* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fund Categories and Basis of Accounting
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Syndicated loan wikipedia , lookup
Private equity wikipedia , lookup
Global saving glut wikipedia , lookup
Shadow banking system wikipedia , lookup
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Fundraising wikipedia , lookup
Mark-to-market accounting wikipedia , lookup
Money market fund wikipedia , lookup
Fund governance wikipedia , lookup
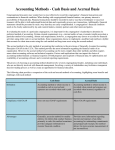
GOVERNMENT AND NON-PROFIT ACCOUNTING Ch. 2 The Use of Funds in Governmental Accounting Note: Focus on Big Picture of Different Funds Overview - Measurement Focus – What is shown on the organization’s financial statements and which resources are being measured - Basis of Accounting – Timing differences of when Assets, Liabilities, Revenue, Expenses are recognized (depends on “measurement” above) - Entity – Scope of “whose” assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses are included in financial statements. Note: Measurement Focus and basis of accounting go together (don’t mix) depending on what trying to measure. Measurement Focus and Basis of Accounting Governments use both Current Financial Resources Measurement focus and Modified Accrual Basis of Accounting. Government use current financial resources and modified accrual basis to account for day-to-day services. Governments also use economic resources and full accrual for “businesstype” activities Reporting on Funds and Aggregating to report on the Entity For profit Businesses uses economic resources and full accrual basis Fund Accounting – Two aspects to an entity (vs. how defined in business): 1. Legally separate unit (e.g. University system) 2. Funds (accounting entities) (e.g. funds w/in state for different activities 1 Entity – GASB #34 – requires reporting on entity as a whole and fund level. Statement No. 34 required two sets of financial statements: 1. Fund Financial Statement – Report on the individual funds, focus on short term. 2. Government-Wide Financial Statement: Adjustments are made to fund financial statements that account for day-to-day activities. Funds that do not financed government activities are removed when preparing government-wide FS. Different measurement and basis used for each Certain accounting adjustments to reconcile between two Different responsibilities a. Fiscal – budget requirements b. Accounting – separate accounting for specific purpose Fund Categories and Basis of Accounting A fund is defined as: “a fiscal and accounting entity with a self-balancing set of accounts recording cash and other financial resources, together with all related liabilities and residual equities or balances, and changes therein, which are segregated for the purpose of carrying on specific activities or attaining certain objectives in accordance with special regulations, restrictions, or limitations.” 1- Governmental Funds Government–type funds are used to account for the accumulation and expenditure of recourses to provide day-to-day operating activities, such as education, police, fire, parks, and highway maintenance. It also used for particular governmental purposes and for the acquisition or construction of general governmental capital assets, such as roadway, maintenance depots, police stations, and firehouse. 2 - Some resources may be legally restricted for specific purpose ( Hotel taxes) - Expenditures controlled by budget – short term focus (usually current year) - General Fund – most significant (property and other taxes affect it) - Balanced Budget – usually close to a “cash” basis Measurement Focus and Basis of Accounting Under the modify accrual basis of accounting, revenues are recognized in the period in which they are measurable and available. Measurable: Refers to the ability to state the amount of revenues in terms of dollar. Available: Means collectible within the current period or soon enough thereafter to be used to pay the bills of the current period. Expenditure under the modified accrual basis of accounting generally are recognized in the period in which services and goods are received and a liability is incurred. Specific exceptions to the general rules could result in different measurement under the modified accrual basis as compared with the accrual basis of accounting. Examples: Compensated absences (exp. & liabs are recognized when liabs mature i.e. Come due for payment when retired, rather than when earned by the employees.) claims and judgment special treatment benefits pensions debt services The term current financial resources measurement focus can be contrast with the economic resources measurement focus: 3 First: the term current in financial resources refers to cash and near-cash items and does not include long-term assets and liabilities. Second: the term financial resources means the capital assets such as buildings and equipment are not included within the accounting measurements. How does the basis of accounting used to implement the measurement