* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Relationships
Lymphatic system wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Acute liver failure wikipedia , lookup
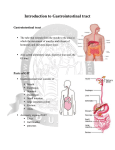
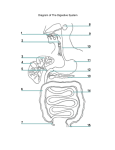
Gastrointestinal tract wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
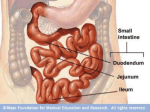
Large intestine wikipedia , lookup
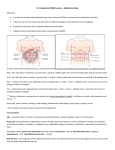
Organ st Superior 1 Part of Duodenum (Superior) 4-3-1-1 2nd Part of Duodenum (Descending) 4-3-3 1) Neck of the Gall Bladder 3rd Part of Duodenum (Horizontal) 4-3-3 1) Head of the Pancreas 2) Superior Mesenteric Artery 3) Superior Mesenteric Vein 4th Part of Duodenum (Ascending) 2-2-1-1 Right Kidney 5-5 Left Kidney 6-6 Right Suprarenal Gland 2-1 Left Suprarenal 1) Body of the Pancreas Inferior 1) Neck of the Pancreas Anterior Posterior 1) Gall Bladder 2) Peritoneum 3) Quadrate Lobe of the Liver 1) Transverse Colon 2) Transverse Mesocolon 3) Some coils of the Small Intestine 1) 2) 3) 4) 1) 1) Superior Mesenteric Artery 2) Superior Mesenteric Vein 3) Coils of the Small Intestine 1) Beginning of the root of the Mesentery 2) Coils of Jejunum 1) Suprarenal Gland 2) Liver 3) Hepatic Flexure of the Colon 4) 2nd part of the Duodenum 5) Small Intestine 1) Suprarenal Gland 2) Stomach 3) Spleen 4) Pancreas 5) Splenic Flexure of the Colon 6) Jejunum 1) Inferior Vena Cava 2) Right Lobe of the Liver 1) Body of the 1) 2) 3) 2) 3) 4) 4) Portal Vein Common Bile Duct Gastroduodenal Artery Inferior Vena Cava Hilus of the Right Kidney Renal Vessels Right Ureter Right Psoas Major Muscle Abdominal Aorta Inferior Vena Cava Right Psoas Major Muscle Right Ureter 1) Left Psoas Major Muscle 2) Left Margin of the Aorta 1) 12th Rib 2) Diaphragm 3) Aponeurosis of Transversus Abdominis 4) Quadratus Lumborum 5) Right Psoas Major Medial 1) Head of the Pancreas 2) Pancreatic Duct 3) Common Bile Duct 1) Head of the Pancreas 11th rib 12th rib Diaphragm Aponeurosis of Transversus Abdominis 5) Quadratus Lumborum 6) Left Psoas Major 1) Right Kidney 1) 2) 3) 4) 1) Abdominal Lateral Gland 1-3 Pancreas Right Upper Lobe of Lung Right Middle Lobe of Lung Uncinate Process of Pancreas Head of Pancreas (including the Uncinate Process) 2-3 Neck of Pancreas 2-3 Body of the Pancreas 4-4 1) First 4 ribs and their costal cartilages 1) 4th and 5th ribs and their costal cartilages 1) Superior Mesenteric Vessels 1) Superior Mesenteric Artery 2) Superior Mesenteric Vein 1) Peritoneum 2) Pylorus of the Stomach 1) Splenic Artery 1) Peritoneum 2) Bed of the Stomach 3) Provides attachment for the Transverse Mesocolon 4) Omental Bursa Spleen Lesser Sac/Omental Bursa 1) Posterior Part of the Coronary Ligament 2) Diaphragm 1) 2) 3) Epiploic Foramen 1) Caudate Lobe of the Liver Transverse Colon Transverse Mesocolon The Greater Omentum 1) First part of the duodenum 1) Posterior Wall of the Stomach 2) Lesser Omentum 1) Hepatoduodenal Ligament (portal vein, common bile duct and proper hepatic Aorta 2) Splenic Artery 3) Stomach 1) Inferior Vena Cava 2) Bile Duct 3) Right Renal Vessels 1) Superior Mesenteric Artery 2) Superior Mesenteric Vein 3) Formation of Portal Vein 1) Aorta 2) Superior Mesenteric Artery 3) Left Suprarenal Gland 4) Left Kidney 1) Superior Pole of the Left Kidney 2) Left colic flexure (Splenic flexure)?? 