* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Region 15: Stomach, Intestines, Liver, Gallbladders, and Spleen
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
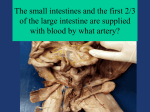
Region 15: Stomach, Intestines, Liver, Gallbladders, and Spleen Stomach --derived from foregut (along with first ½ of duodenum, liver, pancreas) --Location: *upper left quadrant of abdomen --Parts *cardia: portion that is directly continuous with the esophagus *Fundus: upper portion which contains air when a person is standing *Body: portion from fundus to the incisive notch *Pyloric Portion a. pyloric antrum: portion proximal to pyloric sphincter b. pyloric canal: passageway to pyloric sphincter *Greater curvature: left border of stomach *Lesser curvature: right border of stomch --Interior of the Stomach *mucosa that lines the stomach is in longitudinal folds (gastric folds/rugae) --Blood Supply *Located in lesser omentum a. left gastric artery: direct branch of celiac trunk, gives off an esophageal branch b. right gastric artery: branch of proper hepatic artery which comes off the celiac trunk c. right (in lesser curvature) and left (coronary vein) gastric veins --empties directly into portal vein --Lesser Omentum *Hepatogastric ligament: membranous and from liver to lesser curvature of the stomach *Hepatoduodenal Ligament: thicker free edge of lesser omentum a. contains the portal triad --hepatic artery: in anterior left part of ligament --bile duct: in anterior right part of ligament --portal vein: posterior to both hepatic artery and bile duct b. epiploic foramen (of Winslow): opening behind the hepatoduodenal ligament containing the portal triad --it is entrance into lesser sac/omental bursa --Greater Omentum a. Short gastric arteries *branches off splenic artery/directly off celiac trunk b. left gastroepiploic artery *branch off the splenic artery c. right gastroepiploic artery *branch off gastroduodenal a. that comes off hepatic branch of celiac trunk Nerve Supply --Esophageal plexus a. derived from left and right vagus nerves b. provide parasympathetic nerve supply to foregut and midgut *anterior portion: from left vagus *posterior portion: from right vagus c. vagal fibers are preganglionic parasympathetic and d/n synapse until they enter wall of stomach and synapse in myenteric and submucosal ganglia --Greater and Lesser Splanchnic nerves a. sympathetic nerve supply to foregut and midgut b. preganglionic sympathetic fibers synapse with postganglionic nerve cell bodies which make up celiac ganglia in celiac plexus Small and Large Intestine --Jejunum vs. Ileum *thicker walled than ileum *circular folds more prominent than ileum *wall of jejunum more vascular than ileum *number of vascular arcades increase form proximal to distal *aggregated lymph follicles (Peyer’s patches) are in ileum --Large vs. Small Intestine *sacculations (haustra) *taeniae coli: three bands of longitudinal muscle *epiploic appendages: peritoneal-covered tabs of fat --Parts of the Large Intestine a. appendix b. cecum c. ileocecal valve d. ascending colon e. right colic/hepatic flexure f. transverse colon g. left colic/splenic flexure h. descending colorn i. sigmoid colon j. rectum and anal canal Blood Supply to Intestines --Superior mesenteric artery: supply jejunum and ilum a. ileocolic artery: supplies the terminal ileum, cecum, appendix, and lower ascending colon b. right colic artery: supplies the ascending colon c. middle colic artery: supplies most of transverse colon --Inferior Mesenteric Artery a. left colic artery: supplies the last part of transverse colon, left colic flexure and the descending colon b. sigmoid branches: supply sigmoid colon c. arcades: serving large intestine form marginal artery of Drummond d. inferior mesenteric artery terminates in pelvis as superior rectal artery --Portal System: drains all structure derived from fore-, mid-, and hindgut a. superior mesenteric and splenic veins join to form the portal vein b. inferior mesenteric vein typically empties into terminal splenic vein Lymph Drainage of the Intestines --cisterna chili Nerve Supply to Intestine --Superior Mesenteric Nerve Plexus a. parasympathetic preganglionic fibers from posterior vagal trunk b. parasympathetic gangli and posterganglionic fibers that are in the walls of hollow organs c. sympathetic preganglion neurons from thoracic splanchnic nerves --Descending colorn and sigmoid colon (hindgut) are supplied by: a. parasympathetic preganglionic fiers arising from S2, S3, and S4 spinal segments are pelvic splanchnic nerves Liver --largest gland in the body --Ligaments a. Falciform Ligment *attaches to the midline of the abdominal wall from umbilicus up to the anteroinferior surface of the diaphragm where coronary ligament begins *round ligament/ligamentum teres of the liver: lies in free margin of falciform ligament, fibrous remnant of fetal umbilical cord containing umbilical vein b. Coronary Ligament *single layered peritoneal reflections surround the bare area of the liver *right and left extensions are sharp reflections of the coronary ligament and are designated the triangular ligaments c. right and left triangular ligaments --Surface Features a. find an “H” on posterior surface: porta hepatis of the hilum of the liver b. ligamentum venosum c. porta hepatis or hilus of the liver forms the cross bar of the H d. quadrate lobe e. caudate lobe --Blood Supply *hepatic artery: and its branches *portal vein: carries blood rich in nutrients from digestive tract, contributes about 70% of the oxygen supply to the liver *blood drains from the liver via the left, middle, and right hepatic veins Segmentation of the Liver --Anatomical Segmentation: divides the liver into a. large right anatomical lobe: includes caudate and quadrate lobes b. smaller left anatomical lobe --Hepatic triad a. portal vein b. hepatic artery c. hepatic duct Gallbladder and Bile Ducts --consists of a fundus, body, and neck *fundus is at cartilage of rib 9 --supplied by cystic artery (branch of right hepatic artery) --Biliary System a. left and right hepatic ducts drain bile from segments and join to form a common hepatic duct b. common hepatic duct joined by cystic duct of gallbladder to form the common bile duct (cystic duct has spiral valve) c. common bile duct carries bile to second part of duodenum via the free margin of the lesser omentum --Nerve Supply a. visceral afferents: enter cord at T6-T9 segments, pain from gallbladder is perceived in region of ribs corresponding to T6-t9 and radiates to rights scapular region (referred pain) Spleen --oval in shape with its long axis paralleling the 10th rib --suspended between lienorenal and gastrosplenic ligaments a. lienorenal ligament: contains the splenic artery, splenic vein, and tail of pancreas b. gastrosplenic ligament: contains short gastric and left gastroepiploic vessels