focus effect the revenue measurement? Assume a government levies a property tax of $100,000 for a calendar year. It collects $80,000 within the year, and expects to collect$15,000 in the first 60 days of the next year and the remaining $5,000 later in the year. Calculate revenues under each three accounting basis. Under the cash basis, revenue = $80,000 Under accrual accounting, revenue = $100,000 Under modified accrual accounting, revenue = $95,000 ( $80,000 + $15,000) How does the accounting basis affect the expenditure measurements? Assume a government does not incurred against claims resulting from damages caused by the vehicle operators. Its pays $50,000 on claims settled during the year, will pay $8,000 early in the next year on settled claims, and expects to pay $25,000 in future year on claims that were filed during the year, but remain difficult to settle. Under the cash basis, expenditure = $50,000 Under the accrual accounting , expenditure = $83,000 ( 50,000 + 8,000 + 25,000) Under modified accrual accounting, expenditure = $58,000 (50,000 + 8,000) 2- Proprietary Funds Category 4 Are used by governmental activities that operate in a manner similar to that of private sector businesses in that they charge fees for their services. Examples of governmental activities that use proprietary fund accounting are central motor pools, hospitals, electric utilities, mass transit facilities, and lotteries. Measurement Focus and Basis Accounting To measure operating income and financial position, proprietary funds use the economic resources (capital maintenance) measurement focus and accrual basis of accounting, proprietary funds treat expenditure as for capital assets as assets (rather than expenditures) and depreciate them. Revenues are recognized in the period in which they are earned, rather than when they are measurable and available. Expenses are recognized when resources are consumed or liabilities are incurred, without the exception created by the modify accrual basis of accounting. 3- Fiduciary Funds Category Are used to account for resources held by the government in a trustee or agency capacity for others and therefore cannot be used to support the government’s own programs. Others might be individuals, other governments, or private organizations - Examples, pension plan, sales tax collected by a state government on behalf of county and city government. Measurement Focus and Basis Accounting Economic resources and Full accrual 1-Governmental-Type Funds Financial Statements include: 5 - Balance sheet - Statement of Revenues, Expenditures and changes in Fund Balance (IS). Types of Governmental Funds: A. General Fund Every government body must at least have a General Fund. It is used to account for the general operations of government and for any activity not accounted for in another fund. Assets in general funds include cash, investment, receivable (unpaid property tax), and receivable from other funds. (Due from other funds). If receivable are not currently due, they are referred to as advances to other funds. Liability found in general funds are also primarily currently due to be paid. Due to other fund---liabilities currently due. Advance from other fund----liabilities not currently due. Payable to other suppliers. Fund Balance: Unreserved Fund Balance --- currently available for spending. Reserve Fund Balance---- not available for spending. Equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Fund Balance Balance Sheet – Differences - measurement focus - not classified (note: focus is all on short term) - equity section – classified Fund Balance - Fund Balance classified as: Reserved and unreserved 6 Operating Statement – Differences - show other sources/uses (e.g. debt) separately from revenues/expenses - Multi-step format - different measurement focus (e.g. PPE is an expenditure) - FB reconciled on face of statement (vs. business, usually have a separate Stmt of Retained Earnings.) - Shows transfers to/from funds as other sources/uses - Note: transfer will be net out at Government-Wide FS level Note: All different Governmental funds – same accounting – different activity B. Special Revenue Funds To account for resources legally required to be spent for specific purposes, and therefore requiring separate reporting. The resources of revenue for special revenue funds are taxes, rents, and royalties, fees, and intergovernmental items 9 grants, shared revenues) Expenditure from these funds is usually for services and supplies specifically identifies by the law establishing the particular fund. C. Debt Service Funds To account for the accumulation of resources dedicated to payment of interest and principal on general obligation long-term debt. Debt services fund should be used when legally mandate or when financial resources are being accumulated for principal and interest that came due in future year. Debt service fund resources come most often from transfer from the General Fund (or other fund), income from the investment of resources held by the funds, and tax assessed specially to serve the debt. The assets of this fund consist of cash, investment, and sometimes receivables. 