1) It contacts the diaphragm at the 9th to 11th ribs 3) Posterior Abdominal Wall 4) Retroperitoneal structures: pancreas, left suprarenal gland and left kidney Left Boundary: 1) Gastrophrenic Ligament 2) Splenorenal Ligament 3) Gastrosplenic ligament 1) The Inferior Vena Cava 2) Right Crus of the Diaphragm artery) Stomach 1) Liver (mostly the left lobe) is superior to the body and pylorus 1) Transverse Colon and Left Colic Flexure inferior/posterior to the body of the stomach Bare Area of the Liver Left Lobe of the Liver 1) Body and pylorus of the stomach 1) Anterior Abdominal Wall Bed of Stomach (formed by Posterior Wall of the Lesser Sac): 1) Retroperitoneal Structures: Pancreas, Left Kidney, Left Suprarenal Gland, Part of the Diaphragm, Celiac Artery and Proximal Branches, Splenic Artery and Splenic Vein, Terminal Part of the Superior Mesenteric Artery and Vein (9) 2) Peritoneal Structures: Transverse Colon and Spleen (2) 1) Hepatic Veins 2) Inferior Vena Cava 3) Right Suprarenal Gland 4) Part of Right Kidney To the left of the body is the spleen Diaphragm Passages: 1) Caval Opening: @ TV8 2-3 cm from the median plane a. Inferior Vena Cava 2) Esophageal Hiatus: Formed by the Right Crus of the Diaphragm @ TV10 a. Esophagus b. Anterior and Posterior Vagal Trunks 3) Aortic Hiatus: @TV12 a. Aorta b. Azygos Vein c. Thoracic Duct Some Important Pathways Ureters: 1) Transitions from the renal pelvis and descends as a retroperitoneal structure along the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle. It passes posterior to the testicular/ovarian vessels. The left ureter is also crossed by the inferior mesenteric artery and vein. Then, it courses anterior to the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. It makes a sharp bend over the pelvic brim and courses to the bladder in the floor of the pelvis. Inferior Thyroid Vein: 1) Anterior to the trachea. Courses downward anterior to the brachiocephalic artery. ***The Transverse mesocolon attaches to the anterior margin of the pancreas. The pancreas lies posterior to the omental bursa (lesser sac). Important Innervations 1) Kidney: Postganglionic SS Fibers from the Lesser and Least Splanchnic nerves (T10-12) (from aorticorenal ganglion) 2) Ureter: Postganglionic SS from the Lesser and Least and Lumbar and Sacral Splanchnic nerves, VA travel back with the Lesser and Least and Lumbar Splanchnic nerves (T10-L2) 3) Suprarenal Glands- Cortex: Postganglionic SS from Celiac Ganglion, driven by preganglionic fibers from the Greater Splanchnic nerve. (NO SENSORY AFFERENTS or VA) 4) Suprarenal Glands-Medulla: Receive Preganglionic SS Fibers from the Greater Splanchnic Nerve (T5-T9) (NO SENSORY AFFERENTS OR VA) Right Upper Quadrant rt. lobe of liver, gallbladder, pylorus, the first three parts of the duodenum, head of the pancreas, rt. suprarenal (adrenal) gland, rt. kidney, rt. colic (hepatic) flexure, sup. part of ascending colon, rt. half of transverse colon Left Upper Quadrant lt. lobe of liver, spleen, most of stomach, jejunum and proximal ileum, body and tail of pancreas, lt. suprarenal (adrenal) gland, lt. kidney, lt. colic (splenic) flexure, sup. part of descending colon, lt. half of transverse colon Right Lower Quadrant cecum, appendix, most of ileum, inf. part of ascending colon, rt. ovary, rt. uterine tube, rt. ureter, rt. spermatic cord Left Lower Quadrant sigmoid colon, inf. part of descending colon, lt. ovary, lt. uterine tube, lt. ureter, lt. spermatic cord Organ Parietal Pleura Anterior Abdominal Wall Innervation Ventral Primary Rami/Intercostal nerves and phrenic nn. Thoracoabdominal nn. (T7-T11), subcostal n. (T12), iliohypogastric n. (L1) and Referred Pain Via Thoracic and Abdominal Nerves (cutaneous distribution of intercostal nn.) T7- xiphoid process, T10- umbilicus, pubis (L1- via iliohypogastric n.) ilioinguinal n. (L1) Parietal Peritoneum Sensory: Intercostal, Lumbar and Sacral -Sensitive to touch, pain and temperature nn. Sensory of Thoracic Diaphragm: 1) Intercostal nn. to costal margin (peripheral part) of the diaphragm (T5T11) and subcostal n. 2) Phrenic