* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 Review Worksheet
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
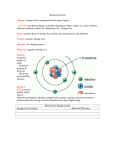
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 11 Review Worksheet 1. What is electromagnetic radiation? Light, it travels in waves, one is the moving electrical charge and one is the magnetic field it creates…they travel at 90o from each-other 2. Sketch a representation of a wave and indicate on your drawing one wavelength of the wave 3. Explain what it means for an atom to be in an excited state and what is means for an atom to be in its ground state Excited state = the atom has absorbed energy, an electron has jumped from a lower energy level to a higher energy level Ground state = no excess energy is in the atom, the electrons are all in their lowest energy levels. 4. What is a photon? A packet of energy, energy when it is traveling like a particle rather than a wave 5. Describe Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom. The nucleus is a dense center made of the protons and the neutrons, the electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus. 6. Explain what is meant by the term orbital. A three dimensional picture of where the electrons spend their time, based in trigonometry. Only two electrons rotate in an orbital. 7. What is the symbol for the lowest-energy hydrogen orbital? 1S 8. Give the symbols for each of the orbitals that constitute the third and fourth principle energy levels of hydrogen. Third – s, p, d Fourth – s, p, d, f 9. Describe electron spin. Electrons are spinning on their axis and rotating around the nucleus at the same time, much like the earth rotates on its axis and rotates around the sun. It is possible to spin in two directions, we refer to it as up or down. 10. What does the Pauli Exclusion Principle tell us about electrons? That electrons can only be in the same orbital if they are spinning in opposite directions. 11. List the order in which the orbitals are filled as the atoms beyond hydrogen are built up. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p 12. How many electrons can be placed in a given s orbital? (2) In a given p subshell? (6) In a specific p orbital? (2) 13. Define the valence electrons and the core electrons in an atom. Valence – outer electrons Core – inner electrons, not the outer layer 14. Sketch the overall shape of the periodic table and indicate the general regions of the table that represents the various s, p, d, and f orbitals being filled. 15. Write the electron configuration for the following atoms: a. Sodium: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 b. Nitrogen: 1s2 2s2 2p3 c. Beryllium: 1s2 2s2 d. Strontium: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 16. Define the term ionization energy? Ionization energy = the amount of energy it takes to remove an electron from an element 17. Define the term and atomic radius? Atomic radius = the size of the atom, usually measured from the nucleus to the outer edge 18. How do the ionization energies and atomic sizes of elements vary, both within a vertical group of the periodic table and within a horizontal row? Up to down, the atoms get bigger….left to right the elements get smaller (more power in the nucleus, bigger pull on the electrons) 19. How does an excited atom return to its ground state? The atom emits a photon to get rid of the extra energy that it absorbed, the more energy emitted, the more blue the color. 20. How is the wavelength (color) of light related to the energy of the photons being emitted by an atom? How is the energy of the photons being emitted by an atom related to the energy changes taking place within an atom? Longer wavelength = red, shorter wavelength = blue The more blue the color emitted from the atom, the farther the electron is falling. This also means that the electron absorbed a lot of energy and jumped into a high excited state.