* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download review blood and heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
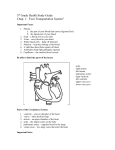
REVIEW BLOOD AND HEART 1. The normal pH of the __________ is about 7.4. 2. A high salt diet and a exercise would _________________ blood pressure. 3. The arterial system that supplies the brain with blood is the ___________ system. 4. Another word for high blood pressure is ____________________. 5. If your heart is beating too fast you are said to have ____________________. 6. _______________ results when the blood coagulates. 7. _______________ is the respiratory pigment in RBCs that binds oxygen 8. ______________ is the liquid portion of the blood. 9. The veins that directly empty the capillary beds are called ________________. 10. All arteries of the systemic circulation branch from the _________________. 11. Blood normally clots in _________ min 12. The carotid artery is located in the ____________ 13. There is an average of ______________ white blood cells per cubic mm of blood. 14. The arterial system that supplies the liver with blood is the ____________system. 15. The erythrocyte count _______________ when an individual goes from a low to a high altitude because the concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes. 16. In the healthy adult, erythrocytes are formed in the _______________ marrow. 17. An obstruction in the ______________vena cava would hamper the return of blood from head and neck. 18. The type of Leukocytes that would increase rapidly during allergies and infections of parasitic worms are ________________. 19. The Axillary artery is located in the ___________. 20. The process by which white blood cells move into and out of the blood vessel is called ______________. 21. When the heart is beating to slow it is called ______________. A:\REVIEW CH 10 AND 11 BLOOD AND HEART.doc 22. Platelets are fragments of _____________. 23. Permitting the exchange of nutrients and gases between the blood and tissue cells is the primary function of _________________. 24. Deoxygenated blood is received by the ______________. 25. ________________ means deficiency of blood. 26. ________________ is pain in the arm or chest because of lack of blood flow. 27. ____________ results when there is any decrease in oxygen-carrying ability of the blood. 28. Vagus nerve stimulation would result in a ____________ in heart rate. 29. The ________ ventricular wall of the heart is thicker than the right wall in order to pump blood against greater resistance. 30. The myocardium (heart) receives its blood supply directly from ______________ arteries. 31. 170/96 blood pressure readings would be indicative of _______________. 32. The ___________ valve is located on the left side of the heart. 33. Exercise causes ___________ of the heart muscle 34. All arteries of pulmonary circulation branch from the _____________ artery. 35. ________________ carry blood away from the heart. 36. The right ventricle the pulmonary artery and the left atrium are all involved in ______________ circulation. 37. Epinephrine and increased Carbon dioxide would lead to a ___________ in heart rate. 38. Making more red blood cells is called _________________. ALSO KNOW*********** THE PATH OF BLOOD THROUGHT THE HEARTBE ABLE TO LABEL: A HEART, THE CARDIAC CYCLE AND A VEIN, ARTERY AND CAPPILLARY and THE BLOOD TYPE CHART ANSWERS TO REVIEW CIRCULATORY SYSTEM A:\REVIEW CH 10 AND 11 BLOOD AND HEART.doc 1. blood 2. increase 3. carotid 4. hypertension 5. tachycardia 6. clotting 7. hemoglobin 8. plasma 9. Venuoles 10. aorta 11. three to six 12. neck 13. 4,000 to 11,000 14. hepatic 15. increases 16. red bone 17. superior 18. eosinophil 19. armpit 20. diapedesis A:\REVIEW CH 10 AND 11 BLOOD AND HEART.doc 21. bradycardia 22. megakaryocyte 23. capillaries 24. right atrium 25. ischemia 26. angina 27. anemia 28. decrease 29. left 30. cornary 31. hypertension 32. bicuspid 33. hypertrophy 34. pulmonary 35. arteries 36. pulmonary 37. increase 38. erythropoiesis A:\REVIEW CH 10 AND 11 BLOOD AND HEART.doc