* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ELC191 Study Guide 2rev3
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
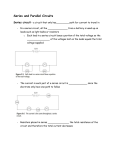
COURSE: Basic Principles/Industrial Electricity COURSE#: ELC191 TOPIC: Study Guide 2 INSTRUCTOR: Mr. Lombardo There are three types of circuits: series, parallel, or a combination of series and parallel. A series circuit has only one path for current flow. A parallel circuit has 2 or more paths for current flow A circuit is either open or closed. An open circuit does not have a complete path and is considered to be “off”. A closed circuit has a complete path and is considered to be “on”. The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge. Neutrons have no charge. Orbiting the nucleus are electrons. Electrons have a negative charge. The outer shell or orbit is called the valence shell. The valence shell will never have more than 8 electrons. A conductor will have 1, 2, or 3 electrons. A semi-conductor will have 4, 5, or 6 electrons. An insulator will have 7 or 8 electrons. Conductors allow the flow of electrons. Insulators resist the flow or electrons. Semi-conductors can either be a conductor or an insulator. The conventional theory states that electrons flow from a positive charge to a negative charge. The electron theory states that electrons flow from a negative charge to a positive charge. The best conductor is silver which has one electron in its valence shell. Copper has one electron in its valence shell and is used in electronics. Aluminum has 3 electrons in its valence shell and is not as good a conductor as copper but is less expensive. Voltage is a pressure. It is the force that pushes the electrons in a wire. Another name for voltage is EMF (electromotive-force) or potential difference. Current is the rate of flow of electrons and is called amperage. Resistance is the opposition to current flow in an AC or DC circuit. The symbol for voltage is the letter “E” or “V”. The symbol for current is the letter “I” or “A”. The symbol for resistance is the letter “R” or “Ω”. The unit of measurement for voltage is the volt. The unit of measurement for current is the ampere or amp. The unit of measurement for resistance is the ohm. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/. Page 1 of 2 Rev 02/2013 FRL Power is the rate of doing work or energy. It is stated in watts or volt-amps. The symbol for power is the letter(s) “W” or “VA”. The unit of measurement for power is the watt or volt-amp. Ohm’s law formula is E=IxR. The power formula is P=ExI. In series circuit total voltage of the circuit adds up from all the voltage drops across all the resistances. In a series circuit amperage is the same at any point of the circuit. In a series circuit all resistance adds together to give the total resistance of the circuit. A series circuit is also called a voltage divider circuit. In a parallel circuit voltage is the same at any point in the circuit. In a parallel circuit amperage adds up from all the current drops in the circuit. In a parallel circuit total resistance is the reciprocal of the sums of the reciprocals resistance of the circuit. The total resistance of a parallel circuit will never be greater than any single resistance of that circuit. A parallel circuit is also called a current divider circuit. The definition of electricity is the flow of electrons. There are 6.25x1018 electrons in a coulomb. A coulomb is a quantity measurement for electrons. One ampere is equal to one coulomb flowing past any given point in one second. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/. Page 2 of 2 Rev 02/2013 FRL