7 Liabilities are generally for matured interest and principal that have net yet been paid. Long-term liability for principal not currently due is not reported in the Debt Services Fund balance sheet. D. Capital Projects Funds To account for receipt and disbursement of resources used to acquire major capital facilities through purchase or construction. Not used account for such assets acquired by Enterprises Fund, an Internal Services Fund, or trust fund for individuals, private organization. Not used for capital assets purchased directly with current revenues of the General Fund or a Special Revenue Fund. Purchases of automobile, furniture, and minor equipment are not required the use of Capital Project Fund. E. Permanent Funds Are used to report resources that are legally restricted so that only the earnings generated by the principal, and not the principle itself, may be used to support programs that benefit the government or its citizens. An example of Permanent Fund is a perpetual-care public cemetery fund, endowment made to a public library. Permanent Fund revenues generally include investment income (interest, dividends, net increase or decrease in the fair value of investments). Distribution (expenditure) of revenues to the fund designated as the beneficiary of Permanent Fund revenues ------ usually a Special Revenue Fund--- are reported as transfer out. 8 2- Proprietary – Type Funds Use when a governmental unit handles its financial operations in a manner generally similar to that of business enterprises. Focus on determining operating income to recover costs and determine fees to charge. Example of activities includes the operation of electric utilities, airports, mass transit facilities, golf courses, and central motor pool. Economic resources and full accrual are used in this Fund. Types of Proprietary-Type Funds: A. Enterprise Funds Are used to account for any activities whose products or services are sold for a fee to external users, such as the general public. Enterprise Fund must be used if any one of the following criteria is met: o Activities financed with debt secured solely by fees. o Laws or regulations require goods/services to be recovered by fees rather than with tax. o Pricing policies designed to recover costs Financial Statements (more like a business) - show restricted assets and liabilities - Net assets classified as restricted, unrestricted, invested in PPE - Operating statement is multi-step: o Non operating $ o Capital o Extraordinary items (same definition as business) o Special items (either/or (not both), control of management) 9 B. Internal Service Funds Are used to account for providing goods or services within the governmental unit, or to other governmental unit, on a user-charge, cost-reimbursement basis. Example like purchasing, MIS. Reasons to establishing this type of activity include: o Reduce cost of obtaining goods or services. o Improvement in the distribution of goods or services within the governmental unit. - FS same basis and format as Enterprise - Bill other funds (revenue to Internal Services Fund and expense to others) - Keep separate fund for each type of activity Financial Statements - Statement of net assets (Balance Sheet) 3 categories of net assets: a. Invested in capital assets, net depreciation/debt b. Restricted c. Unrestricted - Statement of revenues, expenses and changes in fund net assets - Cash Flows (similar to for-profit) 3- Fiduciary-Type Funds Are used to account for assets held by government in a trust or agency capacity on behalf of others (individual, other government, or private organizations). Resources are “not” available to support government operations. Economic resources measurement and Full Accrual Basis are used. Financial Statements: - Statement of Fiduciary Net Assets (held in trust for others) - Statement of Changes in Fiduciary Net Assets 10 Types of Fiduciary type Funds: A. Pension (and Other Employee benefit) Trust Funds To account for resources held in trust for employee retirement plans and other employee benefit plans. B. Investment Trust Funds To account for resources of an external investment pool managed by a sponsoring government - Manage resources for several others – external - Any investments “internal” are reported in the respective government unity C. Private Purpose Trust Funds To account for resources of other trust arrangements maintained by a governmental unit for the benefit of individuals, other governments, and private organizations. An example of a Private-Purpose trust Fund is an Escheat Property Fund. Escheat property is private property that reverts to a governmental entity in absence of legal claimants or heirs. D. Agency Funds To account for resources held in a custodial capacity for some other organization and that must be disbursed according to law or contractual agreement. - Example: collect sales taxes and submit to local government. - No net assets, only A = L 11