* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleon number
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
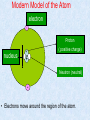
MATTER Learning Outcome At the end of this topic, students should be able : (a) Identify and describe proton, electron and neutron as subatomic particle. (b) Define proton number, Z, nucleon number, A and isotope. Write isotope notation. INTRODUCTION • Matter Anything that occupies space and has mass. e.g air, water, animals, trees, atoms, ….. • All matter consist of tiny particles called atoms TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 1) Identify and describe protons, electrons and neutrons as sub-atomic particles This page will revises the simple ideas about atomic structure that you have come across in an introductory chemistry course (i.e. SPM). You need to be confident about this before you go on to the more difficult ideas about atom. THE SUB-ATOMIC PARTICLES An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element/compound. In an atom, there are three subatomic particles: Proton (p) Neutron (n) Packed in a small nucleus Electron (e) Move rapidly around the nucleus of an atom Back to content Modern Model of the Atom electron - Proton nucleus + ( positive charge) + Neutron (neutral) • Electrons move around the region of the atom. TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes Proton no. Nucleon no. Isotopes Nucleon number or mass number A Z X Atomic symbol Proton number or atomic number Pre-test Example Exercise Past year Question Back to content TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes Proton no. Nucleon no. Isotopes Nucleon number or Proton number (Z) is the number of protons mass number in the nucleus of each atom of an element. Also known as atomic number A Atomic symbol In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number Z of electrons. X Proton number or atomic number Pre-test Example Exercise Past year Question TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes Proton no. Nucleon no. Isotopes Nucleon number or mass number Nucleon number (A) is the total number of neutrons and protons present in the nucleus of an atom A of an element. X Atomic symbol Also known as mass number Z Proton number or atomic number Pre-test Example Exercise Past year Question TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes Proton no. Nucleon no. Nucleon number or mass number Isotopes Isotopes, atoms that have the same proton number but different nucleon number. Ai.e. Hydrogen has three Atomicisotopes symbol 2 1 3 Z H H 1 1 1H X Proton number or atomic number Pre-test Example Exercise Past year Question TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes Proton no. Nucleon no. Nucleon number or mass number Isotopes Nucleon number = proton no. + no. of neutrons. So, the number of neutrons is equal to the different between the nucleon no. & the proton no. or ( A-Z). Ex. Nucleon no. of fluorine is 19 & proton no. is 9. Thus, the no. of neutrons in fluorine is 19 – 9 = 10. Note: proton no., nucleon no. &symbol no. of neutrons all Atomic must be positive integers (whole numbers) A Z X Proton number or atomic number Pre-test Example Exercise Past year Question TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes Proton no. Nucleon no. Nucleon number or mass number Isotopes In a neutral atom the no. of protons is equal to the no. of electrons, so the proton no. also indicates the no. of electrons present in the atom. A For example, the proton Atomic symbol no. of nitrogen is 7. This each neutral nitrogen atom has 7 Z means thatprotons and 7 electrons. X Proton number or atomic number Pre-test Example Exercise Past year Question TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes The X represent of atom of an element. For example atom of uranium with nucleon numbers of 235 and proton numbers of 92. So the uranium can Nucleon no. beIsotopes denoted as:- Proton no. 235 92 U Nucleon number or mass number A Z X Atomic symbol Proton number or atomic number Pre-test Example Exercise Past year Question Ex: Number of protons = proton number = 13 Number of neutrons = nucleon number – proton number = 27 - 13 = 14 Number of electron = proton number – charge carried by species = 13 – ( +3) = 10 Q: determine the number of proton, neutron and electron in the following species. solution 90 38 Sr Sr Number of protons = proton number = 38 Number of neutrons = nucleon number – proton number = 90 – 38 = 52 Number of electron = proton number (species is neutral) = 38 35 17 Cl- Number of protons = proton number = 17 Number of neutrons = nucleon number – proton number = 35 – 17 = 18 Number of electron = proton number – charge carried by species = 17 – (-1) = 18 TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes 1. State the sub-atomic particles of an atom? 2. Define proton numbers and nucleon numbers? 3. What is isotopes? Use hydrogen as an example. ANSWER 1. Protons, electrons & neutrons 2. Proton numbers = number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Nucleon numbers = total no. of protons & neutrons in atom 3. Isotopes = atoms that have the same no. of protons but have different nucleon numbers. TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes 1. Give the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in each of the following species: (a) 17 8 O (b) 199 80 Hg (c) 200 80 Hg ANSWER * Recall that the superscript denotes nucleon number & the subscript denotes proton number. (a) Proton number = 8, so there are 8 protons. Nucleon number = 17, so the number of neutrons is 17-8 = 9. The number of electrons is the same as the number of protons, that is 8. (b) Proton numbers = 80, so there are 80 protons. Nucleon number = 199, so the number of neutrons is 199-80 = 119. The number of electrons = 80. (c) Number of protons = 80. Number of neutrons, 200-80 = 120. Number of electrons = 80. TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes 1. Isotopes of an element are having A the same nuclear charge B similar physical properties C the same number of neutrons D the same relative abundance 2. All the following statements are true EXCEPT A Nucleus is the positively charged centre of an atom B Protons number indicates the number of protons in an atom C Isotopes are atoms of the same element but with different nucleon number D Nucleon number is the total number of electrons and protons in an atom ans TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes 1. Isotopes of an element are having A the same nuclear charge B similar physical properties C the same number of neutrons D the same relative abundance 2. All the following statements are true EXCEPT A Nucleus is the positively charged centre of an atom B Protons number indicates the number of protons in an atom C Isotopes are atoms of the same element but with different nucleon number D Nucleon number is the total number of electrons and protons in an atom next TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes 3. Which of the following is a pair of isotopes? A 13858J and 13860K B 7432L and 7533M C 8336N and 8436O D 23592P and 23994Q 4. Which of the following species has 24 neutrons? A 24Mg B 45Sc C 51V D 52Cr ans TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes 3. Which of the following is a pair of isotopes? A 13858J and 13860K B 7432L and 7533M C 8336N and 8436O D 23592P and 23994Q 4. Which of the following species has 24 neutrons? A 24Mg B 45Sc C 51V D 52Cr next TOPIC 1: MATTER SUB TOPIC: Atoms and Molecules Objective: At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 2) Define proton number, nucleon number and isotopes WELL DONE! Try some past paper questions