* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download B-field hw3
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
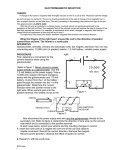
STCC S.5 Physics B-field hw3 Mr. Yau 1. The following figure shows a simple d.c. motor connected to a battery. (a) What is the direction of the forces acting on the sides AB and CD of the coil? (2 marks) (b) There is a force acting on BC. Explain briefly why the force does not affect the rotation of the coil. (1 mark) (c) What is the rotation direction of the coil as viewed by the observer? (1 mark) 2. (d) Name the component X and explain its function. (5 marks) (e) Suggest three ways to increase the speed of the coil. (3 marks) A simple electric motor is shown below. The solenoids, PQ and RS, and the coil ABCD are connected in parallel to the battery. commutator hollow paper cone brush observer battery Fig a (i) Draw the magnetic field lines around PQ and mark the polarities of it. (3 marks) (ii) What is the direction of the forces acting on the sides AB and CD of the coil? (2 marks) (iii) What is the rotation direction of the coil as seen by the observer? (1 mark) (iv) Explain the function of the commutator. (4 marks) (v) Explain the effect on the rotation direction of the motor if the battery is reversed. (2 marks) 3. The figure below shows a metal block and a galvanometer used in an experiment on Hall effect. 0.5 cm 0 1 cm centre-zero galvanometer The metal block is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 2 T. The galvanometer deflects to the right and gives a reading of 3 A. A Hall voltage of 1 10–6 V is measured. (a) Find the drift velocity of the charge carriers inside the metal block. (b) Find the number of charge carriers per unit volume. (2 marks) (2 marks) (c) If the sign of the charge carriers in the metal block is negative, in which direction are the charge carriers deflected under the magnetic field? (2 marks) (Given the charge of each charge carrier = 1.6 10–19 C) 4. A metal strip moves in a uniform speed v in a magnetic field of 1.2 mT as shown below. The Hall voltage measured is 4 V. (a) State the direction of the magnetic force acting on a charge carrier inside the strip. (b) Which side of the metal strip has a higher potential? (c) Calculate the speed v. (1 mark) (2 marks) (1 mark)