* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ocean Ch 15 Animals-Ben
Sea in culture wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
The Marine Mammal Center wikipedia , lookup
Brown algae wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Marine life wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
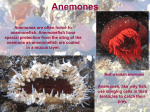
☰ Search Explore Log in Create new account Upload × 1 MAY 2011 Oceanography Ch # 15. Animals in the Benthic Environment Approx. 95% of marine organisms live on the sea floor, which varies from rocky to sandy to muddy. 15 -1. Distribution of Benthic Organisms Most biomass depends on the productivity of the surface waters. Sunlight penetrates to the bottom where the water is shallow. 15 -2. Communities along Rocky Shores Organisms on the rocky surface (epi-fauna) are either permanently attached or move on it. The biodiversity varies widely (algae, crabs). The rocky shore can be divided into: A spray zone (supra tidal) located above the highest tide zone. Species have hard shells and avoid drying out. An intertidal zone. Residents in this zone include rock lice and sea roaches, and scavengers. In the High tide zone, organisms have a protective covering to prevent drying out. Rock weeds are among the first to colonize the area. In the middle Tidal zone, are primarily algae and soft bodied animals. Acorn barnicles, various mussels. Carnivorous snails and sea stars feed on the mussels. Sea anemones, hermit crabs, sea urchins feed on algae in intermittent pools. In the low tide zone, almost always submerged, there are abd. Algae and shore crabs, who hide during daylight hours and feed at night. 15 -3. Communities along sediment covered shores In-fauna organisms are abundant. They burrow into the sediment. The water infiltrates into the sediment carrying nutrients and oxygen. Intertidal zones are similar to those on a rocky shore. Sandy beaches – organisms (mollusks, worms, crustaceans) burrow into the sand, which is moist and has a constant temp. Mudflats have a large population of turtle grass, and fiddler crabs. 2 15 -4. Communities on the shallow offshore ocean floor. Extends from low tide to the continental shelf edge. The biodiversity ranges from low to moderate. Benthic organisms diversity is lowest beneath upwelling waters. Rocky bottoms are covered by various types of macroscopic algae, kelp and forest kelp. Lobsters and oysters are also present. Coral reefs are constructed by polyps extracting CaCO3 . Polyps live throughout the sea, but build structures only in warm, shallow, clean marine areas with rocky substrate. (limits N35 Deg and S 35 Deg). Polyps live in a symbiotic relationship with Algae. Water temp must be < 86 Deg F and > 64 Deg F. 15 -5. What Communities exist on the Deep Ocean Floor? Deep sea Hydrothermal Vents 1977 discovery. Water temp 46 to 54 Deg F. on the Galapagos Ridge. Tube worms > 1 met long. Baja California Vent 662 Deg F. Black smoker emits sulfides, are acidic and toxic (H2S and heavy metals) Other vents have a limited life span. The Dead whale Hypothesis is used to explain the movement from one vent to another. Additional seeps are Hypersaline at depths 10,500 ft. Hydrocarbons at 2300 ft. Subduction zones the water is slightly warmer than expected The deep biosphere is a new Frontier. Discovered microbial communities within the porous part of the sea floor. Download 1. Science 2. Earth Science 3. Oceanography Ocean Ch 15 Animals-Ben.doc Chapter 6 PowerPoint Arthropod Jeopardy - Jutzi Lesson planning Performa- copy and use for each text Class/ Year Notes: Food Chains and Levels of Organization in Ecology Procedure Part 1: Evaluating Risks BOILER WATER TREATMENT AND CONDENSATE RETURN LINE PROTECTION ECOLOGY: Chapters 3, 4, 5, & 6 American Powerpoint studylib © 2017 DMCA Report