* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solar System Fact Sheet - University of South Alabama
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Solar System Fact Sheet
I.
II.
III.
IV.
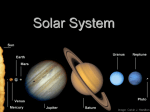
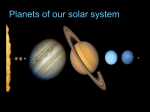
General Structure of the Solar System
A. Eight planets. From nearest to Sun to farthest:
1. Mercury
2. Venus
3. Earth
4. Mars
5. Jupiter
6. Saturn
7. Uranus
8. Neptune
9. Pluto (no longer a planet, just a dwarf planet)
B. Terrestrial Planets
1. Have high average density
2. Rocky structure
3. relatively small planets
4. near the Sun
5. includes Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
C. Jovian Planets
1. Have low average density
2. Gaseous structure
3. relatively large planets
4. far from the Sun
5. all have a ring system
6. includes Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
D. All planets orbit the sun in same direction
E. All orbits of planets are near the plane of the ecliptic
1. Pluto's orbit is tilted 17o with respect to the ecliptic
F. All orbits of planets are nearly circular
1. Pluto's orbit is very eccentric
G. The asteroids are almost all found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter
H. Jupiter is the largest and most massive planet
I. Mercury is the smallest and least massive planet
J. Venus is the hottest, Neptune is the coldest
Mercury
A. Surface is heavily cratered
B. Large scarps on surface due to contraction of the crust
C. Has an impact basin called the Caloris Basin
Venus
A. About the same size as the Earth
B. Always covered by clouds largely made of Sulfuric acid
C. Atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide
D. Greenhouse effect has heated surface to to over 700 K
E. Ishtar Terra and Aphrodite Terra are major highland areas
F. The only planet with retrograde rotation; it rotates in the opposite direction it orbits the Sun
Mars
A. Schiaparelli and Lowell responsible for idea of canals on Mars
B. Due to weak gravity, Mars has almost no atmosphere
C. All ground water has boiled away
1. May be subsurface water
2. Strong evidence for water in the past, based on erosion patterns in the surface
D. Red from iron oxide in rocks
E. Polar caps are made of water ice and dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide)
F. Valles Marineris is huge canyon (largest known in solar system)
G. Olympus Mons is a huge volcano (largest known in the solar system)
H. Two moons: Phobos and Deimos
V.
VI.
VII.
VIII.
IX.
Jupiter
A. We see tops of clouds in upper atmosphere, probably has no surface
B. Emits more heat than it receives from the Sun
1. due to left over heat from Jupiter's formation
C. The Great Red Spot is a large storm, twice the size of the Earth
D. The Galilean moons are Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto ("I Eat Green Cheese")
E. Io has many volcanoes
1. Interior of Io is heated due to being warped by tidal forces from Jupiter
2. Orangish color caused by presence of lots of Sulfur
F. Europa has surface of water ice
1. Large ocean of liquid water underneath the surface
2. Crust is broken by upward pressures, causing liquid water to flow onto surface
3. Has many cracks and grooves in surface from upwelling water
G. Ganymede has an ice crust broken by tectonic activity
H. Callisto has impact basin named Valhalla
Saturn
A. Similar to Jupiter in structure
B. Density less than density of water (it floats!!)
C. Rings are made of rocks about the size of a human orbiting Saturn
1. Rings from a moon (or moons)
2. moon(s) broken into pieces by tidal forces when it crossed the "Roche Limit"
D. Large gap in rings is called Cassini's Division
E. Very thin F ring kept in place by gravitational forces of "shepherd moons"
1. Shepherd Moons are small moons just inside and outside of the ring.
F. Titan is a very large moon of Saturn
1. Because of size and low temperature it has a thick atmosphere
2. Always covered by clouds
G. Mimas is a small moon with a very large crater so that it resembles the Death Star in Star Wars
H. Enceladus is a bright moon, reflecting almost all the sunlight striking it
I. Other moons include Dione, and Iapetus
Uranus
A. Discovered by William Herschel in 18th century
B. Always covered by clouds
C. Blue-green appearance due to Methane in the atmosphere
D. Axis tilted about 90o to the ecliptic
E. Moons are named after Shakespearean characters
F. Miranda is a moon of Uranus with huge angular ridges and craters
G. Other moons include Titania, Oberon, Umbriel, Ariel
Neptune
A. Discovered in 19th century by John Couch Adams and Jean Leverrier
1. They calculated its presence and position from gravitational perturbations of Uranus caused by
gravitational forces between Uranus and Neptune
B. Very similar to Uranus in structure
C. Has large storms in its atmosphere from internal heating
D. Great Dark Spot was a large storm seen by Voyager 2
E. Triton is a large moon of Neptune
Pluto
A. Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930
B. One large moon named Charon
C. Demoted to a dwarf planet in 2006