n. (C3-5) to central diaphragm Stomach PS: Vagus n. (primarily the Anterior Vagal Trunk) SS: Greater Splanchnic n. (T5-9) and postganglionics from the celiac ganglion VA: pain via greater splanchnic n. Gall Bladder PS: Vagus n. SS: Greater Splanchnic n. (T5-9) and postganglionics from the celiac ganglion VA: pain via greater splanchnic n. Duodenum Spleen Small Intestine (Jejunum and Ileum) PS: Vagus n. SS: plexus on pancreaticoduodenal arteries PS: Vagus n. (celiac and superior mesenteric plexuses) SS: Splanchnic nn. (celiac and superior mesenteric plexuses) VA: pain via splanchnic nn. Celiac Plexus Celiac and Superior Mesenteric Plexuses Cecum and Appendix Ascending Colon Transverse Colon Celiac and Superior Mesenteric Ganglia Celiac and Superior Mesenteric Ganglia Superior Mesenteric Plexus Pancreas T5-9 (Left Epigastrium Quadrant) via Left Greater Splanchnic n. T5-9 (Right Epigastrium Quadrant) via Right Greater Splanchnic n. **If bile spreads to the inferior surface of the diaphragm, pain follows Right Phrenic n. (Right Shoulder C3-5) Insensitive to most painful stimuli, including cutting and burning. But it is sensitive to distention. Descending Colon Sigmoid Colon Diaphragm Kidney Ureter Suprarenal Gland- Cortex Suprarenal Gland- Medulla Appendix Lumbar part of the Sympathetic Trunk and the Superior Hypogastric Plexus Superior Hypogastric Plexus and Pelvic Splanchnic nn. Motor: Phrenic n. (C3-5) Sensory: Phrenic n. and peripheral areas via 6th and 7th intercostal nn. and the subcostal n. SS: Preganglionics from Lesser and Least Splanchnic nn. (T10-12) to aorticorenal ganglion (functioning to Increase renin secretion, which increases blood pressure) PS: Vagus n. VA: Least Splanchnic n. (T12) PS: Vagus and Pelvic Splanchnics (S2-4) SS: Lesser and Least Splanchnics and Lumber and Sacral Splanchnics (Increase ureteric peristalsis) VA: Lesser and Least Splanchnics and Lumbar Splanchnics (T10-L2) SS: Preganglionic fibers from Greater Splanchnic n. (T5-9) to the celiac ganglion, postganglionics go to blood vessels NO VA! (NO SENSORY AFFERENTS) no PS SS: Direct input from preganglionic sympathetic fibers from the Greater Splanchnic n. (T5-9) NO VA (NO SENSORY AFFERENTS) no PS Shoulder region (C4-C5 ventral rami) Costal margin (via intercostal nn.) Lower Quadrant (Subcostal) via Least Splanchnic n. (T12) (costal angle of the back) T10-L2 as the stone passes through the ureter (along the posterior costal margin) Distal portion of the ureter (L1-L2) (suprapubic region, the genitals, medial thigh and leg) Chromaffin cells = postganglionic sympathetic neurons T10- umbilicus (via lesser splanchnic n.) as pain spreads it will go to L1-L2, the right lower quadrant (via the right lumbar splanchnic nn.) Organ Primary blood supply Esophagu Sup./ascendi s ng esophageal, inf. thyroid Innervatio Function n Esophage Transmits food al plexus (vagus + SCG) Sup. contents Oropharynx Inf. Ant. contents contents Stomach Larynx, L main bronchus, LA, diaphragm Stomach Upper Mechanical & Diaphragm, abdominal chemical digestion liver, and plexus pancreas Transver Diaphragm and se colon body wall Upper Buffering of abdominal chyme, digestion, plexus absorbtion of nutrients Upper Digestion/absorbti abdominal on of nutrients plexus Neck of Peritoneum, gall pancreas bladder, quadrate lobe of liver Inf. Transverse duodenu colon/mesocolon, m small intestine Duodenu msuperior L/R gastric, L/R gastroomenta l Sup. pancreaticoduodenal Duodenu Sup./inf. mpancreaticodescendin duodenal g Duodenu minferior Sup./inf. pancreaticoduodenal Duodenu Gastrooment mal ascending Jejunum Sup. Neck of gallbladder Sup. duodenum Upper Digestion/absorbti Pancreas Inf. abdominal on of nutrients head/uncinat mesenter plexus