* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Darwin and Evolutionary Biology
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
On the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
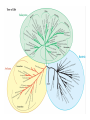
Darwin and Evolutionary Biology NASC 120 Darwin on HMS Beagle 1831-1836 http://darwin-online.org.uk/ Captain Robert Fitzroy Galapagos Islands Establishing a respectable career • 1838-43 Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle (5 parts) • 1839 Journal of Researches (Voyage of the Beagle) • 1842 The Structure and Distribution of Coral Reefs • 1844 Geological Observations of Volcanic Islands • 1846 Geological Observations of South America Establishing a respectable career • 1838-43 Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle (5 parts) • 1839 Journal of Researches (Voyage of the Beagle) • 1842 The Structure and Distribution of Coral Reefs • 1844 Geological Observations of Volcanic Islands • 1846 Geological Observations of South America • 1851-54 Monograph on Cirripedia (Barnacles) 4 vols. http://darwin-online.org.uk/EditorialIntroductions/Richmond_cirripedia.html Lippson, A.J. & Lippson, R.L. 1984. Life in the Chesapeake Bay. Johns Hopkins University Press. Barnacles: anatomy, morphology, taxonomy, developmental history http://www.hps.cam.ac.uk/whipple/explore/microscopes/darwinsmicroscopes/ Establishing a respectable career • 1838-43 Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle (5 parts) • 1839 Journal of Researches (Voyage of the Beagle) • 1842 The Structure and Distribution of Coral Reefs • 1844 Geological Observations of Volcanic Islands • 1846 Geological Observations of South America • 1851-54 Monograph on Cirripedia (Barnacles) 4 vols. all the while being more and more convinced of a heresy…Transmutation Erasmus Darwin (1731-1802) 1794 Jean Baptiste de Lamarck (1744-1829) 1809 Robert Chambers (1802-1871) • Vestiges of the History of Natural Creation (1844), Anonymous • ‘A Victorian Sensation’ Secord (2001) http://pages.britishlibrary.net/phrenology/images/ch ambers.jpg Herbert Spencer (1820-1903) “The Development Hypothesis” (1852) “Progress: Its law and cause” (1857) Darwin’s Observations • 1) Geographic distribution of species • 2) Fossil assemblage of South America • 3) flora and fauna of the Galapagos Islands Geographic distribution • Species are not uniformly spread over different regions and climates – similar species appear ‘clumped’ in specific regions – Especially noticeable where there is geographic isolation; e.g. islands and mountain ranges – Could environment be molding organisms to fit local conditions? Mt Ararat Wallace Line Galapagos Islands • Hypothesis 1: Noah’s Ark – Distribution of flora and fauna from central location in Turkey • Hypothesis 2: Evolution and adaptation to new locales and changing geological formations (islands, mountain ranges etc.) Establishing a respectable career • 1838-43 Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle (5 parts) • 1839 Journal of Researches (Voyage of the Beagle) • 1842 The Structure and Distribution of Coral Reefs • 1844 Geological Observations of Volcanic Islands • 1846 Geological Observations of South America • 1851-54 Monograph on Cirripedia (Barnacles) 4 vols. Working on a big book, ‘Natural Selection’, when suddenly… Alfred Russel Wallace (1823-1913) “On the tendency of varieties to depart indefinitely from the original type” (1858) Darwin’s Key Supporters Lyell (1797-1875) Hooker (1817-1911) Huxley (1825-1895) Darwin http://darwin-online.org.uk/ • • • • • • • Nov. 24, 1859 1st edition 1860 2nd ed. 1861 3rd ed. 1866 4th ed. 1869 5th ed. 1872 6th ed. 1876 6th ed. with additions and corrections (final version) http://darwin-online.org.uk/ The Origin of Species • 1) – amasses a large and diverse amount of evidence that evolution (transmutation) occurs – “descent with modification” • 2) – provides a naturalistic & materialistic mechanism of how it occurs – Natural selection Descent with modification • All species of plant and animals (etc.) derived from a common ancestral primitive form of life, modifying, diversifying over great lengths of time as environment changes • Short argument: • Competition + random variation + natural selection evolution (species change) Darwin’s argument: the long form • 1. Malthusian Reproduction – more organisms are produced than available resources can support • 2. This results in a competition for resources (food, space, mates, sunlight etc.) • 3. There is a natural variability of traits in any population (no two organisms exactly alike) – This variation is ‘random’, i.e. not directed or aiming at anything – nonteleological • 4. Some traits are better adapted (more fit) to the local environment • 5. 2 + 4 some individuals have a competitive edge over others (they will reproduce in greater numbers) • 6. Organisms pass on traits to their offspring (Inheritance) • 7. This results in more of the adaptive traits being passed on in next generation (Natural selection for more adaptive traits) Evolution –a change in the frequency of certain traits in a population (microevolution) • 8. Over great lengths of time this micro evolutionary change will accumulate into large macro-evolutionary changes, resulting in the origin of new species • • • • • • • 1838-43 1839 1842 1844 1846 1851-54 1859 • 1862 • • • • • • • • • • 1868 1871 1872 1875 1875 1876 1877 1879 1880 1881 Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle Voyage of the Beagle The Structure and Distribution of Coral Reefs Geological Observations of Volcanic Islands Geological Observations of South America Monograph on Cirripedia (Barnacles) 4 vols. On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life On the Various Contrivances by which British and Foreign Orchids are Fertilised by Insects Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex The Expression of Emotions in Man and Animals Movement and Habits of Climbing Plants Insectivorous Plants The Effects of Cross and Self-Fertilisation in the Vegetable Kingdom The Different Forms of Flowers on Plants of the Same Species The Life of Erasmus Darwin The Power of Movement in Plants The Formation of Vegetable Mould Through the Action of Worms Speciation Darwinian Evolution: a two-step process 1. Random (non-directed) variation of traits in a population 2. Selection by environment for adaptive or favourable ranges of this naturally occurring variation The Species Problem • Problem of Diversity: Why so many species? – Adaptive radiation to fill available niches, divergence and adaptation by natural selection • Problem of Homology: Why so many similarities? – Descent from a common ancestor (species look related because they really are) • Problem of Adaptedness: Why do organisms appear so well designed for their environments and ways of life? – Natural selection weeds out non-adaptive traits, favours adaptive traits