* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inspecting Electrical
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Fuse (electrical) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Overhead line wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical connector wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Aluminum building wiring wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring wikipedia , lookup
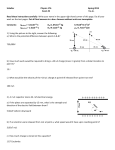
Inspecting Electrical Inspection Includes: Service entrance & masthead Main panel and subpanels (if any) Branch circuit wiring Junction boxes, outlets & fixtures National Electric Code Governs all electrical installations for both commercial and residential NEC does NOT require updating to older homes with new code revisions The MOST important aspect of the electrical inspection is to be on alert for SAFETY HAZARDS Required to Inspect Service entrance Main distribution panel Branch circuit wiring GFCIs within 6 ft of interior plumbing fixtures Polarity & grounding of representative number of interior receptacles and ALL carport receptacles Not Required to Inspect Low voltage systems Telephone, security, cable TV, intercoms or other ancillary wiring DO NOT: Insert tool, probe or testing device inside panel Test or operate overcurrent devices except GFCIs Dismantle any electrical device or control other than to remove main panel cover Inspecting Service Entrance Service entrance • • • • Overhead or underground Secure attachment to house Copper, aluminum, or copper-clad aluminum Amperage 60A (round meter base), 100A (square meter base), or 200A (rectangular meter base) • By today's standards, 100-amp service is considered minimal service. Typical Service Entrance Wiring Typical Service Entrance Cables Wire Size Amperage Rating Width #4/0 200 Amps Aluminum 1 7/16 inches #2/0 150 Amps Aluminum (AL)200 Amps Copper (CU) 1 5/16 inches #2 100 Amps Aluminum 125 Amps Copper 1 5/16inches #4 100 Amps Copper 3/4 inch #6 60 Amps Aluminum 3/4 inch Service Drop & Masthead If service comes in below roof level, it must be at least 3’ from windows If service comes in above roof level, it must be at least 3’ above roof Service wires must: • Be 12’ above driveways • At least 10’ above ground • At least 8’ above a flat roof & 18” above roof ridges Voltage Rating Service drops: • Number of wires going to masthead indicates voltage • Three wires with one tied back & two entering = 120 V • Three wires entering = 240V Service Panel Check box for heat. Don’t open of warm..cause for immediate concern. If OK remove cover: Inspect for any “tapping before the main” …SAFETY HAZARD If no main disconnect, must be able to power down in six hand movements Inspect for properly sized wires to properly sized breakers or fuses Wiring to Branch Circuits & Breakers AWG# COPPER COPPERCLAD AL OR ALUMINUM 18 Typically lampcord wiring and low voltage applications 16 Typically lampcord wiring and low voltage applications 14 15 Amps 12 20 Amps 15 Amps 10 30 Amps 20 Amps 8 50 Amps 30 Amps 6 65 Amps 50 Amps 4 100 Amps 70 Amps 3 110 Amps 80 Amps 2 125 Amps 100 Amps 1 150 Amps 110 Amps 1/0 175 Amps 125 Amps 2/0 200 Amps 150 Amps 3/0 175 Amps 4/0 200 Amps Service Panel Inspection Overview Look for signs of corrosion outside and at interior connections Look for circuit breakers that have more than one conductor attached • (Double or triple tapping is normally prohibited) Double Tapping Breaker Service Panel Inspection Check for loose or unattached conductors Check wires for signs of arcing, charred metal or burnt wire insulation Evaluate cables entering box for proper protection and fastening Main Service Panel Inspection Report wires smaller than #8 (fire hazard) Clearance around panel should be: • 6-6” headroom • 30” all around • 36” clear in front Grounding Conductor Grounding releases unwanted electricity to “ground” (earth) Ground wire must come from the neutral to the plumbing system or to a steel rod driven into earth. (Both reqd since 1987) Check for continuity of plumbing and dielectric connectors! Common Defects To Report: Recommend an Electrician Be Called Double tapped circuits Broken or cracked fixtures or outlets Melted insulation Handyman wiring Loose ceiling fans Permanently installed extension cords & temporary wiring Missing or inoperable GFCIs Oversized breakers & fuses Safety Hazards: Report & Recommend An Electrician Be Called Masthead within reach of occupants Frayed entrance cable Tapping before main Oversized fuses or breakers System not grounded More than 6 hand movements to power down