* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
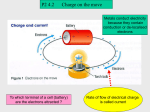
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Cambridge Physics for the IB Diploma Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Topic 5, Worksheet 5 1 a The gravitational field strength at the position of the Earth is the Earth’s 2 2πr 2 v 4π 2 r T centripetal acceleration; hence g 2 ; r r T 2 11 4π 1.5 10 g 5.95 103 N kg 1 (365 23 3600) 2 g b [3] GM 5.95 10 3 (1.5 1011 )2 5.95 10 3 N kg 1 M 2 r 6.67 10 11 M 2.0 1030 kg 2 3 4 A plastic rod rubbed with a cloth will become charged by friction and will repel a similar plastic rod that has also been rubbed by a cloth ; a glass rod rubbed in cloth will also repel a glass rod rubbed in cloth ; but a glass rod and a plastic rod that have been rubbed attract suggesting the existence of 2 types of electric charge. The original force is proportional to F 4 8 32 ; the new charges on the spheres 8 (2) will be 3 nC; and so the force will be proportional to F 3 3 9 ; so it 2 9 will be times the original force; and repulsive as opposed to attractive. 32 The kinetic energy of the accelerated particles is qV and so m p v 2p m v2 5 [2] a b c Ep E [3] [4] qV 1 ; hence 2qV 2 vp m p v 2p 1 1 2 ; so 2 v 2 4m p v 2 [3] The force is F qE 1.6 1019 2.4 103 ; so F 3.8 1016 N [2] 2.4 103 E ; hence B 5.9 10 4 T ; the magnetic force 6 4.1 10 v must be directed to the left and so the magnetic field must be directed into the page. [3] The electric force on the alpha particle will double but so will the magnetic force; hence the net force will be zero and so the path will be undeflected. [2] qvB qE B 6 Conductors have lots of free electrons; whereas insulators do not. [2] 7 Electric current means the transfer of electric charge in a given direction; electrons move but in random directions so there is no net transfer of charge in any given direction. [2] Copyright Cambridge University Press 2012. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 2 Cambridge Physics for the IB Diploma 8 9 By definition, static electricity deals with situations where the electric current is zero; if there was an electric field inside the conductor, there would be a force on the free electrons and hence a motion of electrons (opposite to the direction of the electric field) and hence an electric current. [2] By the right hand force rule for magnetic force (or any other method you know of) the forces have directions Right; Left; Out of the page; and zero (since in the last case the velocity is antiparallel to the field). [4] Copyright Cambridge University Press 2012. All rights reserved. Page 2 of 2