phalanxes c. helots b. polis d. hoplites 45. Philosophers who equated pleasure with good a. Stoics c. Epicureans b. Cynics d. Socialites 46. Made tribes, not families or social groups, the basis for elections a. Cleisthenes c. Draco b. Peisistratus d. Solon 47. Philosophers who emphasize reason, self-discipline, emotional control, and personal morality a. Stoics c. Epicureans b. Cynics d. Socialites 48. An alliance of several Greek city-states led by Athens formed after the Persian Wars a. Peloponnesian League c. Athenian League b. Delian League d. Spartan Alliance 49. The basic political unit in Greece was the a. agora c. helot b. hoplite d. polis 50. Female Greek lyric poet a. Cleisthenes c. Sappho b. Antigonus d. Eratosthenes 51. Which of the following gods or goddesses was the deity of war? a. Athena c. Hera b. Apollo d. Ares 52. The first battle of the Persian Wars was fought at a. Nike c. Sparta b. Athens d. Marathon 53. The last battle of the Persian Wars was fought at a. Plataea c. Thermopylae b. Salamis d. Marathon 54. After the Persian Wars, Athens was rebuilt largely due to the efforts of a. Perseus c. Pericles b. Leonidas d. Cleisthenes 55. Greek drama began as a festival to honor the god a. Zeus c. Aphrodite b. Dionysus d. Apollo True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Mark A for True and B for False 56. From artwork historians have learned that Minoan life was tied to the sea. 57. The Mycenaeans were probably peaceful traders with little or no military. 58. Greeks gathered every four years at Olympia for the Olympic Games to compete against each other and to honor the gods. 59. The Persian emperor Darius attacked the Greek mainland to gain control of Greece’s vast natural resources. 60. The leadership of Athens in the Persian Wars, its access to the treasury of the Delian League, and the patronage of Pericles led to the Golden Age of Athens. 61. Macedonia was able to take control of all of Greece in the 340s BC because the Persian Empire had soundly defeated Athens and Sparta. 62. A terrible plague struck Athens in 430 and 429 BC, changing the course of the Peloponnesian War. 63. Since Plato believed that only philosophers should lead governments, he opposed Athenian democracy. 64. Greek drama had its roots in Athens and was created as part of religious festivals honoring Dionysus, the god of wine and celebration. 65. Hellenistic culture blended elements of Greek civilization with ideas from Persia, Egypt, Central Asia, and other regions. 66. Alexander the Great discouraged Greeks from mingling with people from the places he conquered. 67. Stoicism, a new school of philosophy created in the Hellenistic world, placed great emphasis on reason, selfdiscipline, emotional control, and personal morality. 68. Democratic city-states were the basic political unit in the Hellenistic world. 69. After the death of Alexander the Great, Seleucus became the pharaoh of Egypt. 70. Alexander the Great built the world’s largest empire up to that time. Chapter 5 Test A Answer Section 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. D D C B C 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. A C B B D 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. B C B A A 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. A A C D B 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. A C D C B 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. C B D A C 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. A B D D A 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. C B A D C 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. B A B D C 46. A 47. A 48. B 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. D C D D A C B TRUE/FALSE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. T F T F T F T T T T F T F F T