* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I. THE HEART
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
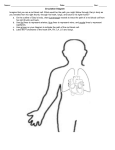
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM All organisms must be able to transport nutrients and wastes. Smaller organisms rely on _________ for this movement; humans require an organized circulatory system for the movement of substances through the body. We have a ________________ circulatory system, which means our blood is ______________________________________. The human circulatory system includes the heart, the blood vessels, and the blood. I. THE HEART (pp. 943-946) The function of the heart is to ___________________________________________. The heart itself is mostly composed of ________________ muscle which forms a thick layer of tissue known as the _______________________. Humans have a ______-chambered heart, divided by a ____________________ into right and left sides. A. Structure 1. Chambers a. Atria (atrium = singular) _____________ chambers of the heart that ____________ blood. b. Ventricles - _______________ chambers of the heart that ____________ blood. 2. Valves – Flaps of tissue that keep blood flowing __________________________________ to increase pumping efficiency of the heart; prevent _________________________. a. Tricuspid valve – Valve between ____________________ and __________________ b. Mitral valve – Valve between _____________________ and ____________________ c. Pulmonary valve – Valve between __________________ and ___________________ d. Aortic valve – Valve between ____________________ and _____________________ B. Pathway of Blood Through the Heart __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM All organisms must be able to transport nutrients and wastes. Smaller organisms rely on _________ for this movement; humans require an organized circulatory system for the movement of substances through the body. We have a ________________ circulatory system, which means our blood is ______________________________________. The human circulatory system includes the heart, the blood vessels, and the blood. I. THE HEART (pp. 943-946) The function of the heart is to ___________________________________________. The heart itself is mostly composed of ________________ muscle which forms a thick layer of tissue known as the _______________________. Humans have a ______-chambered heart, divided by a ____________________ into right and left sides. A. Structure 1. Chambers a. Atria (atrium = singular) _____________ chambers of the heart that ____________ blood. b. Ventricles - _______________ chambers of the heart that ____________ blood. 2. Valves – Flaps of tissue that keep blood flowing __________________________________ to increase pumping efficiency of the heart; prevent _________________________. a. Tricuspid valve – Valve between ____________________ and __________________ b. Mitral valve – Valve between _____________________ and ____________________ c. Pulmonary valve – Valve between __________________ and ___________________ d. Aortic valve – Valve between ____________________ and _____________________ B. Pathway of Blood Through the Heart __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ THE HEART aorta aortic valve atrium (left & right) bicuspid (mitral) valve myocardium pulmonary artery pulmonary valve pulmonary vein septum tricuspid valve vena cava ventricle (left & right) C. Circulatory Pathways 1. Pulmonary Circulation – The blood entering the right atrium from the body is __________ in oxygen and ________ in carbon dioxide. The flow of blood from the right side of the heart to the ____________ and back to the heart is referred to as __________________ circulation. 2. Systemic Circulation – The blood entering the left atrium from the lungs is _________ in O2 and ________ in CO2. The flow of blood from the left side of the heart to the ______ and back to the heart is referred to as ____________________ circulation. D. The Heartbeat 1. Stimulus for Contraction Although the brain can change the rate & force of contraction, the heart generates and maintains its own beat. There is a small cluster of cardiac muscle cells in the ____________________ referred to as the ______________________. They trigger an ________________ impulse that stimulates the contraction of cardiac muscle cells. 2. The Pulse The powerful contraction of the ________________________ causes a surge of blood to leave through the ___________. This surging action of the blood continues into the ______________ that branch off from the aorta. Each contraction of the left ventricle results in another surge of blood in the arteries leading away from the heart. This surge can be felt and is known as the _________.