* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Compounds of Life Chart
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
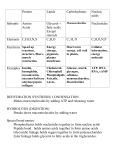
Name Date Period Compounds of Life Chart C H O Monomer Important Information Name and Parts monosaccharide Found in potatoes, pasta, and soft drinks These are a main source of energy for the body, involved in recognizing each other, and in the membrane structure of cells Monosaccharides – made of one sugar o Fructose (found in fruit and honey) o Glucose (a source of energy in animals and plants) use for energy Carbohydrates - A sugar or starch that living things Compound Atoms & Definition Disaccharides – 2 monosaccharides bonded together o Maltose, lactose (found in milk) and sucrose (table sugar) Polysaccharides – made of two or more monosaccharides o Starch (how plants store glucose) o Cellulose (dietary fiber in animals, component of cell walls in plants) o Glycogen (how animals store glucose) Lipids - A macromolecule that is not soluble in water Compound Atoms & Definition C H O Monomer Important Information Name and Parts fatty acid + glycerol Found in butter, lard, and oil Provides a STORED source of energy for your body to use when it needs it Triglycerides = 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids Saturated – solid (no double bonds between carbon atoms), animal fats (like lard and butter) Unsaturated – liquid (like fish and vegetable oils), double or triple bond between carbon atoms Polyunsaturated – many double or triple bonds between carbon atoms Trans fats – unsaturated fatty acids that have been changed to saturated fatty acids Phospholipids – have hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail, help to make up the cell membrane (lipid bilayer) Steroids – contain four attached carbon rings (cholesterol, vitamin D, and hormones) Compound Atoms & Definition C Monomer Name and Parts amino acid Proteins - a chemical used by cells to grow and work H O N Important Information Found in meat, beans, eggs, nuts, dairy products, and fish Dipeptides – 2 amino acids joined together Amino acids have a central carbon atom covalently bonded to 1) an amino group 2) a carboxyl group 3) a hydrogen atom and 4) an R group Polypeptides – several amino acids joined in a string Are able to contract, become shorter or longer (like our muscles) Are enzymes that can bring about a chemical reaction in an organism Provide support needed for hair, feathers, ligaments, and spider webs Used as storage in seeds and eggs Used for transport (like hemoglobin transports oxygen in our blood) Nucleic Acids - A large macromolecule that stores important (genetic) information in a cell Compound Atoms & Definition C Monomer Name and Parts nucleotide H O N P Important Information DNA – contains genes, the hereditary blueprints for all life DNA has a double helix shape Nucleotide has Sugar and phosphate make up the backbone of DNA, nitrogen three parts bases make up the rungs 1) a sugar 2) a phosphate and 3) a nitrogen base 4 bases are adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C) RNA – single stranded with ribose sugar