* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Persuasion Techniques
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
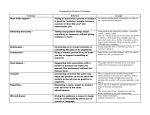
COMMON PERSUASION/PROPAGANDA TECHNIQUES 1. Emotional Appeal: Writers may appeal to fear, anger or joy to sway their readers. They may also add climax or excitement. This technique is strongly connected to the essay's mood. 2. Word Choice (Diction): Is a person "slim" or "skinny"? Is an oil spill an "incident" or an "accident"? Is a government expenditure an "investment" or a "waste"? Writers tend to reinforce their arguments by choosing words which will influence their reader's perception of an item or issue. Diction may also help to establish a writer's "Voice" or "Tone". 3. Hyperbole: This is one of the more enjoyable persuasive techniques. It involves completely overstating and exaggerating your point for effect. (Like when your mom says, "I must have asked you a million times to clean your room!" Get it?) 4. Testimonial: using words of an expert or famous person to persuade- the famous person uses the product, so should you. 5. Bandwagon: persuade people to do something by letting them know others are all doing it. Everyone else is doing it, why aren't you? 6. Transfer: using names or pictures of famous people, advertisers hope that the consumer will tend to transfer these qualities to the product and purchase the item. 7. Free or Bargain: a speaker suggests that the public can get something for nothing or almost nothing. 8. Glittering Generalities: in glowing terms and offering no evidence the speaker or advertiser supports a candidate or a solution to social problems. 9. Name Calling: describing bad aspects of a competitor's product so that the advertised product seems better. 10. Plain Folk: using actors who represent "average" people to suggest that, because people in advertisements resemble friends and neighbors, the product they are using must be good. Backto-Nature or Just the way Grandma used to make 11. Repetition: repeating an element within one advertisement so that viewers will remember the advertisement and will buy the product; also refers to the repetition of the same advertisement. For example, the Gecko in the Geico commercials or the Duck in the Afflac commercials are repeated in each one. 12. Humor: People may tend to remember an ad if It makes them laugh and may purchase the product because of a positive association with it. 13. Symbols: Associating the power of a cultural symbol with a product. For example, An American flag used in the ad to associate a product with patriotism. 14. Magic Ingredients: The suggestion that a miraculous discovery makes a product effective. For example, often seen in ads for diet pills. 15. Scientific Language: Ads using scientific sounding language to make a product seem more effective. For example, does the ad contain scientific diagrams or statistics? 16. Card Stacking: Ads giving only the positive side of a product or service, ignoring negative aspects. For example, soda advertisements that neglect to mention the large amount of empty calories contained in the product.