* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physical Processes STEW
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil governance wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
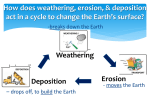
Processes Shaping the Earth (S.T.E.W.) Take a guess. What are the processes that could be currently shaping the earth RIGHT NOW?? Try to complete the acronym above for these processes. Four Spheres of the Earth One of the ways geographers describe the earth is by spheres Physical processes that take place in the spheres create, maintain, and/or modify the features and environments of the earth. S.T.E.W.– Soil Building Bits of rock, mixed with decaying plants and animals. The type and quality of soil determines what can grow in a particular place Alluvial plain – soil is rebuilt in a regular cycle by flood waters leaving behind sediment S.T.E.W.– Tectonic Forces The push/pull of the major plates of the earth. What is common where these two plates meet? Why? Three types of tectonic plate boundaries Divergent – plates move apart from one another Convergent – plates move together Transform – plates slide across each other Useful Prefixes! Di – two; apart Con – with; together Trans - Across Divergent Boundaries Spreading ridges: 1) Plates move apart 2) New material is erupted to fill the gap Contributes to creation of volcanoes and islands Convergent or Subduction Boundaries Plates collide into each other creating high mountains Himalayas Andes Transform Boundaries Where plates slide past each other •Above: View of the San Andreas transform fault •Major source of earthquakes Tibetan video? Epicenter – origin of an earthquake S.T.E.W. – Erosion Material is moved by the action of WIND, WATER, or ICE WATER: Motion of water picks up soil – river Abrasive action of waves – grind down rock, carries soil away. WIND: wind carries soil, stronger wind heavier particles can be carried. ICE/GLACIER: As ice moves it carved and grinds the rocks, also transporting soil. (Fjords & Valleys) https://youtu.be/J-ULcVdeqg Bill nye S.T.E.W. - Erosion/Weathering Erosion - the process by which broken down rock is moved Main Physical Processes – Erosion and Weathering Weathering – the gradual wearing down of rocks by wind, water, or ice. Can be mechanical or chemical Chemical v Mechanical Weathering Chemical changes composition by chemical decay Mechanical/Physical changes by physical force Chemical Weathering Acid Rain and Statues Watch Carefully. If rain can do this to a statue over a relatively short period of time, then how else might acid rain affect the earth? Main Physical Processes – WEATHER or Climate Meteorological conditions such as temperature, precipitation, wind, etc. (often combine with soil building and erosion) Review What does S.T.E.W. stand for? Soil Building Tectonic Forces Erosion ( and Weathering) Weather (or Climate)