* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monster Genetics Lab
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
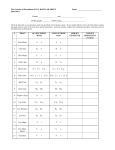
Name: ____________________________ Period: Date: ___________ Monster Genetics (female) Heredity is the passing on of traits, or characteristics, from parent to offspring. The units of heredity are called genes and different versions of the same gene are called alleles. The combinations of genes and their alleles for each trait occur by chance. Important vocabulary: Heredity Allele F2 generation Sex-linked Inheritance Phenotype Gene Chromosome Co-dominant Inheritance Genotype Trait Punnett square Incomplete Inheritance Dominant P generation Homologous Mendelian Inheritance Recessive F1 generation Chromosome After completing your pre lab you should be familiar with four patterns of inheritance: Sex-linked Inheritance, Codominant Inheritance, Incomplete Inheritance, Mendelian Inheritance. In this investigation, you will create a monster and observe how based on various patterns of inheritance and different allele combinations certain traits are produce. Part One: Make your Monster 1. Flip a coin twice to determine the genotype for each trait and record it in the data table. Heads = allele 1, Tails = allele 2 (Example: if you flipped heads twice, your monster will have two copies of allele 1 for his genotype.) 2. Determine the phenotype resulting from the allele pair for each trait. 3. Repeat steps 1-2 for each trait and complete your monster. 4. Draw a picture of your monster in the space provided. 5. You have a Female Monster Give your monster a name. Table 1: Genotypes & Phenotypes for Female Monster Unless otherwise noted all traits result from Simple Mendelian Inheritance. Trait Allele 1 Allele 2 Genotype Eye Two small eyes (E) One large eye (e) Eye Color (Incomplete) Red (R) White (R’) Nose Skin Color (Co-dominant) Hair on top of head Small (N) Green (G) Yes (H) Large (n) Blue (B) No (h) Body Shape Oval (B) Square (b) Tail Shape Curly (C) Straight (c) Tail Color (Sex-linked) Tail Teeth (Co-dominant) Feet Purple (XP) Have tail (T) Sharp (S) Four toes (F) Orange (Xp) No tail (t) Round (R) Three toes (f) Horn Color Ear shape (Sex-linked) Purple (W) Pointy (XA) White (w) Round (Xa) Ears Claws (incomplete) Four ears (E) Long (L) Two ears (e) Short (L’) Phenotype Monster Genetics (male) Heredity is the passing on of traits, or characteristics, from parent to offspring. The units of heredity are called genes and different versions of the same gene are called alleles. The combinations of genes and their alleles for each trait occur by chance. Important vocabulary: Heredity Allele F2 generation Sex-linked Inheritance Phenotype Gene Chromosome Co-dominant Inheritance Genotype Trait Punnett square Incomplete Inheritance Dominant P generation Homologous Mendelian Inheritance Recessive F1 generation Chromosome After completing your pre lab you should be familiar with four patterns of inheritance: Sex-linked Inheritance, Codominant Inheritance, Incomplete Inheritance, Mendelian Inheritance. In this investigation, you will create a monster and observe how based on various patterns of inheritance and different allele combinations certain traits are produce. Part One: Make your Monster 1. Flip a coin twice to determine the genotype for each trait and record it in the data table. Heads = allele 1, Tails = allele 2 (Example: if you flipped heads twice, your monster will have two copies of allele 1 for his genotype.) For the sex linked traits heads = X chromosome with allele A, Tails = X chromosome with allele B 2. Determine the phenotype resulting from the allele pair for each trait. 3. Repeat steps 1-2 for each trait and complete your monster. 4. Draw a picture of your monster in the space provided. 5. You have a Male Monster Give your monster a name. Table 1: Genotypes & Phenotypes for Male Monster Unless otherwise noted all traits result from Simple Mendelian Inheritance. Trait Allele 1 Allele 2 Eye Two small eyes (E) One large eye (e) Eye Color (Incomplete) Red (R) White (R’) Nose Skin Color (Co-dominant) Hair on top of head Small (N) Green (G) Yes (H) Large (n) Blue (B) No (h) Body Shape Oval (B) Square (b) Tail Shape Curly (C) Straight (c) P p Tail Color (Sex-linked) Tail Teeth (Co-dominant) Feet A=Purple (X ), B= Orange (X ) Horn Color Ear shape (Sex-linked) Purple (W) A=Pointy (X ), B= Round (X ) White (w) Y Ears Claws (incomplete) Four ears (E) Long (L) Two ears (e) Short (L’) Have tail (T) Sharp (S) Four toes (F) A a Y No tail (t) Round (R) Three toes (f) Genotype Phenotype Part Two: Making Monster Babies The female and male monsters at each table are getting married and they plan to have baby monsters. They are interested in finding out the probabilities of which traits their offspring will have. Complete Punnett squares to predict what traits would result from a cross between your two monsters. Write out the genotypic & phenotypic ratios for eyes, body shape, Tail, & horn color. Eyes ________ x ________ Teeth Genotypic ratio ________________ Phenotypic ratio ________________ Body Shape ________ x ________ Nose Genotypic ratio ________________ Phenotypic ratio ________________ Tail ________ x ________ Feet Genotypic ratio ________________ Phenotypic ratio ________________ Horn color ________ x ________ Hair Genotypic ratio ________________ Phenotypic ratio ________________ Skin color eye color Tail color 1. How many different genotypes for horn color could be produced in your monsters’ offspring? 2. What is the probability of your offspring producing a female carrier for round ears? 3. Write out three possible parental crosses that could produce a child with a heterozygous genotype for tail shape (Cc). Critical Thinking and Application: ANSWER IN COMPLETE SENTENCES!!! 1. How might it be possible for the baby monster to show traits that neither of the parents exhibit? a. Could your Monsters produce offspring that had traits that neither of the parents exhibited? Which trait(s). 2. Do you think the baby monster could have some traits of the grandparents? 3. A small monster colony has a large amount of monsters that have an abnormal amount of horns. Why might this trait be so prevalent in this colony? Using you’re the Punnett Squares you have made crossing the male and female monsters at your table draw an offspring on the designated paper. NOTE: you may need to complete a couple more Punnett squares in order to have one for every monster trait. When you are finished drawing your monster baby compare your monster baby with the monster babies made using the same parent monsters at your table. While your monster babies may resemble each other they should not be identical. Which of Mendel’s Laws is demonstrated here? Explain Female Monster Male Monster