e, sup. ic a./v. mesenteric a./v. Upper Digestion/absorbti Pancreas Jejunum abdominal on of nutrients body plexus Upper Absorbtion of Transverse Sigmoid Sup. mesenteric a./v., small intestine Post. L contents contents Thoracic duct, L lung hemiazygous v. post. intercostals, aorta Spleen, L Spleen kidney, lesser sac Bile duct, portal v., IVC, gastroduoden al a. R kidney hilus, renal vessels, ureter, R psoas major m. R psoas major m., IVC, aorta, R ureter Stomach R contents R lung Pancreas, duodenum, liver, IVC, aorta R kidney, liver, R colic flexure Pancreas R kidney, head, liver, R colic pancreatic/bi flexure le ducts Ascending duodenum Mesentery roots, L psoas major Peritoneal jejunum m., L. margin recesses of aorta Greater Mesentery/bo Descending Descending duodenum Pancreatic head Ascending mesenteric Ileum Organ Colon cecum abdominal plexus IMA, iliocolic Upper abdominal plexus Primary Innervatio blood supply n Ileocolic, Upper appendicular, abdominal ant./post. plexus cecal nutrients Absorbtion of nutrients Function Water/electrolyte absorbtion colon, duodenum Transverse colon, duodenum Sup. contents Ascending colon colon omentum Sigmoid colon Greater omentum Inf. Ant. contents contents Appendix Body wall , iliacus m., iliac vessels, inguinal canal Cecum Body wall dy wall, kidneys Mesentery/bo dy wall, kidneys Post. contents Iliac vessels colon Ileum R paracolic gutter Lumbar plexus branches, transversus abdominis aponeurosis Duodenum, sup. mesenteric a./v. Lumbar plexus branches, transversus abdominis aponeurosis Ileum/jejunu m R paracolic gutter L colic flexure R colic flexure L paracolic gutter Ileum/jejunu m Descending colon L contents colon, duodenum Ascending colon, duodenum R contents Colon R colic ascending Upper Water/electrolyte abdominal absorbtion plexus R colic flexure Colon transvers e Middle colic Upper Water/electrolyte abdominal absorbtion plexus Stomach, liver Small intestine Greater omentum Colon L colic descendin (ascending g and descending, IMA) Water/electrolyte absorbtion L colic flexure, spleen, stomach Sigmoid colon Body wall Colon sigmoid Water/electrolyte absorbtion Descending colon, small intestine Rectum, Body wall L inguinal canal Iliacus m., external iliac a./v. L paracolic gutter Ileum/jejunu m Water/electrolyte absorbtion Sigmoid colon, small intestine Sup. contents Great Anal canal Middle sacral a. L rectal aa. R rectal aa. Post. contents Aorta, L contents R contents L lung R lung Rectum Organ Heart Upper/low er abdominal plexus, lumbar sympatheti c trunk Sigmoid Lower abdominal plexus, pelvic splanchnic nn. Sup./mid./inf. Lower rectal abdominal plexus Primary Innervatio blood supply n Coronoary Cardiac Function Pump blood Bladder, pubic symphysis Inf. Ant. contents contents Diaphrag Thymus, ribs, plexus (SCG, vagus) vessels m, sternum fibrous pericardi al attachme nt Celiac trunk, Inf./asc. Pylorus (head), splenic a. duodenu stomach m, sup. mesenter ic a./v. Pancreas Splenic, pancreaticoduodenal Vagus, Digestive splanchnic exocrine, some (pain), endocrine upper abdominal plexus Spleen Splenic Celiac plexus Liver Proper hepatic, portal v. Upper Blood filtration, abdominal bile secretion plexus Diaphragm Gall bladder Cystic Celiac Bile storage & ganglia, concentration vagus, greater splanchnic s Liver Lymphatic, RBC storage Diaphragm L colic flexure, L kidney Gallblad der, stomach, R colic flexure, duodenu m Duodenu m Stomach esophagus, R/L main bronchus IVC, renal Spleen a./v., bile duct (head), portal v. (neck), aorta, SMA, L adrenal g., L kidney (body) L kidney Diaphragm (sup.) Sup./desc. duodenum Stomach, pancreas Diaphragm, body IVC, stomach, Stomach wall esophagus Diaphragm Liver Liver Duodenum, Duodenum hepatoduoden al lig.